
Scans used, for the first time, to examine relationship between neocortex and cognitive decline.

Scans used, for the first time, to examine relationship between neocortex and cognitive decline.

T1 mapping has the potential to determine neuroblastoma aggressiveness, as well as early efficacy of treatment.
Convolutional neural network accurately identifies “mass effect” lesions in more than 50 disease entities.
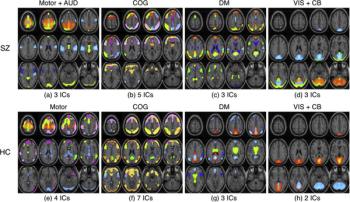
Image analysis method allows clinicians to more accurately see changes in the brains of patients with schizophrenia based on specific therapies.

Diagnostic Imaging Weekly Scan: June 26, 2020
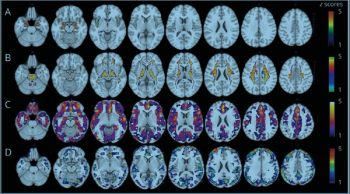
Women score worse than men in four key brain health areas associated with Alzheimer’s biomarkers.
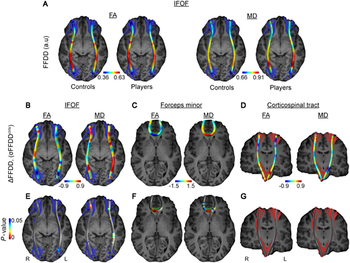
Modified dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI can pinpoint a leaky blood-brain barrier in both active and retired players.
Diagnostic Imaging's Weekly Scan: June 19, 2020
MRI images captured on female rugby players reveal long-lasting impacts of head impacts on the brain.
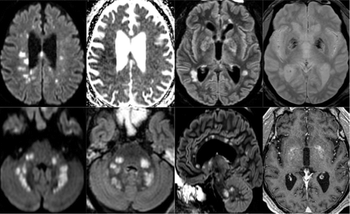
Three patterns emerge in patients analyzed in multi-institutional study.
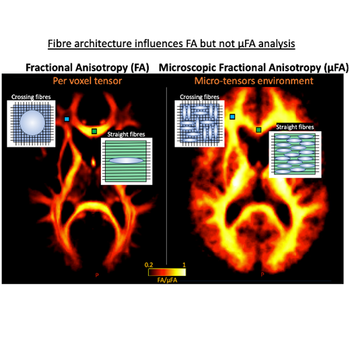
New method improves detection of disease changes.

Three MRI techniques can help neuroradiologists more effectively target pea-sized area of the brain that affects movement with fewer side effects.
Diagnostic Imaging's Weekly Scan: June 12, 2020
Three-stage system can help providers assess patients, as well as guide future treatment and research efforts.
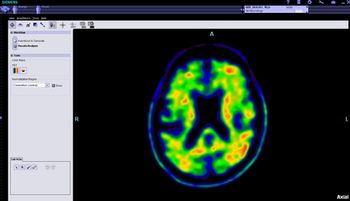
Scans show greater amyloid accumulation in the brains of older adults who get less than six hours sleep nightly.
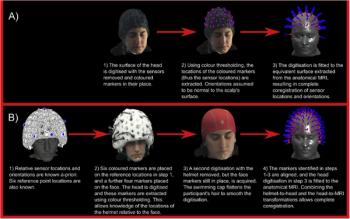
49-channel device tracks the brain’s electrophysiological processes and can be an effective imaging option for children or patients who have difficulty being still.
Duke researchers determined task-fMRI does not produce reliable predictions individuals will respond in particular circumstances or future mental health.
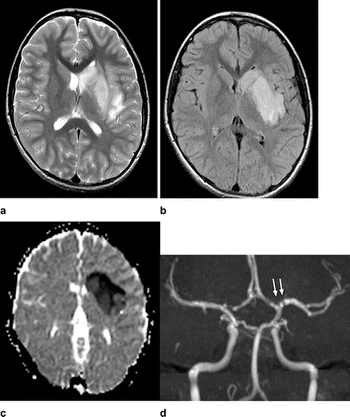
Iranian researchers diagnosed ischemic stroke in COVID-19-positive child with no other symptoms.
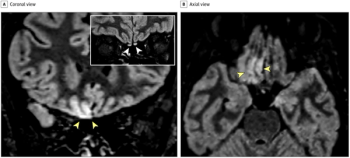
Technologist positive for the virus experienced a loss of smell and altered sense of taste.

For use with PET imaging, the radiopharmaceutical helps estimate density and distribution of tau, a marker of Alzheimer's disease.
Half of patients hospitalized who have neurological findings for acute stroke could die.

Diagnostic Imaging poses five questions about recent COVID-19 and neurological research to UCSF Radiology Chair Christopher Hess, M.D.
Concentration on virus-related scans largely sidelines other imaging needs.
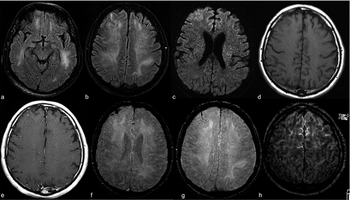
Multiple brain regions and cerebral spinal fluid can be affected.

Deep-learning model outperformed neuroradiologists in predicting risk for disease development.