Cancers on ultrasound elude CAD
Researchers from Seoul National University Medical Center found that ultrasound-only-detected breast cancers are not very sensitive to a mammography computer-aided detection system.
Researchers from Seoul National University Medical Center found that ultrasound-only-detected breast cancers are not very sensitive to a mammography computer-aided detection system.
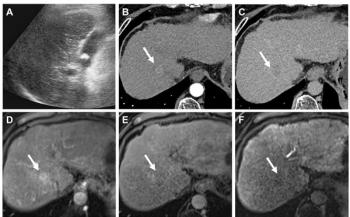
Dr. Sang Kyu Yang and colleagues applied CAD to 96 bilateral mammograms obtained on a full-field digital system. The patient population consisted of 26 women with 29 ultrasound-detected cancers (all normal on mammography) and 70 women with 70 mammography-detected cancers. Patients in the latter group had negative findings at clinical exam.
In the ultrasound group, CAD produced 17 marks on masses and five on calcifications, correctly identifying six masses. The false-positive rate was 0.15 per image and 0.62 per case.
In the mammography group, the CAD system scored 116 marks on masses and 185 on calcifications, resulting in 58 and 139 true positives, respectively. The false-positive rate was 0.37 per image and 1.48 per case.
The sensitivity of CAD, based on radiologic primary features, was 17% for the ultrasound-detected cancers and 96% for the mammography-detected cancers. This information may be useful when applying CAD to screening mammography and adjunct ultrasound to detect early breast cancers, according to the researchers, who presented their work in a poster presentation at the 2005 Radiological Society of North America meeting.
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.