Chest CT Study Suggests Marijuana Smokers May Have Higher Emphysema Risk Than Tobacco-Only Smokers
A new computed tomography study reveals that people who smoke marijuana may have a 70 percent higher risk of developing emphysema than non-smokers, and an age-matched subgroup analysis suggests marijuana use could be associated with a 26 percent higher risk of emphysema in comparison to tobacco-only smoking.
Does marijuana smoking lead to a significantly higher risk of emphysema?
In a
The study authors found that 75 percent of marijuana smokers (42 of 56) had emphysema in comparison to 67 percent of tobacco-only smokers (22 of 33) and 5 percent of non-smokers (three of 57). However, a subsequent age-matched subgroup analysis that included 30 marijuana smokers and 33 tobacco-only smokers showed a 26 percent higher risk of emphysema for marijuana smokers (93 percent, 28 of 30) in comparison to tobacco-only smokers (67 percent, 22 of 33), according to the study.
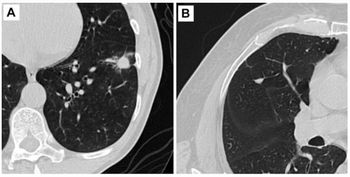
In other thoracic CT findings from the larger study, the researchers found that marijuana smokers had a twofold higher prevalence of paraseptal emphysema (48 percent) in comparison to tobacco-only smokers (24 percent). The authors noted that inhalation maneuvers utilized by marijuana smokers may contribute to the development of microbarotrauma and apical bullae.
“In our study, paraseptal emphysema was the predominant pattern seen in marijuana smokers while centrilobular emphysema was the predominant pattern seen in tobacco-only smokers. This may represent an earlier stage of apical bulla formation reported in marijuana smokers and may explain the absence of the typical pulmonary function test changes of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in marijuana smokers,” wrote Giselle Revah, M.D., FRCPC, an assistant professor in the Department of Radiology at the University of Ottawa, and colleagues.
The researchers conceded that a limited ability to quantify marijuana use (with only half of the marijuana smokers specifying daily amounts) and concurrent tobacco smoking in 50 out of 56 marijuana smokers were a couple of the factors that prevented “ … a definite association between marijuana smoking and emphysema or bullous disease.”
However, Revah and colleagues also pointed out that mucoid impaction, bronchial thickening, and bronchiectasis were 31 percent, 22 percent, and 17 percent more prevalent, respectively, in marijuana smokers than tobacco-only smokers.
“Our findings suggest that smoking marijuana leads to chronic bronchitis in addition to the airway changes associated with smoking tobacco. This is especially striking given the extensive smoking history of patients in the tobacco-only group (smoking history, 25-100 pack years),” noted Revah and colleagues. “In addition, our results were still significant when comparing the non-age-matched groups, including younger patients who smoked marijuana and who presumably had less lifetime exposure to cigarette smoke.”
Noting the limitations of the small sample size and the retrospective study design, the study authors said larger prospective studies are needed to further examine CT chest findings and related risks among people who smoke marijuana.
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.