Contrast-enhanced Mammo Detects More Primary Tumors
Bilateral dual-energy contrast agent-enhanced digital mammography is as effective as MRI in detecting known primary breast tumors.
Bilateral dual-energy contrast agent-enhanced digital mammography is as effective as MRI in detecting known primary breast tumors and is more effective than conventional digital mammography, according to a study published in the December issue of the journal
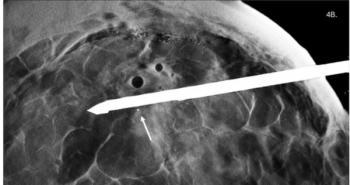
The small study began by testing the feasibility with 10 women who were newly diagnosed with breast cancer. They were injected with the imaging agent iohexol, dose of 1.5 mL per kg of body weight, and were imaged between 2.5 and 10 minutes following the injection. Following confirmation of the feasibility, the researchers enrolled 52 women with newly diagnosed breast cancer who had undergone previous MR imaging of the breast.
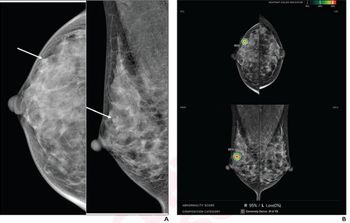
The results showed that the length of time between injection of the contrast and scanning did not affect the quality of the dual-energy contrast agent-enhanced (DE CE) digital mammography images, up to 10 minutes. Fifty-two index tumors were detected by both MR imaging and DE CE digital mammography, while only 42 were found by conventional mammography. The sizes of the tumors varied from 4 mm to 67 mm, with the median being 17 mm.
“DE CE digital mammography depicted 14 (56 percent) of 25 additional ipsilateral cancers compared with 22 (88 percent) of 25 for MR imaging,” wrote the authors.
The researchers did note that the DE CE digital mammography reported two false-positives, fewer than the 13 false-positives reported with the MR imaging.
The authors concluded that use of bilateral DE CE digital mammography was feasible and easy to accomplish, “with a lower sensitivity for detecting additional ipsilateral cancers than did MR imaging, but the specificity was higher.”
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.