Contrast-enhanced ultrasound shows new marker for atherosclerosis
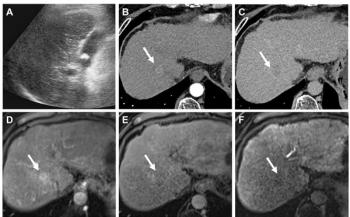
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the carotid artery can identify the presence and degree of vascularization in atherosclerotic plaque, providing a noninvasive way to measure the existence and degree of atherosclerosis, according to a recent study.
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the carotid artery can identify the presence and degree of vascularization in atherosclerotic plaque, providing a noninvasive way to measure the existence and degree of atherosclerosis, according to a recent study.
Atherosclerotic plaque requires a blood supply from the small capillaries to the outer layers of the large blood vessels such as the carotid artery. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound reveals neovascularization within the plaque and can be used as a surrogate marker for atherosclerosis.
Dr. Steven Feinstein, Falak Shah, and colleagues in the cardiology section of the internal medicine department at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago published their study in the November issue of Vascular Medicine. They describe how they used contrast-enhanced ultrasound to measure atherosclerosis.
They studied 15 patients with a total of 17 significant cases of atherosclerotic carotid artery disease. All patients received contrast-enhanced carotid ultrasound exams before undergoing a carotid endarterectomy. Two patients received bilateral endarterectomies. The ultrasound results were compared with histological studies of carotid plaque samples removed during surgery.
All of the plaque samples were stained with the specific vascular markers CD31, CD34, von Willebrand factor, and hemosiderin to measure the presence and degree of neovascularization.
The contrast-enhanced carotid ultrasound measurements of neovascularization most closely correlated with the measurements obtained from the CD31 stain, with a correlation value of 0.68 using Spearman's rank method. The other vascular markers all produced a correlation value of 0.50.
The researchers concluded that contrast-enhanced carotid ultrasound measurements correlate well with histological measures of neovascularization in atherosclerotic plaque and could be used as a surrogate marker for atherosclerosis. The FDA has not approved use of contrast in ultrasound in the U.S., though it is in use in Europe and other regions.
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.