Newly FDA-Cleared AI Software Facilitates Advanced Denoising and Accelerated Scan Times for MRI
Enabling up to 80 percent faster MRI scan times, the SubtleHD software is included in the newly launched AI software suite Subtle-Elite.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted 510(k) clearance for SubtleHD™, an artificial intelligence (AI) software that reportedly decreases magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan times by up to 80 percent for certain sequences.
The SubtleHD software also offers advanced denoising that one can apply for MRI assessment of any body region, according to Subtle Medical, the manufacturer of SubtleHD.
SubtleHD™, an artificial intelligence (AI) software that reportedly enables significant reduction in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan times, has garnered 510(k) clearance from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (Images courtesy of Subtle Medical.)
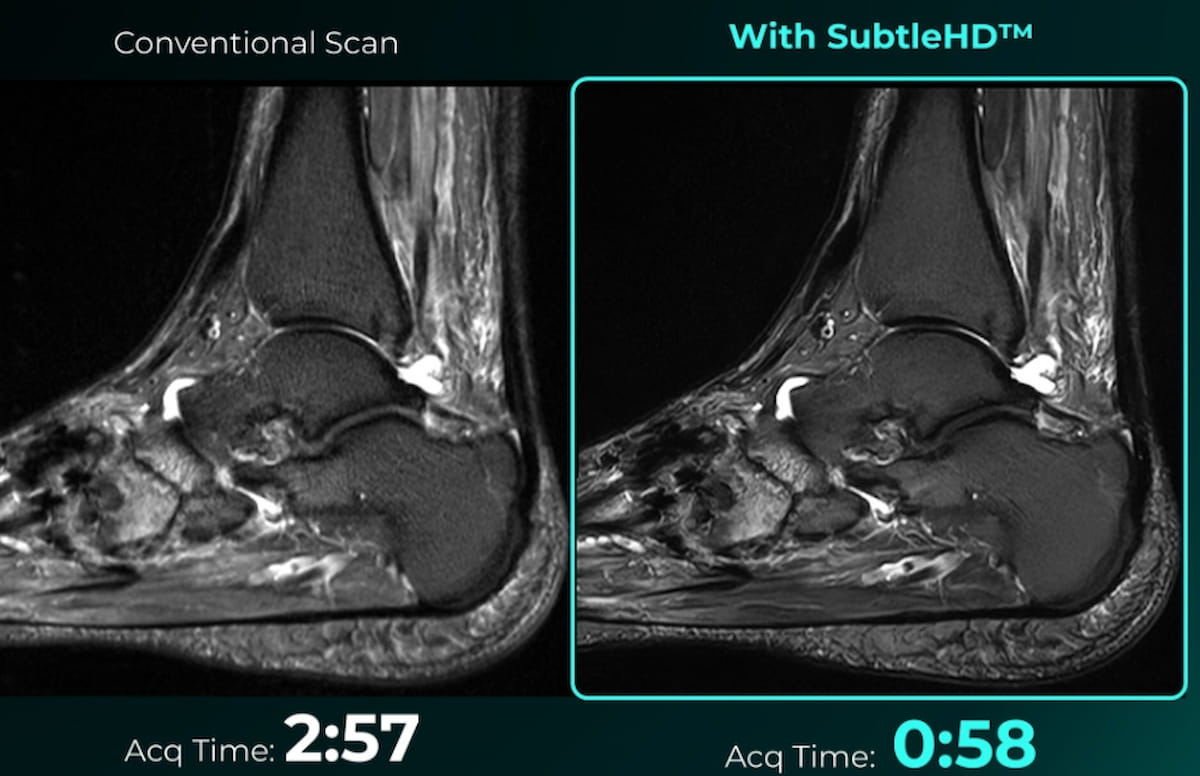
The company is including SubtleHD in a new Subtle-Elite AI software suite that also includes the previously FDA-cleared SubtleSynth, which utilizes deep learning to provide synthetic short tau inversion recovery (STIR) images from T1 and T2-weighted MRI, and SubtleAlign, which provides optimal anatomical alignment for brain MRI scans.
"The FDA clearance of Subtle-HD™ marks a significant milestone in AI-driven radiology, giving hospitals and imaging centers a powerful solution to increase efficiency, improve image quality, and optimize workflows — all without additional hardware costs," noted Ajit Shankaranarayanan, Ph.D., the chief product officer at Subtle Medical. "By combining SubtleHD, SubtleSYNTH, and SubtleALIGN into a single, comprehensive package, Subtle-ELITE™ is setting a new benchmark for the future of MRI."
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.
Stroke MRI Study Assesses Impact of Motion Artifacts Upon AI and Radiologist Lesion Detection
July 16th 2025Noting a 7.4 percent incidence of motion artifacts on brain MRI scans for suspected stroke patients, the authors of a new study found that motion artifacts can reduce radiologist and AI accuracy for detecting hemorrhagic lesions.