FDA Clears AI Software for Fetal Heart Ultrasound Assessment
Reportedly developed on over 90,000 ultrasound exams, the BrightHeart AI software identifies suspicious findings suggestive of congenital heart defects through AI-powered evaluation of fetal heart morphology.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted 510(k) clearance for BrightHeart’s artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled software, which may bolster ultrasound detection of congenital heart defects (CHDs) that have been estimated to occur in one of every 100 newborns.
Employing AI algorithms that were developed on over 90,000 ultrasound exams, BrightHeart’s AI software provides automated video stream analysis and detailed assessment of fetal heart morphology, which detects or rules out findings suggestive of CHDs, according to BrightHeart.
Offering detailed assessment of fetal heart morphology and automated video stream analysis, the newly FDA-cleared AI software from BrightHeart may enhance ultrasound detection of congenital heart defects. (Image courtesy of BrighHeart.)
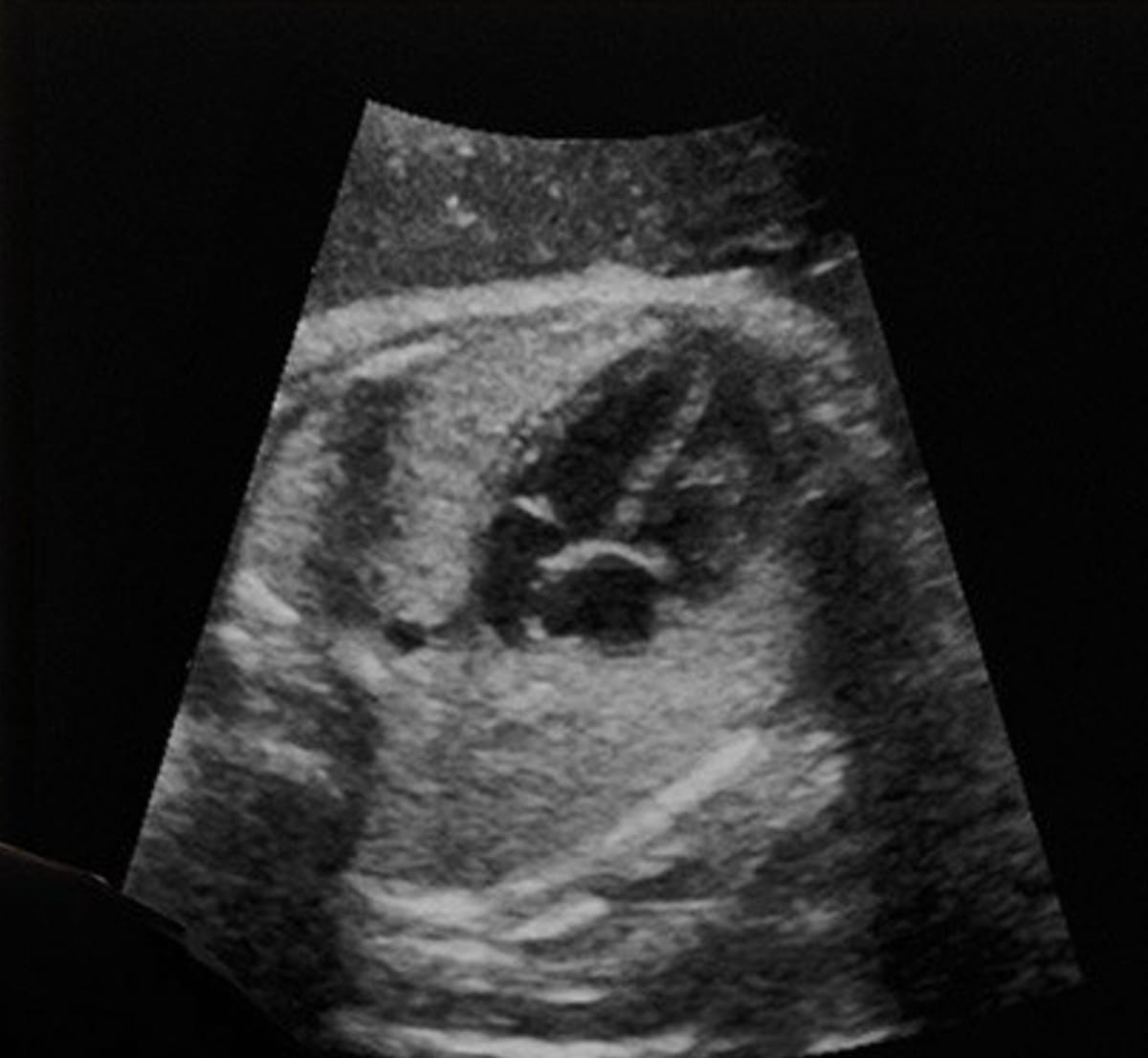
The company says the software also offers AI assessment as to the completeness of fetal heart ultrasound exams and facilitates smooth integration into existing ultrasound workflows.
“Fetal heart assessments are among the most technically demanding aspects of prenatal ultrasound,” said Cécile Dupont, the CEO of BrightHeart. “Our AI-powered solution not only assists clinicians in detecting signs of potential abnormalities earlier but also enhances their confidence in confirming normal findings, which is equally critical for the peace of mind of expectant families.”
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.
Mammography Study: AI Facilitates Greater Accuracy and Longer Fixation Time on Suspicious Areas
July 8th 2025While noting no differences in sensitivity, specificity or reading time with adjunctive AI for mammography screening, the authors of a new study noted a 4 percent higher AUC and increased fixation time on lesion regions.