FDA Clears Cardiac and Lung AI Applications for Exo Iris Handheld Ultrasound
The artificial intelligence (AI)-powered applications reportedly allow clinicians to diagnose pulmonary edema and measure left ventricle ejection fraction within seconds.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted 510(k) clearance for the addition of cardiac and lung artificial intelligence (AI) applications for the Exo Iris handheld ultrasound device.
With rapid identification of B-lines, the lung AI application allows quick detection of pulmonary edema, according to Exo. Whether one is utilizing parasternal long axis (PLAX) or apical four-chamber views, Exo said the cardiac AI application enables clinicians to ascertain stroke volume and measure left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) in seconds.
Newly FDA-cleared cardio and lung AI applications for the Exo Iris handheld ultrasound device may facilitate assessments of left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) and pulmonary edema in seconds, according to Exo, the manufacturer of the Exo Iris device. (Images courtesy of Exo.)
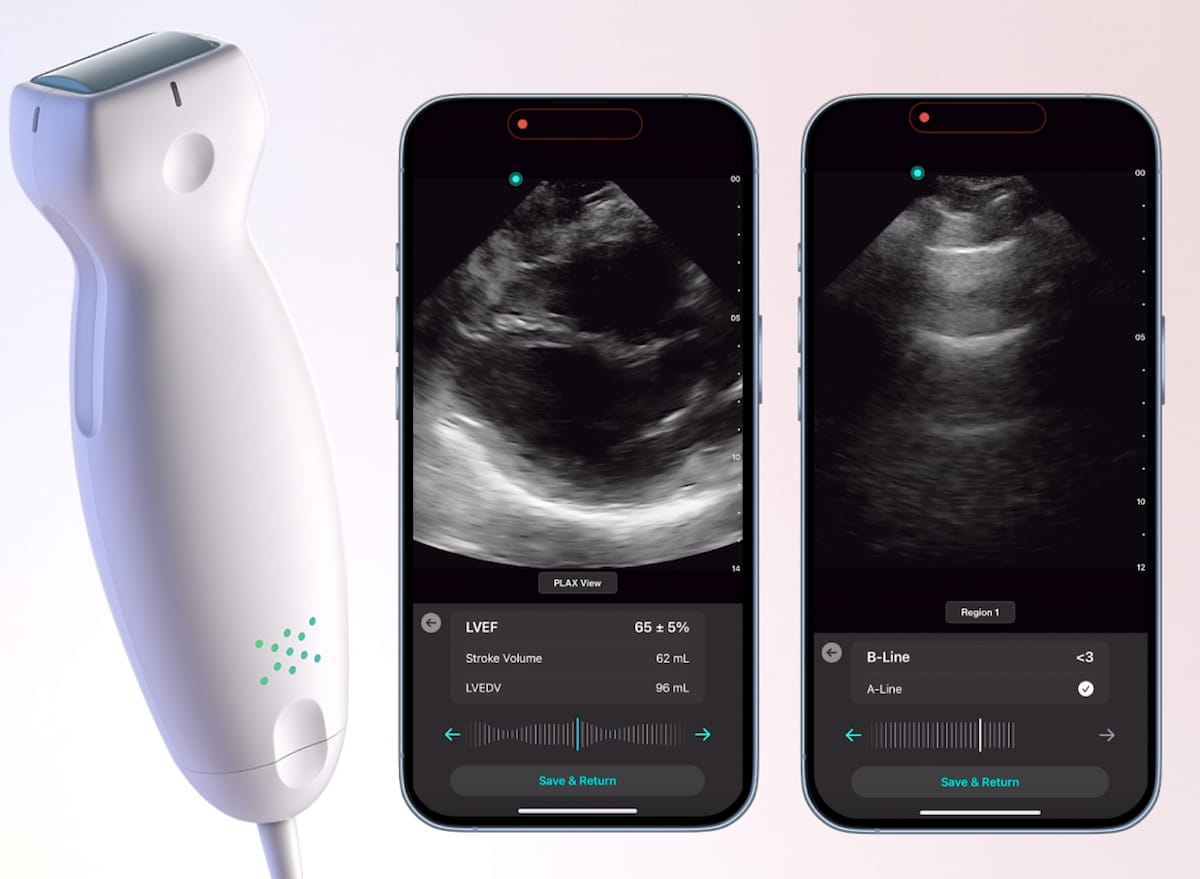
Emphasizing that the AI applications have been trained over 100,000 ultrasound images, including point-of-care images taken in critical care units and emergency room settings, Exo maintained that the cardiac and lung AI applications provide real-time recognition of key imaging landmarks, even with less than perfect scans.
“Exo’s cardiac and lung AI applications are a game-changer,” said Ted Koutouzis, M.D., a clinical instructor in emergency medicine at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago. “Now I have a fast and reliable clinical tool to help easily distinguish between COPD and CHF patients for precise and timely care.”
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.
Stroke MRI Study Assesses Impact of Motion Artifacts Upon AI and Radiologist Lesion Detection
July 16th 2025Noting a 7.4 percent incidence of motion artifacts on brain MRI scans for suspected stroke patients, the authors of a new study found that motion artifacts can reduce radiologist and AI accuracy for detecting hemorrhagic lesions.