FDA Clears Gleamer’s ChestView AI Software for CXR
Adjunctive use of the AI-powered software led to an average 38.6 percent increase in the detection of pneumothorax by general radiologists, according to a 2023 study.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted 510(k) clearance for ChestView, an artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled software, which may enhance detection of a variety of abnormalities on chest X-rays (CXRs).
In a 2023 retrospective study involving 500 patients, researchers found that adjunctive use of the ChestView software led to an average increased detection of 26.2 percent for pneumothorax, 8.5 percent for pleural effusion and 14.1 percent for consolidation.
Without AI assistance, only two out of 12 reviewing radiologists were able to detect a right paravertebral mass in the case above. With the use of the newly FDA cleared AI software ChestView, all 12 radiologists detected the mass. (Images courtesy of Radiology.)
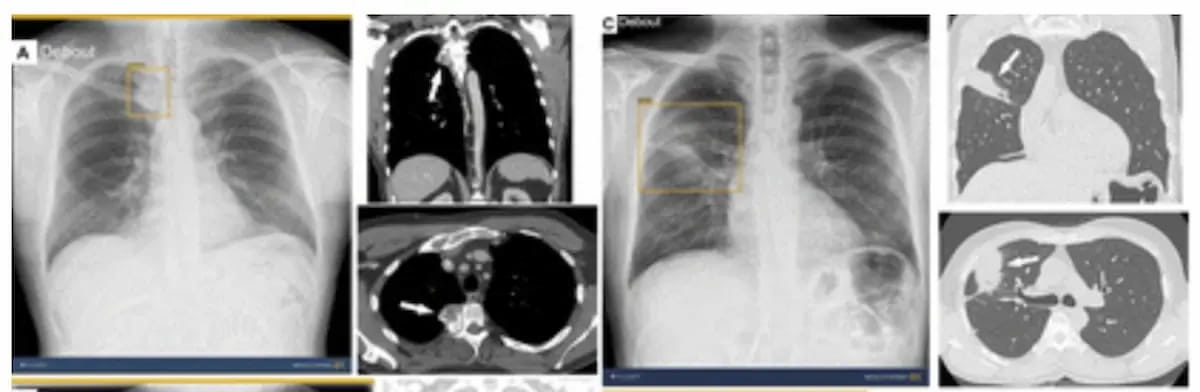
The authors of the study, published in Radiology, also noted an overall mean 31 percent reduction in CXR reading time with the use of ChestView. Specifically, researchers pointed out a 27 percent reduction in CXR reading time for thoracic radiologists and a 30 percent reduction for radiology residents.
"We believe ChestView will transform how chest X-rays are analyzed, making healthcare delivery faster, safer, and more effective for millions of patients,” noted Christian Allouche, the chief executive officer at Gleamer.
Considering Breast- and Lesion-Level Assessments with Mammography AI: What New Research Reveals
June 27th 2025While there was a decline of AUC for mammography AI software from breast-level assessments to lesion-level evaluation, the authors of a new study, involving 1,200 women, found that AI offered over a seven percent higher AUC for lesion-level interpretation in comparison to unassisted expert readers.
Can CT-Based Deep Learning Bolster Prognostic Assessments of Ground-Glass Nodules?
June 19th 2025Emerging research shows that a multiple time-series deep learning model assessment of CT images provides 20 percent higher sensitivity than a delta radiomic model and 56 percent higher sensitivity than a clinical model for prognostic evaluation of ground-glass nodules.
FDA Clears Ultrasound AI Detection for Pleural Effusion and Consolidation
June 18th 2025The 14th FDA-cleared AI software embedded in the Exo Iris ultrasound device reportedly enables automated detection of key pulmonary findings that may facilitate detection of pneumonia and tuberculosis in seconds.