RSNA preview: CAD improves detection of pulmonary embolisms
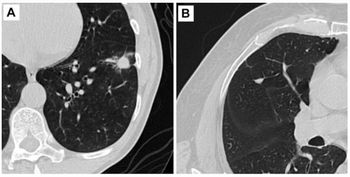
Computer-aided detection significantly improves the sensitivity of pulmonary embolism imaging, according to a study that will be presented at the 2008 RSNA meeting. Other studies show that specially developed CAD schemes can detect flat lesions that are often missed in CT colonography.
Computer-aided detection significantly improves the sensitivity of pulmonary embolism imaging, according to a study that will be presented at the 2008 RSNA meeting. Other studies show that specially developed CAD schemes can detect flat lesions that are often missed in CT colonography.
"There has been steady improvement over the years in the sensitivity and specificity of nodule detection," said Dr. Heber M. MacMahon, director of thoracic imaging at the University of Chicago Medical Center.
The most urgent issue and the biggest barrier to the use of CAD technology has been its lack of integration with PACS, he said.
"They have not been tightly integrated into PACS, so it takes a lot of time to evaluate," MacMahon said. "If it takes more than a few minutes to bring up the interface and extract results, people won't use it in their practice because of the pressure to read large amounts of scans."
CAD and PACS developers have worked together to improve the software so that nodule detection can be done more quickly and reliably, he said.
Regarding the rate of false positives, MacMahon said all detection systems have false positives, and recent software improvements have lowered them into an acceptable range.
In another study, a specially developed CAD scheme was used to detect flat lesions in the colon, because existing CAD schemes are designed for detecting the common bulbous polyp shape. Researchers developed a CAD scheme consisting of colon segmentation based on histogram analysis and mathematical morphology, detection of polyp candidates based on intensity and morphologic feature analysis, and linear discriminant analysis for classification into polyps or nonpolyps.
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.