Subsolid Lung Nodules Higher Risk in Women Than Men
CHICAGO-Women with subsolid lung nodules detected by CT have a higher risk of lung cancer than do men.
Subsolid nodules detected by CT are associated with a higher risk of lung cancer for women than for men, according to a study to be presented next week at RSNA.
Researchers from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School in Boston, MA, compared the differences in relative risk of lung cancer by nodule and sex in the CT arm of the National Lung Screening Trial. “We know there are differences in cancer risk among different lung nodule consistencies, but we were unaware of any published reports that looked at the differences in lung cancer risk for nodule subtypes between women and men,” study lead author Phillip Boiselle, MD, said in a release. [[{"type":"media","view_mode":"media_crop","fid":"43629","attributes":{"alt":"","class":"media-image media-image-right","id":"media_crop_2338669048348","media_crop_h":"0","media_crop_image_style":"-1","media_crop_instance":"4796","media_crop_rotate":"0","media_crop_scale_h":"0","media_crop_scale_w":"0","media_crop_w":"0","media_crop_x":"0","media_crop_y":"0","style":"height: 182px; width: 130px; border-width: 0px; border-style: solid; margin: 1px; float: right;","title":"Phillip Boiselle, MD. ©RSNA 2015.","typeof":"foaf:Image"}}]]
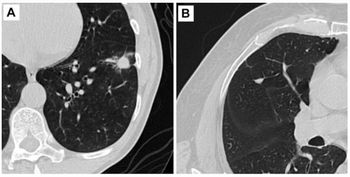
There were 26,455 participants in the CT arm of the trial. The researchers assessed all CT-detected nodules measuring 4 to 30 mm, characterized by consistency (solid, nonsolid/ground glass, and part-solid). They calculated sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) for lung cancer for both men and women.
The results showed that of the 26,455 participants, 9,994 (37.8%) had a positive screen at one or more time points. A total of 8,062 (81%) had one nodule consistency and 1,932 (19%) had one or more nodule consistency.
The relative risk for lung cancer was significantly higher for women:
“The main difference we found was that women were 50 percent more likely than men to have ground-glass nodules and, when these nodules were present, women had a substantially higher risk of developing lung cancer,” Boiselle said in the release.
Women also demonstrated a higher sensitivity than men for subsolid nodules:
The PPV was different for women and men between part-solid and solid nodules:
“By looking at the rate at which lung cancers grow on serial CT scans, we can develop a better understanding of how often to obtain follow-up CT scans in men and women,” Boiselle concluded.
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.














