Take Lung Tumor CTs with a Grain of Salt
Quirks associated with CT measurement can give a false impression of lung-tumor growth, according to a new study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Quirks associated with CT measurement can give a false impression of lung-tumor growth, a
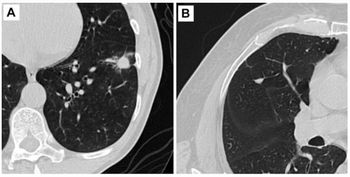
Gregory J. Riely, MD, PhD, led a Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center team in the work. The study involved 33 patients with late-stage non-small-cell lung cancer who consented to undergo two chest computed tomography exams within 15 minutes of each other. Such scans would normally happen months apart, and scans indicating even slight tumor growth can be part of the clinical justification for additional treatment.
All the patients had lesions larger than 1 cm in diameter. Three radiologists measured the diameter of the target lesions on the two scans side-by-side.
The radiologists found that 57 percent of the apparent changes exceeded 1 mm in magnitude, and 33 percent of the changes exceeded 2 mm. The median increase and decrease in tumor measurements was 4.3 percent and minus-4.2 percent, respectively, and ranged from 23 percent shrinkage to 31 percent growth.
Measurement changes were within plus-or-minus 10 percent for 84 percent of measurements. Three percent of measurements met the 20-percent growth criteria for progression according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST). Small lesions had greater variability measurement change.
Riely and colleagues concluded that apparent changes in tumor diameter exceeding 1 to 2 mm are common upon immediate reimaging, and that radiologists should be aware that apparent size differences of less than 10 percent may stem from the inherent variability of reimaging.
“Caution should be exercised in interpreting the significance of small changes in lesion size in the care of individual patients and in the interpretation of clinical trial results,” the researchers concluded.
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.














