TeraRecon Launches Updated Intuition 4.10 Cardiac MRI Software
The updated software reportedly provides access to more than 200 enhanced features including optimized hanging protocols with a cardiac MRI viewer and perfusion quantification analysis.
Offering a range of enhanced features to facilitate precision with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), TeraRecon has launched an updated version of its software-as-a-service (SaaS) platform Intuition 4.10.
In addition to facilitating expedited measurements and reporting on cardiac MRI cases, the Intuition 4.10 software provides a dedicated cardiac MRI viewer with hanging protocols and over 200 enhanced features, according to TeraRecon.
The updated software-as-a-service (SaaS) platform Intuition 4.10 from TeraRecon reportedly offers more than 200 enhanced features for cardiac MRI assessment and workflow. (Images courtesy of Adobe Stock.)
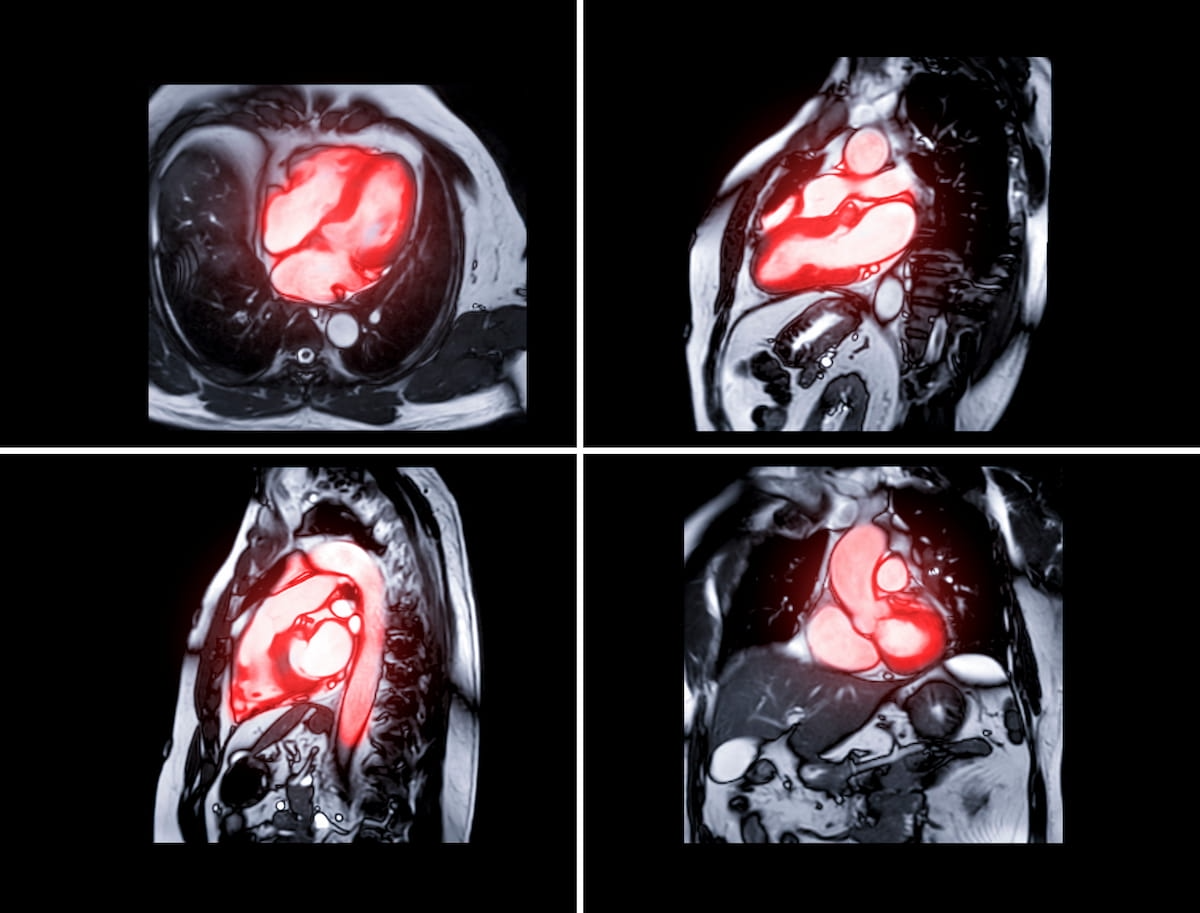
The company added that features such as extracellular volume (ECV) mapping, 2D flow analysis and a new global strain analysis workflow provide significant quantification tools for cardiac MRI analysis.
"TeraRecon's Intuition 4.10 release includes significant new enhancements to cardiac MR workflows," noted Christopher Maroules, M.D., the chief of cardiothoracic imaging at the Naval Medical Center Portsmouth in Portsmouth, Va. “This release allows me to start standardizing my post-processing cardiac workflows onto a single, broad tool for imaging workflows. The versatility of the dedicated cardiac MR viewer and various cardiac MR workflows enable me to conduct my day-to-day cardiac MR analysis in a streamlined and consistent manner."
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.