Mammography Study: Paying for Adjunctive AI Screening Led to 43 Percent Higher Rate of Breast Cancer Detection
In a multicenter study involving over 747,000 women who had mammography screening, those who paid for AI-enhanced screening had a 21 percent higher recall rate and a 15 percent higher positive predictive value (PPV) for breast cancer, according to research presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.
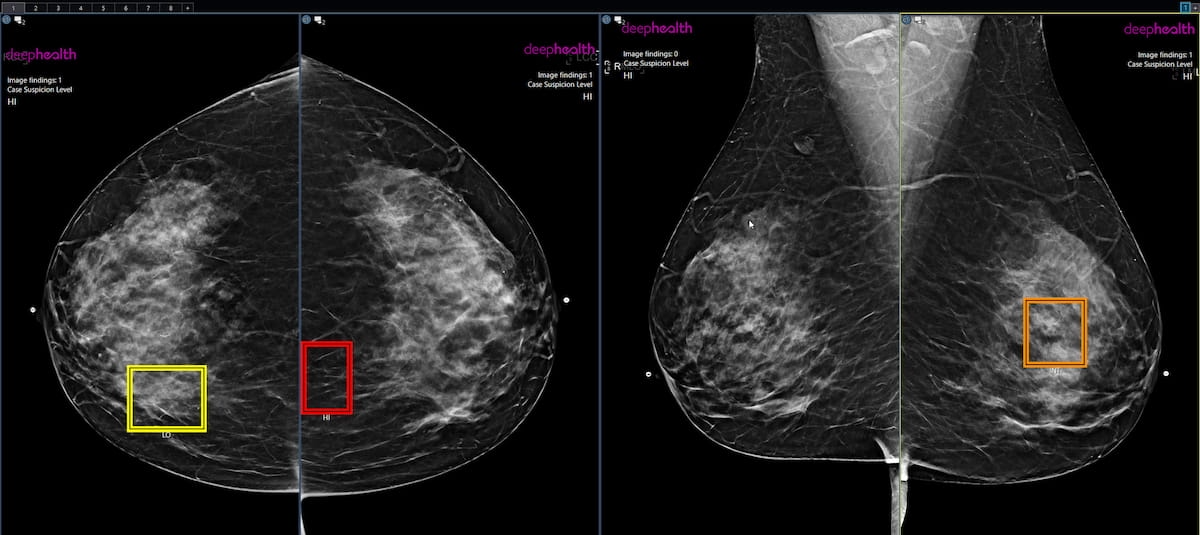
Emerging multicenter research suggests that over one-third of women are willing to pay for artificial intelligence (AI)-enhanced mammography screening and had a 43 percent higher average cancer detection rate (CDR) than those who did not have adjunctive AI screening.
For the multicenter study, presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference, researchers reviewed mammography screening data from 747,604 women and compared the CDR, recall rate and positive predictive value (PPV) for women who opted to self-pay for AI-enhanced screening and those who did not.
At one year, the researchers found that women who had adjunctive AI screening had a 43 percent higher CDR (5.95 vs. 4.15 per 1000). The study authors noted that the use of adjunctive AI accounted for 21 percent of the increased CDR and maintained that 22 percent of the increased CDR was due to patients at higher risk for breast cancer enrolling more frequently for adjunctive AI screening.
In a multicenter study evaluating patient self-pay for the use of adjunctive AI in mammography screening, researchers found that adjunctive AI led to a 43 percent higher cancer detection rate, a 21 percent higher recall rate and a 15 percent higher positive predictive value in comparison to women who did not have adjunctive AI.
“These data indicate that many women are eager to utilize AI to enhance their screening mammogram, and when AI is coupled with a safeguard review, more cancers are found,” noted Gregory Sorensen, M.D., a senior author of the study and chief executive officer of DeepHealth.
The use of adjunctive AI yielded a 21 percent higher recall rate (10.9 percent vs. 8.8 percent) but also led to a 15 percent higher PPV (5.4 percent vs. 4.6 percent), according to the study authors.
(Editor’s note: For additional coverage from the RSNA conference, click here.)
“The AI-driven enhanced review program leverages AI in a novel workflow to ensure women with suspicious findings get expert level care that could help detect many more breast cancers early,” emphasized Bryan Haslam, Ph.D., a co-author of the study and chief product officer at DeepHealth. “The number of women electing for this program is now at 36% and growing, and the rate of cancer detection continues to be substantially higher for those women.”
Reference
1. Sorensen AG, Haslam B, Louis L, Holt JS, Storella JM. Patient self-pay for AI-driven enhanced review program in screening mammography: initial experience. Poster presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) 2024 110th Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting Dec. 1-5, 2024. Available at: https://www.rsna.org/annual-meeting .
SNMMI: Botox May Facilitate Relief from Dry Mouth Side Effect of PSMA-Targeted Radiopharmaceuticals
June 25th 2025For patients being treated with radiopharmaceutical agents for metastatic prostate cancer, the combination of botulinum toxin and an anti-nausea patch led to a 30 percent reduction in PSMA uptake in the salivary glands, according to preliminary research findings presented at the SNMMI conference.
The Reading Room: Artificial Intelligence: What RSNA 2020 Offered, and What 2021 Could Bring
December 5th 2020Nina Kottler, M.D., chief medical officer of AI at Radiology Partners, discusses, during RSNA 2020, what new developments the annual meeting provided about these technologies, sessions to access, and what to expect in the coming year.
Could an Emerging PET Tracer be a Game Changer for Detecting Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
June 23rd 2025In addition to over 90 percent sensitivity in detecting hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the glypican-3 (GPC3) targeted PET tracer 68Ga-aGPC3-scFv appeared to be advantageous in identifying HCC tumors smaller than one centimeter, according to pilot study findings presented at the SNMMI conference.
RSNA 2020: Addressing Healthcare Disparities and Access to Care
December 4th 2020Rich Heller, M.D., with Radiology Partners, and Lucy Spalluto, M.D., with Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, discuss the highlights of their RSNA 2020 session on health disparities, focusing on the underlying factors and challenges radiologists face to providing greater access to care.
SNMMI: What a New Meta-Analysis Reveals About Radiotracers for PET/CT Detection of PCa
June 22nd 2025While (68Ga)Ga-PSMA-11 offers a pooled sensitivity rate of 92 percent for prostate cancer, (18F)-based radiotracers may offer enhanced lesion detection as well as improved imaging flexibility, according to a meta-analysis presented at the Society for Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) conference.
SNMMI: Can Multimodal Monitoring Bolster Outcomes with Pluvicto in Treating mCRPC?
June 22nd 2025Multimodal treatment monitoring, including SPECT/CT exams 24 hours after treatment with Lu-177 PSMA-617, may have facilitated significantly shorter therapy durations and reduced side effects in patients with mCRPC, according to a two-year study presented at the Society for Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) conference.