
When general clinicians were educated about and given access to low-dose computed tomography, more lung cancers were diagnosed.

When general clinicians were educated about and given access to low-dose computed tomography, more lung cancers were diagnosed.

Pelvic CT with filtered back projection and 50% ASIR reduces dose.

Filtered back projection and ASIR50 reduces dose in pelvic CT.

Study measures size-specific dose estimates and contrast-to-noise ratio in overweight patients.

Study examines ASIR effect on normal and overweight children who underwent chest CT.

Study evaluates whether LDCT lung cancer screening is equally beneficial for younger and older patients.

Cone-beam CT is preferential to multislice spiral CT for hard-contrast objects, study says.

NCCN Group 2 high-risk patients to benefit from CT lung screening, study says.

CT images reconstructed with low dose model-based iterative reconstruction did not compromise image quality.

States found to have a high percentage of people at risk for lung cancer do not have an adequate number of LDCT screening centers.

New CT scanners’ variability affects cardiovascular risk classification.
Mainstream media may report CT overuse, but double thoracic CT is used appropriately, study says.

Experienced and inexperienced radiologists had similar eye tracking, so errors may be occurring during other phases of the study.

CCTA may be effective in screening CAD in adult survivors of Hodgkin’s lymphoma.

Automatic tube voltage selection automatically adjusts the tube current depending on patient size and attenuation.

Patients who underwent low-dose CT for lung cancer screening and received false-positives benefited from counseling.

Study identifies lowest possible radiation dose that still allows for detection of pleural effusions, thickening and calcification.

Study shows patients are positioned too low, negatively impacting radiation dose and image noise in chest CT.

Tomosynthesis provides better visualization of architectural distortion than mammography.

Study tackles why women with most treatable form of breast cancer pursue most aggressive prophylactic measures; MRI false-positives have no effect.

Combining MRI and mammography in an organized breast screening program for high-risk women is effective.

The controversy of covering low-dose CT for lung cancer screening continues, as groups argue lives saved versus dollars spent.

Short but intensive training was effective in training radiology staff on dose reduction.

Timing of DTI is not restricted by the menstrual cycle, but is sensitive to menopause and milk in lactating women.

Preoperative MRI in early breast cancer can reduce reexcision rates and, therefore, minimize patient anxiety.

In cost comparison of screen-film mammography and digital mammography, digital is more cost-effective.

Discrepancies in dose among institutions reveal underutilization of reduced-dose techniques.

Applying the same dose-reduction protocols to all patients may have adverse effects.

Ultrasound remains most sensitive imaging modality when diagnosing placenta accreta.

Women treated with chest radiation as children have an increased risk for developing breast cancer later in life, a study says.

Published: July 12th 2013 | Updated:

Published: July 12th 2013 | Updated:
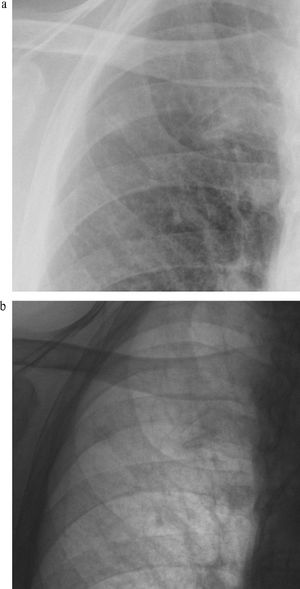
Published: August 7th 2013 | Updated:

Published: August 13th 2013 | Updated:

Published: August 30th 2013 | Updated:

Published: August 30th 2013 | Updated: