- Diagnostic Imaging Vol 31 No 6
- Volume 31
- Issue 6
Philips MultiTransmit adjusts radiofrequency to patient anatomy
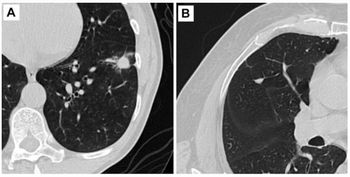
Image quality derived from echo liver imaging at 3T (A, left) improves (A, right) when applying Philips MultiTransmit technology, which eliminatesdielectric shading, an artifact commonly found at this field strength.
Image quality derived from echo liver imaging at 3T (A) improves when applying Philips MultiTransmit technology, which eliminates dielectric shading, an artifact commonly found at this field strength. Unveiled at RSNA 2008, MultiTransmit technology automatically adjusts multiple radiofrequency signals to accommodate the anatomy of specific patients, thereby improving image uniformity and increasing overall image consistency, according to the company. The technology, which is unique to the company’s Achieva 3.0T TX, is particularly helpful in patients with liver cirrhosis and ascites (B). These ascites can be challenging to image due to shielding effects of fluids (B, inset). MultiTransmit solves the problem, decreasing B1 inhomogeneity and, thereby, improving lesion visualization. The first installations of the Achieva 3.0T TX with MultiTransmit began operating earlier this year at Tokai University in Tokyo, Bonn University in Germany, and Fletcher Allen Health Care in Burlington, VT. Users are focusing on breast, spine, and abdominal imaging. (Provided by University of Bonn)
Articles in this issue
over 16 years ago
CT reveals traits of drug-resistanttuberculosisover 16 years ago
Hospital relations power Alliance Healthcare's growthover 16 years ago
Falling U.S. demand for CT opens door for bargain huntersover 16 years ago
ER bellyaches lead to more CT bellyachingover 16 years ago
Healthcare reform proposals highlight economic privilegeover 16 years ago
Demonstrations and skits add pizzazz to SIIM meetingover 16 years ago
Philips, Toshiba enter hand-carried ultrasound marketover 16 years ago
Broader coverage for PET could simplify cancer careover 16 years ago
Rival hypoxia agents vie for premier treatment roleover 16 years ago
Raman spectroscopy sets new multiplexing standardNewsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.