Is the current OLA process a viable alternative for assessing our skills?

Is the current OLA process a viable alternative for assessing our skills?

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
The upgraded RefleXion X2 platform offers a 20 cm field of view that may bolster visualization of moving tumors.
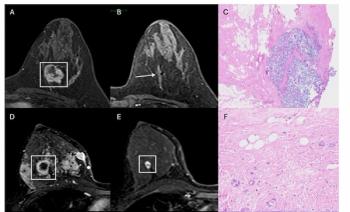
For patients with triple-negative breast cancer being treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and immunotherapy, MRI demonstrated a 94.3 percent sensitivity for predicting pathologic complete response, according to a new study.
In addition to offering a variety of AI features, the Magnetom Flow 1.5T MRI system reportedly facilitates a 56 percent reduction in annual energy consumption in comparison to previous MRI scanners.
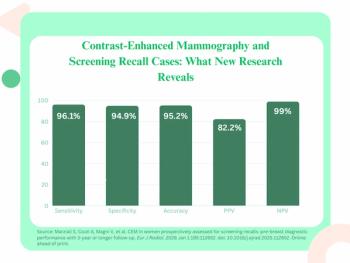
The use of contrast-enhanced mammography in nearly 200 cases of screening recalls yielded a 96.1 percent per-breast sensitivity rate and a 99 percent negative predictive value.

In a recent interview, Onofrio Catalano, M.D., Ph.D., discussed new research findings demonstrating robust sensitivity and specificity in detecting hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with LI-RADS 3 presentations.
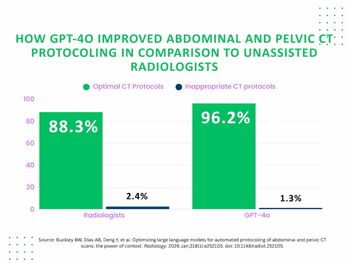
In a study involving over 1,400 patients who had abdominal or pelvic CTs, the large language model GPT-4o selected optimal protocols in 96.2 percent of cases in comparison to 88.3 percent for radiologists.
The Echo Stewardship Program, which allows non-sonographer clinicians to perform focused cardiac ultrasound exams under physician guidance, is now cleared for use across handheld, laptop and cart-based ultrasound platforms
In a recent interview, Jeremie Calais, M.D., Ph.D., discussed new research examining the prognostic capacity of PSMA PET parameters in predicting hematologic toxicity and outcomes for patients treated with (177Lu)Lu-PSMA-617 for mCRPC.
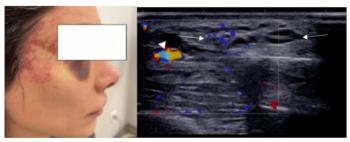
In a new literature review, researchers discuss common patterns and complications with cosmetic fillers that can be revealed on ultrasound imaging.

Catch up on the most popular radiology podcasts from 2025.
How active are you in steering your career course in radiology?
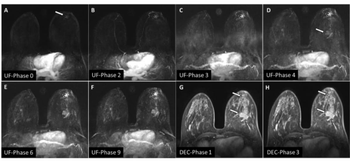
Employing a 77-second scan time for obtaining ultrafast breast MRI views, researchers found a 92.1 percent AUC for differentiating between benign and malignant lesions, according to new prospective study.

Catch up on the most well-read Eric Postal, M.D.-penned radiology blogs from 2025.
Catch up on the most well-viewed MRI content from 2025.

Catch up on the most well-viewed video interviews in December 2025.

Catch up on the most well-viewed radiology content from 2025.

In a recent interview, Michael Hofman, MBBS, FRACP, discussed preliminary research findings and the potential utility of the positron emission tomography (PET) agent ITM-94, which recently garnered a fast track designation from the FDA for clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC).
Catch up on the most well-viewed mammography content from 2025.
From controversial research on radiation-induced long-term cancer risks with computed tomography (CT) scans and the emerging prognostic value of AI-enabled plaque quantification to the potential impact of deep learning and AI-enhanced radiomics in thoracic radiology, here is a look back at the most well-viewed CT content from 2025.
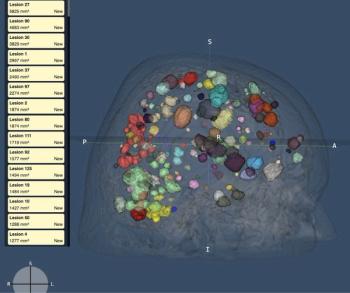
The cloud-based Brain Mets software reportedly provides accelerated detection, measurement and tracking of metastatic brain lesions based on routine brain MRI sequences.
What behaviors and aptitudes for learning may be conducive to a future career in radiology?

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
In addition to advanced mammography image processing and integrated MQSA tracking, the MammoIQ system enables viewing of adjunctive modalities including MRI, ultrasound and PET imaging.
Catch up on the most well-viewed prostate cancer imaging content from 2025.

Catch up on the most well-viewed video interviews from 2025.
Catch up on the most well-viewed ultrasound content from 2025.

Savvy negotiating for a new radiology gig requires a deft blend of flexibility and problem solving, and a willingness to walk away if you’re not seeing the same attributes on the other side of the table.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.