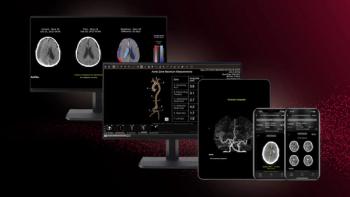
The new FDA 510(k) clearances for RapidAI include Rapid LMVO, which facilitates assessment of ischemic stroke, and Rapid MLS, which aids in the quantification of midline shifts with potential brain injuries.

The new FDA 510(k) clearances for RapidAI include Rapid LMVO, which facilitates assessment of ischemic stroke, and Rapid MLS, which aids in the quantification of midline shifts with potential brain injuries.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
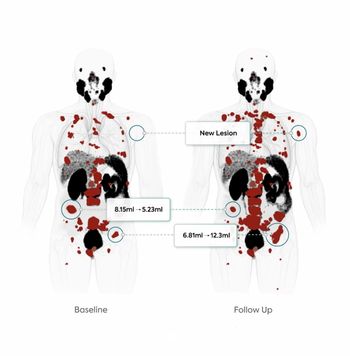
Utilizing the AI-enabled TrackPSMA to monitor the effectiveness of radioligand therapy for prostate cancer may allow more timely decisions to adjust treatment dosage or switch to a more effective modality.

Deep learning assessment of adrenal gland volume on computed tomography (CT) scans may provide an objective assessment of chronic stress with significant links to adverse cardiovascular outcomes, according to new research to be presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) annual meeting.

In a recent interview, Nina Kottler, M.D., discussed key trends that are leading to a renewed focus on improved enterprise imaging platforms and the potential promise of integrating Cognita Imaging’s Mosaic Drafting vision language model technology into the MosaicOS platform.
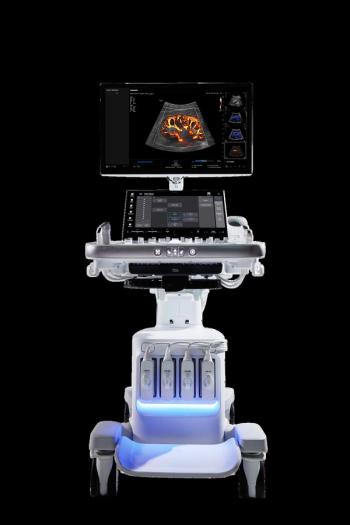
Combining AI advances and ergonomic innovation, the R20 ultrasound platform reportedly offers a variety of automated tools and design features to facilitate a smoother, efficient imaging workflow.
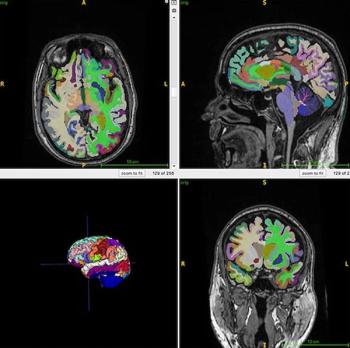
In MRI findings to be presented at the upcoming RSNA meeting, researchers demonstrated that the combination of higher muscle mass and lower visceral fat may have an impact on brain aging.
Asking those with at least five years of post-residency experience to share their ideas for reforming health care may lead to some common themes that could emerge as the basis of a health care constitution for change.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Comparing annual emergency department encounters that involved a head CT in 2007 and 2022, researchers noted a 51 percent increase and also found significant disparities in access to head CTs for Black patients, those on Medicaid and patients in rural hospital settings.
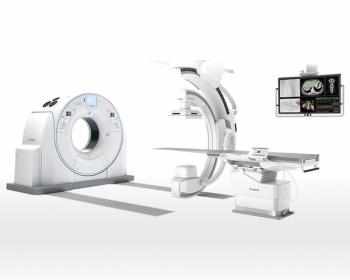
Geared toward interventional radiologists, the Alphenix 4D CT with Aquilion One/Insight Edition combines angiography capabilities with advanced features in computed tomography.
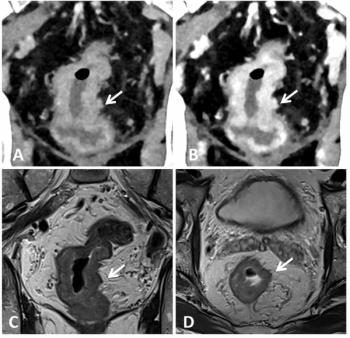
For T3-T4 rectal cancer staging, a new study showed that optimal photon-counting CT offered an AUC range between 80 and 86 percent in comparison to an AUC range between 78 and 88 percent for rectal MRI.
The recently launched PIV Assist reportedly offers a variety of features including real-time calculation of the catheter-to-vein ratio and pre-scan differentiation of veins and arteries to facilitate vascular access planning.
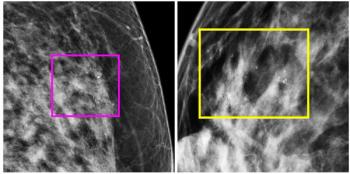
The use of radiomics for mammography may help predict the development of occult invasive cancer in women with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), according to a new study.

In a recent interview, Christoph Lee, M.D., discussed key findings from the ASSURE study, which evaluated the use of AI in detection and triage in a multicenter trial involving over 579,000 women who had digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) exams.

The Synapse One platform reportedly offers a variety of enterprise imaging capabilities and may facilitate reduced third-party integration complexities and costs.

Along with the capability of automated measurements and 3D reconstructions of the aorta, Rapid Aortic may facilitate earlier detection of aortic aneurysms and dissections on computed tomography exams.
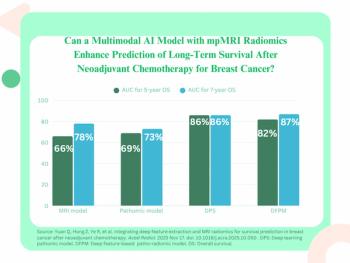
Incorporating mpMRI radiomics, clinical characteristics, deep learning and pathomic features, a multimodal model offered 82 percent and 87 percent AUCs for predicting overall survival outcomes at five years and seven years, respectively, for women treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer.
The newly launched Compass AI software platform reportedly facilitates a 94 percent compliance rate for documentation of point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) exams.
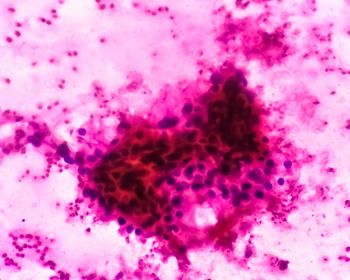
The gallium-68 radiolabeled PET imaging agent ITM-94 is currently being evaluated in a phase 1/2 trial for its utility in detecting ccRCC and differentiating indeterminate renal masses.
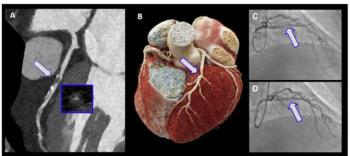
Photon-counting computed tomography demonstrated over 20 percent accuracy at the patient level and nearly 14 percent higher accuracy level at the vessel level in comparison to energy-integrating detector CT for detecting > 70 percent stenosis, according to a newly published study.
Exploring ways to bolster efficiency in an ongoing manner can help mitigate the strain of burgeoning worklists and improve morale.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a recent interview, Ibrahim Danad, M.D., Ph.D., discussed new research findings from the multicenter CONFIRM2 trial and use of the AI-CT software to obtain automated quantification of plaque burden based off coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) scans.
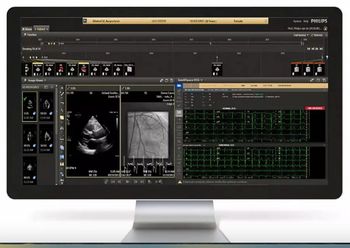
The latest update of the Cardiovascular Workspace software reportedly emphasizes secure cloud deployment and accelerated adoption of AI tools for increased efficiency.
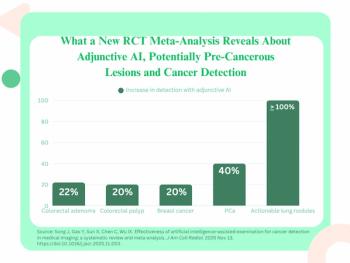
Use of AI provided a pooled 22 percent increase in adenoma detection but no significant impact for advanced adenomas, according to an analysis of 39 randomized controlled trials examining AI’s impact in detecting colorectal cancer.
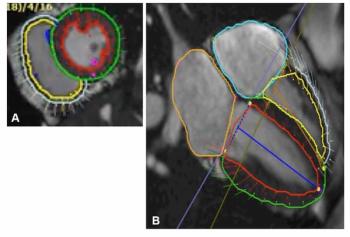
Multivariable analysis from a new study revealed that those with low right ventricular global longitudinal strain were 16 percent more likely to suffer heart failure.
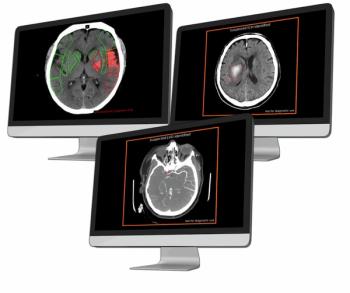
The launch of the AVI imaging platform reportedly facilitates direct integration into PACS and RS systems, and automated access to adjunctive CT-based AI applications for a variety of conditions including pulmonary embolism, intracranial hemorrhage and large vessel occlusion
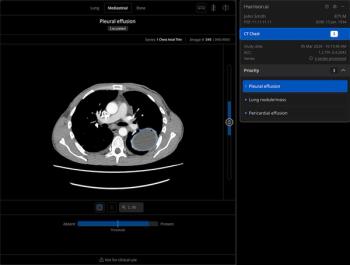
Offering a “safety net” in emergency and inpatient settings, the Chest CT software reportedly provides enhanced triage capabilities and adjunctive detection of 167 radiological features.

In a recent interview, Timothy Fairbairn, Ph.D., and Fatima Rodiguez, M.D., discussed new research findings, recently presented at the American Heart Association (AHA) conference, showing the value of AI-powered quantification of plaque burden from CCTA exams for predicting adverse cardiovascular outcomes.