Articles by Katie Robinson
In what may be the first study to assess the effectiveness of biparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for prostate cancer screening in a large cohort, researchers found that MRI screening had a significantly lower false positive rate and significantly higher positive predictive values (PPVs) than prostate-specific antigen (PSA)-based screening.
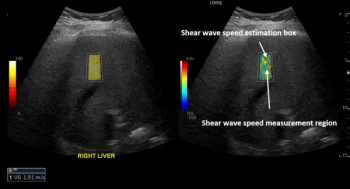
The retrospective study involving the use of ultrasound shear wave elastography showed a significant increase in liver stiffness 44 weeks after the diagnosis of COVID-19 in comparison to pre-pandemic and pandemic controls.
Main pulmonary artery and right ventricular diameters on computed tomography (CT) scans of the thorax were predictors of pulmonary hypertension.
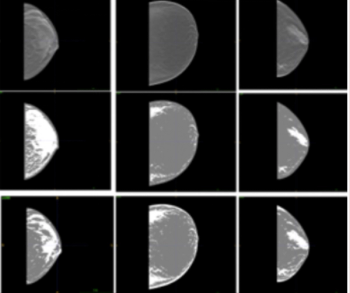
An emerging artificial intelligence algorithm, developed to estimate volumetric breast density from 3D-reconstructed digital breast tomosynthesis images, could potentially facilitate individual risk assessments for breast cancer.
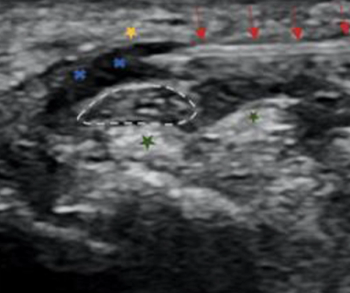
A randomized controlled trial shows that the minimally invasive treatment provided long-term relief of carpal tunnel syndrome.
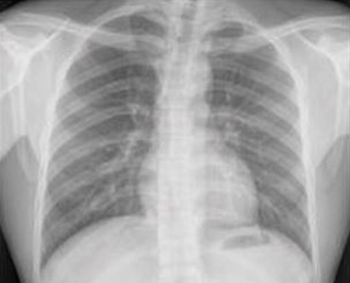
Based on a single existing chest X-ray image, the deep learning model predicts future major adverse cardiovascular events with similar performance to an established risk scoring system and may help identify people for preventive use of statin medication.
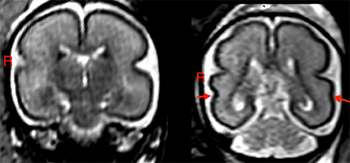
Researchers found that even low amounts of alcohol consumption in pregnant women can lead to early and diffuse structural changes in brain regions related to key functions including language development.
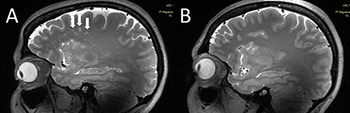
New magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) research suggests a significant link between deep white matter hyperintensity severity and increased quantity of enlarged perivascular spaces in the centrum semiovale among people with migraines.
Study findings suggest that assessment with the simpler and more commonly available non-contrast computed tomography (CT) may widen the indication for treating patients in the extended window.
New research emphasizes roles of anterior collaterals and ischemic core growth rate in assessing patients with large vessel occlusion.
Study findings further highlight the central role of PET/CT in disease response after CAR-T cell therapy.
Early study results suggest that low-field MRI may offer a cost-effective, radiation-free alternative to monitor ventricular volume changes in patients with hydrocephalus.
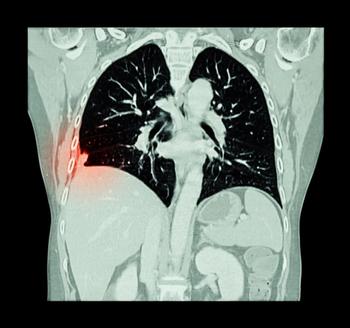
Cost, lower literacy levels and fear of lung cancer diagnosis were highlighted as concerns with lung cancer screening.
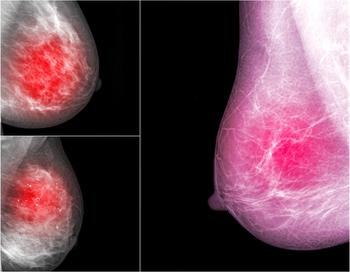
Diffusion-weighted imaging may be useful as a safe and effective screening tool to supplement mammography in women with dense breast tissues.

This study discloses the characteristics of patients using self-scheduled online patient portal screening mammography.
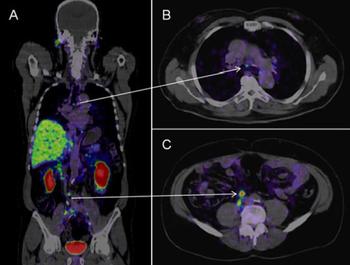
PSMA PET is highly robust in identifying prostate cancer lesions which are otherwise deemed unremarkable.
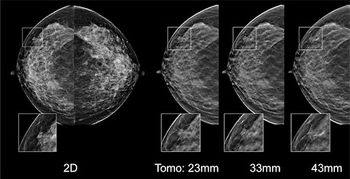
An artificial intelligence for digital breast tomosynthesis enhances radiologists’ performance and efficiency.
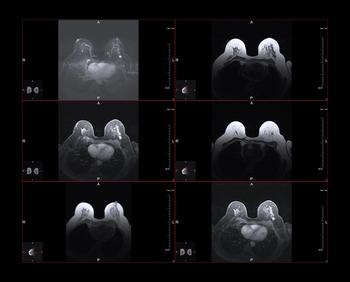
Following breast cancer treatment, women who have access to breast MRI may safely forgo additional mammographic or digital breast tomosynthesis follow-up.
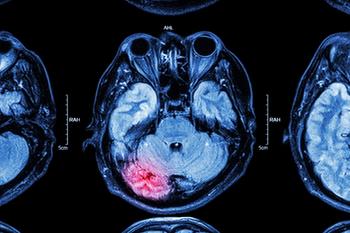
A deep learning model was developed to detect intracranial hemorrhage in computed tomography scans without medical annotation.
Multiparametric MRI can detect pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant therapy in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.

Sonographic quantitative assessment of the deltoid muscle could translate into a dedicated, simple and noninvasive screening method to detect type 2 diabetes.
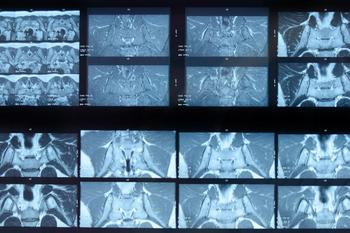
Findings suggest that patients with suspected axial spondyloarthropathy not taking NSAIDs were more likely to have MRI proven inflammation compared with patients taking NSAIDs.
Deep learning models trained on a dataset lacking racial diversity could hinder the detection of pathology in underrepresented minority patients.

Breast ultrasound/MRI fusion significantly improves localization of incidentally detected MRI lesions which are occult on an initial ultrasound survey alone.
COVID-19 can result in cardiac complications including myocarditis, arterial and venous thromboembolism, and cardiomyopathy.

Radiologists should be aware of the possible association of COVID-19 mRNA vaccination and myocarditis.
Study findings have the potential to widen the indication for treating patients in the extended window using simpler and more widespread non-contrast CT.
Clinicians taking care of patients with high-risk prostate cancer being assessed for prostatectomy can use a positive PET scan as a true positive, but a negative scan cannot be used to exclude disease or inform nodal dissection.
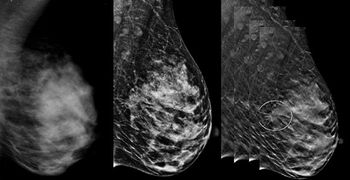
The impact of digital breast tomosynthesis on screening performance and screen-detected cancers appears to generalize beyond trials and academic centers to the community setting.
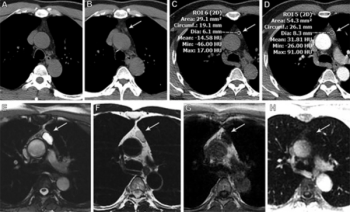
Awareness of the variable imaging characteristics and behavior of thymic cysts over time should help guide clinical management.


































