
Catch up on emerging research from the recent 2024 Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.

Catch up on emerging research from the recent 2024 Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.

Catch up on video interviews from the recent 2024 Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.

In the second part of a three-part interview from the recent RSNA conference, Mark Traill, M.D., emphasizes patience and monitoring with the assessment of AI to ensure optimal use of the technology to help ease the strain of increasing breast imaging volume.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In the first of a three-part interview from the recent RSNA conference, Mark Traill, M.D., discusses current challenges in breast radiology and the potential of AI to help mitigate some of these issues.

In a recent interview at the RSNA conference, Raj Chopra, MD shared his insights on the continued rise of cyberattacks, the impact of these attacks in radiology and keys to prevention and effectively responding to such events.
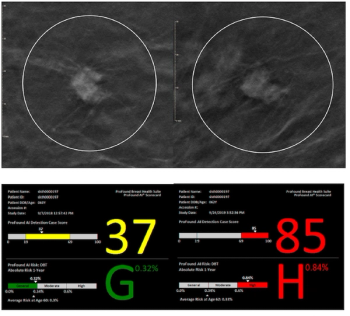
New research suggests that AI-powered assessment of digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) for short-term breast cancer risk may help address racial disparities with detection and shortcomings of traditional mammography in women with dense breasts.

In an interview at the RSNA conference, Sundus Lateef, MD, discussed the rise of silicosis and associated CT findings in a recent study of engineered stone countertop workers.
In patients with PI-RADS 3 lesion assessments, the combination of AI and prostate-specific antigen density (PSAD) level achieved a 78 percent sensitivity and 93 percent negative predictive value for clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa), according to research presented at the Radiological Society of North American (RSNA) conference.
Emerging research from the RSNA conference suggests that two-dimensional mammography would only detect 41 percent of detectable breast cancer.
In a recent interview, Sarah Friedewald, MD, discussed new study findings for an adjunctive AI software for digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) that revealed nearly equivalent sensitivity and specificity rates for breast cancer across a diverse cohort.
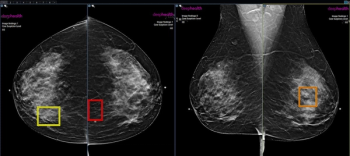
In a multicenter study involving over 747,000 women who had mammography screening, those who paid for AI-enhanced screening had a 21 percent higher recall rate and a 15 percent higher positive predictive value (PPV) for breast cancer, according to research presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.

In a recent interview at the RSNA conference, Shadpour Demehri, MD and Kamyar Moradi, MD discussed new brain MRI research findings that demonstrated a link between increased dementia risk and sarcopenia with the temporalis muscle.
The computed tomography device reportedly offers enhanced post-processing of images as well as bolstered image reconstruction capabilities with an 80 percent reduction in radiation dosing.
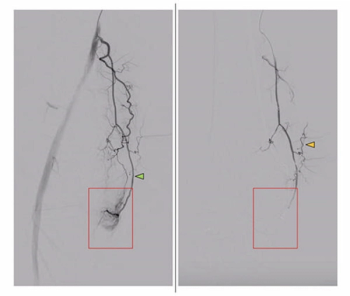
In a cohort of over 160 patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA), including grade 4 in nearly half of the cases, genicular artery embolization led to an 87 percent improvement in the quality of life index, according to research presented at the recent RSNA conference.
Debuting at the Radiological Society of North American (RSNA) conference, the new photon-counting computed tomography (PPCT) scanners Naeotom Alpha.Pro and Naeotom Alpha.Prime reportedly combine rapid scan times with high-resolution precision.

Higher visceral adipose tissue reportedly accounted for 77 percent of the association between Alzheimer’s disease and high body mass index (BMI), according to new research presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Higher repetitive head impacts in adult soccer players were associated with lower fractional anisotrophy and a higher orientation dispersion index in the frontal lobe, orbitofrontal cortex, and the parietal lobe, according to diffusion MRI findings to be presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.
The new mammography system reportedly offers features that promote workflow efficiency as well as patient comfort.

Slower aperiodic activity on magnetoencephalopathy may be associated with higher post-concussion symptomatology in high-school football players, according to new research to be presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.
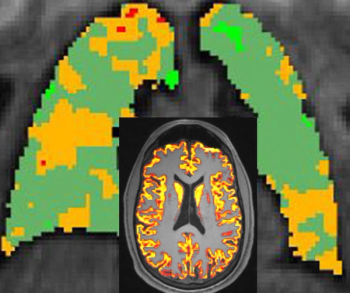
For patients with Long Covid, lower pulmonary gas exchange may be associated with lower gray and white matter volume, according to new MRI research to be presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.

Use of the medication levothyroxine, commonly prescribed for hypothyroidism, was associated with greater long-term loss of total body bone mass in seniors, according to new DEXA research to be presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.
Designed for theranostic imaging applications, the AnyScan Trio SPECT/CT TheraMax scanner was recently unveiled at the annual meeting of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM).

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
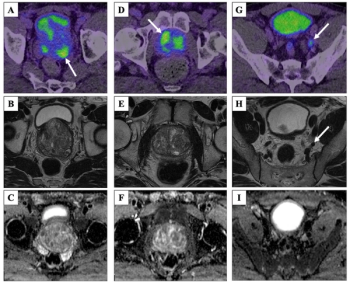
Initial detection of metastatic prostate cancer via 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT was significantly associated with PSA values > 20 ng/ml, ISUP grade > 3 and MRI T-stage > 3, according to research presented recently at the SNMMI conference.

In a recent interview at the SNMMI conference, David Gauden, D.Phil, discussed key findings from new research evaluating the use of the PET radiotracer 18F-flotufolastat in patients with primary prostate cancer (PCa) and men with biochemical recurrence of PCa.
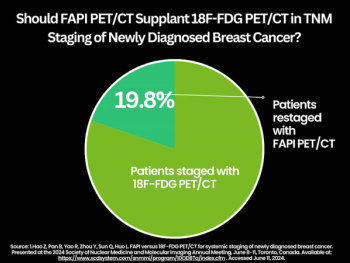
Improved assessment of axillary lymph node status with FAPI PET/CT led to restaging of nearly 71 percent of patients with breast cancer, according to new research presented at the SNMMI 2024 conference.
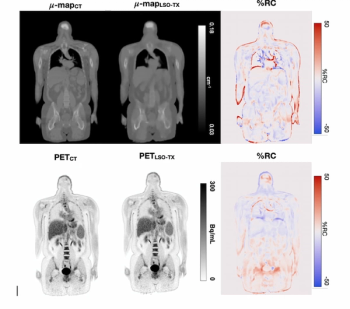
Ultra-low dosing with long axial field-of-view positron emission tomography (PET) scanners facilitates qualitative PET imaging at a more than 50 percent reduction of conventional radiation dosing with PET, according to new research presented at the SNMMI 2024 conference.
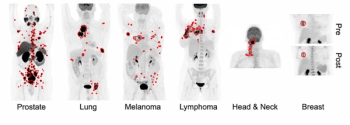
Deep transfer learning may elevate the capability of whole-body PET/CT scans to diagnose multiple cancers, ranging from breast cancer and lung cancer to melanoma and prostate cancer, according to new research presented at the SNMMI conference.