Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in December 2024.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
Catch up on the most well-read ultrasound content from 2024.

Catch up on video interviews from the recent 2024 Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.

Catch up on the most well-read Eric Postal, M.D.-penned blogs from 2024.

In the second part of a three-part interview from the recent RSNA conference, Mark Traill, M.D., emphasizes patience and monitoring with the assessment of AI to ensure optimal use of the technology to help ease the strain of increasing breast imaging volume.
Does the wisdom of experience to make meaningful changes in radiology get usurped by reduced energy and a sense of diminishing returns?

Catch up on the most well-read mammography articles from 2024.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Catch up on the most well-viewed magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) content from 2024.

In the first of a three-part interview from the recent RSNA conference, Mark Traill, M.D., discusses current challenges in breast radiology and the potential of AI to help mitigate some of these issues.
In a new study involving nearly 600 biopsy-naïve men, researchers found that only 4 percent of those with negative prostate MRI had clinically significant prostate cancer after three years of active monitoring.
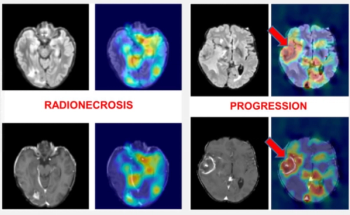
Convolutional neural network-enabled segmentation of brain MRI offered a 25.7 percent higher specificity than a radiomic model for differentiating radionecrosis and metastatic progression in patients treated with stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases.
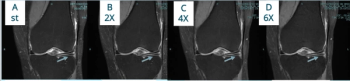
Ten-minute and five-minute knee MRI exams with compressed sequences facilitated by deep learning offered nearly equivalent sensitivity and specificity as an 18-minute conventional MRI knee exam, according to research presented recently at the RSNA conference.
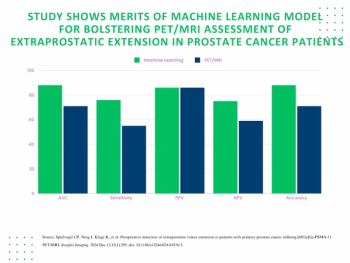
The use of an adjunctive machine learning model led to 17 and 21 percent improvements in the AUC and sensitivity rate, respectively, for PET/MRI in diagnosing extraprostatic tumor extension in patients with primary prostate cancer.
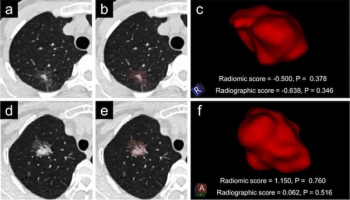
A CT-based radiomic model offered over 10 percent higher specificity and positive predictive value for high-risk lung adenocarcinoma in comparison to a radiographic model, according to external validation testing in a recent study.
Does our pattern recognition expertise in imaging extend to our impressions of tells in the work of our colleagues?

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In a recent interview at the RSNA conference, Raj Chopra, MD shared his insights on the continued rise of cyberattacks, the impact of these attacks in radiology and keys to prevention and effectively responding to such events.
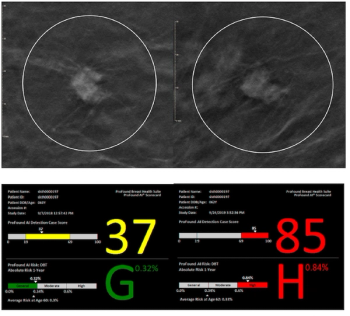
New research suggests that AI-powered assessment of digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) for short-term breast cancer risk may help address racial disparities with detection and shortcomings of traditional mammography in women with dense breasts.
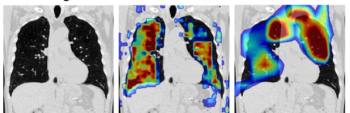
The authors of a new study found that deep learning assessment of single-phase CT scans provides comparable within-one stage accuracies to multiphase CT for detecting and staging chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
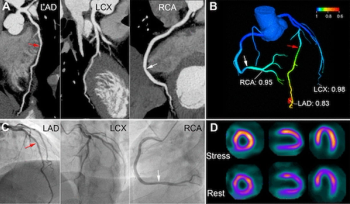
For patients with suspected or known coronary artery disease (CAD) without percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), researchers found that those with a normal CTA-derived quantitative flow ratio (CT-QFR) had a 22 percent higher MACE-free survival rate.

In an interview at the RSNA conference, Sundus Lateef, MD, discussed the rise of silicosis and associated CT findings in a recent study of engineered stone countertop workers.
In a new point-counterpoint discussion published in the American Journal of Roentgenology, researchers debate the merits and limitations of the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) version 2.1.
In patients with PI-RADS 3 lesion assessments, the combination of AI and prostate-specific antigen density (PSAD) level achieved a 78 percent sensitivity and 93 percent negative predictive value for clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa), according to research presented at the Radiological Society of North American (RSNA) conference.
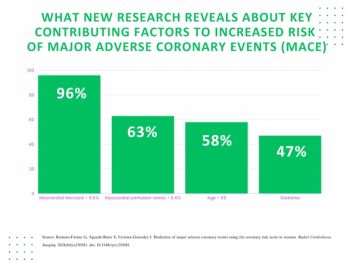
In research involving over 2,200 women who had SPECT MPI exams, researchers found that those who had a high score with the COronary Risk Score in WOmen (CORSWO) model had a greater than fourfold higher risk of major adverse coronary events (MACE).
Do we get mired in the rut of generational grumbling, or do we reframe resentments into perspective of what we have overcome?

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Emerging research from the RSNA conference suggests that two-dimensional mammography would only detect 41 percent of detectable breast cancer.
In a recent interview, Sarah Friedewald, MD, discussed new study findings for an adjunctive AI software for digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) that revealed nearly equivalent sensitivity and specificity rates for breast cancer across a diverse cohort.