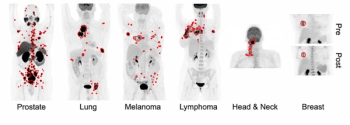
Deep transfer learning may elevate the capability of whole-body PET/CT scans to diagnose multiple cancers, ranging from breast cancer and lung cancer to melanoma and prostate cancer, according to new research presented at the SNMMI conference.


Deep transfer learning may elevate the capability of whole-body PET/CT scans to diagnose multiple cancers, ranging from breast cancer and lung cancer to melanoma and prostate cancer, according to new research presented at the SNMMI conference.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Facilitating additional consultation on chest and abdominal CT scans, the Second Opinions teleradiology platform now features FDA-cleared AI tools for cardiac, bone and liver assessments.
Offering comparable sensitivity to radiologists for detecting contralateral breast cancer on mammography images, an emerging adjunctive AI software may also facilitate earlier diagnosis, according to study findings presented at the at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting.
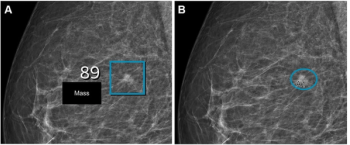
In a retrospective study involving nearly 119,000 women, researchers found that implementation of AI into mammography screening increased the positive predictive value by 11 percent, increased small cancer detection by 8.3 percent and reduced reading workload by approximately 33 percent.
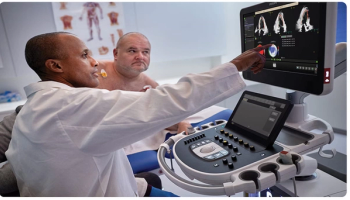
Featuring a combination of automated measurement capabilities and workflow enhancements, the new AI-powered cardiovascular ultrasound platform also provides automated assessment of regional wall motion abnormalities.
An AI algorithm that incorporates scoring of coronary inflammation based on coronary CT angiography (CCTA) may enhance long-term cardiovascular risk stratification beyond conventional risk factor and imaging assessments, even in patients without obstructive CAD.

Offering access to over 110 AI applications, the enterprise imaging platform enables radiologists to test, deploy and monitor the use of AI technologies.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
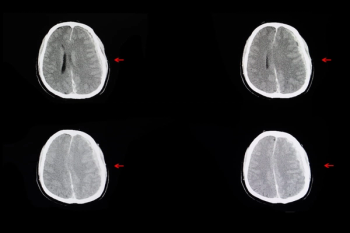
The AI-powered Heuron ICH software reportedly has an 86 percent sensitivity rate for diagnosing intracranial hemorrhage on computed tomography (CT) scans.

An AI model that includes extracted radiomic features from CT scans more than doubled the sensitivity rate for preoperative prediction of lung cancer recurrence in comparison to traditional TNM staging, according to study findings to be presented at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting in Chicago.
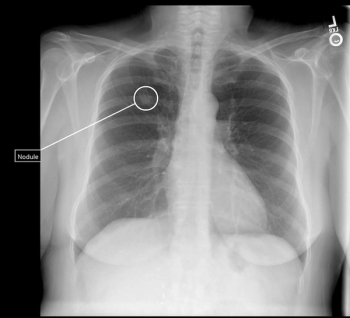
In addition to detecting missed lung nodules on X-rays, the AI-powered Qure.ai lung cancer continuum platform reportedly automates lung nodule measurement on CT scans and facilitates multimodality reporting.
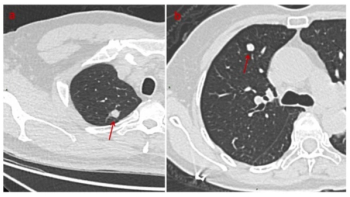
One deep learning model had a 72.4 percent accuracy rate for differentiating between benign and malignant solid pulmonary nodules on non-contrast CT while another deep learning model demonstrated an 87.1 percent AUC for differentiating benign and inflammatory findings.
Emphasizing restriction spectrum imaging (RSI), the recently launched prostate MRI software OnQ Prostate may enhance PI-RADS assessments and workflow efficiency.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
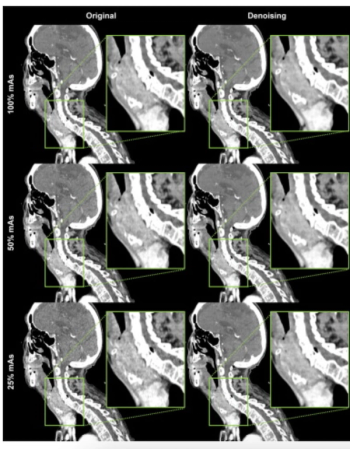
Image quality, sharpness, and contrast with AI-based denoising were significantly enhanced for neck CT in comparison to conventional CT image reconstruction at 100 percent and 50 percent mAs, according to newly published research.
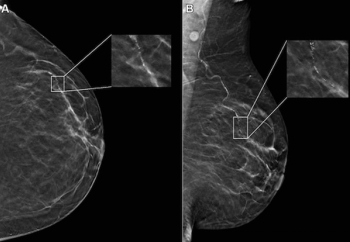
Researchers also noted that mammography-based AI software was associated with over a threefold higher likelihood of false-positive risk scores in patients 61 to 70 years of age in comparison to women 51 to 60 years of age.
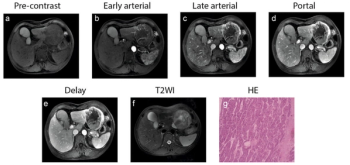
Incorporating dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI, a deep learning model demonstrated a 20 percent higher AUC in external validation testing than clinical factors alone and over a 17 percent higher AUC than radiological factors alone in predicting proliferative hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Reportedly trained on thousands of computed tomography scans, the e-Lung software utilizes machine learning to detect and assess the progression of features associated with interstitial lung diseases.
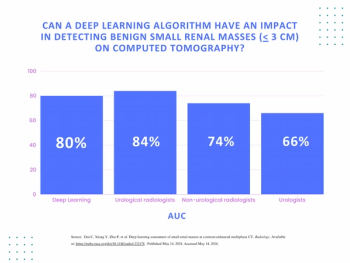
An emerging deep learning algorithm had a lower AUC and sensitivity than urological radiologists for differentiating between small renal masses on computed tomography (CT) scans but had a 21 percent higher sensitivity rate than non-urological radiologists, according to new research.

The artificial intelligence (AI)-powered module provides a prostate segmentation tool for MRI-guided transurethral ultrasound ablation (TULSA) procedures in patients with prostate cancer.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
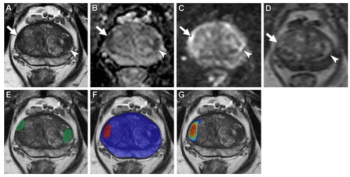
In a study involving over 1,000 visible prostate lesions on biparametric MRI, a deep learning algorithm detected 96 percent of clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa) in comparison to a 98 percent detection rate for an expert genitourinary radiologist.
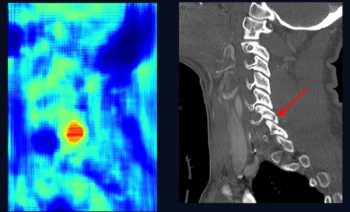
Researchers found a 98.3 percent concordance between attending radiology reports and AI assessments for possible cervical spine fractures on CT, according to new research presented at the 2024 ARRS Annual Meeting.