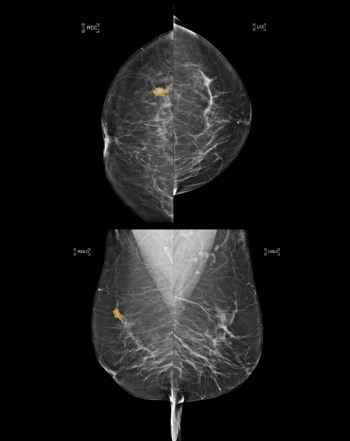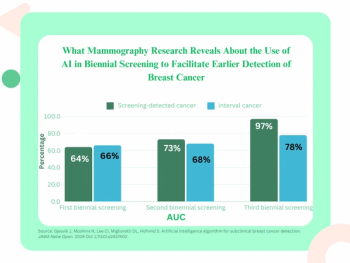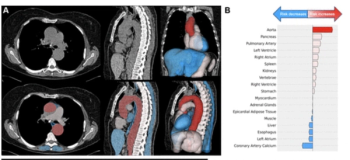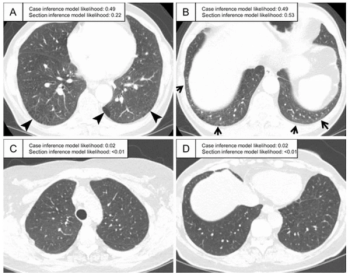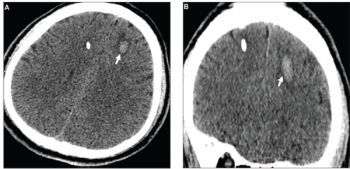
Four Medicare administrative contractors (MACs) will provide coverage of AI-enabled coronary plaque analysis and quantitative coronary tomography assessment of coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) for Medicare beneficiaries starting in November 2024.