For patients undergoing curative treatment for lung cancer, coronary artery calcification scoring via computed tomography has a 97 percent likelihood of determining their risk for major cardiovascular events, according to a new meta-analysis.


For patients undergoing curative treatment for lung cancer, coronary artery calcification scoring via computed tomography has a 97 percent likelihood of determining their risk for major cardiovascular events, according to a new meta-analysis.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
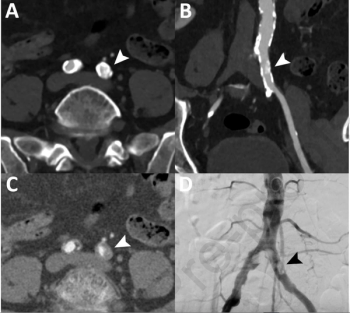
New research demonstrates that photon-counting computed tomography angiography (PC CTA) provides sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy rates of 90 percent and higher for the detection of stenotic disease in patients with peripheral artery disease (PAD).
The Spectral CT 7500 RT system reportedly combines 4D conventional computed tomography (CT) with the enhanced quantification and visualization of spectral CT to facilitate improved precision with radiotherapy.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Facilitating optimal use of contrast, the Medrad Centargo CT Injection System reportedly combines user-friendly features with workflow efficiency for high-volume CT departments.
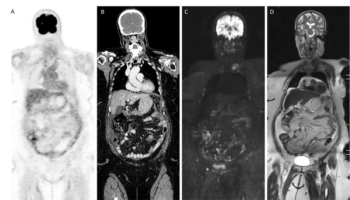
In newly published guidelines, researchers discuss the utility of CT, MRI and PET/CT in the diagnosis, staging, treatment monitoring and follow-up imaging for peritoneal metastases in patients with ovarian or colorectal cancer.
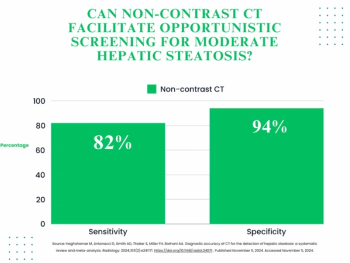
Non-contrast computed tomography offered 82 percent sensitivity and 94 percent specificity for the diagnosis of moderate hepatic steatosis, according to a 42-study meta-analysis.

In recent interviews, Eric Rohren, M.D., and Krishna Nallamshetty, M.D., discuss the potential of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) to progress into life-threatening consequences and an emerging AI-powered tool that may bolster adherence to best practice recommendations in radiology reporting of incidental AAA findings on CT and MRI.
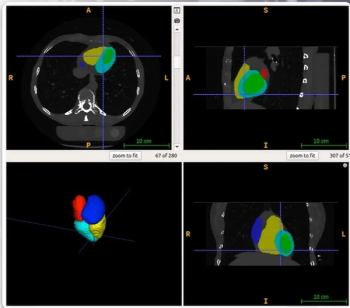
The AI-enabled AutoChamber software also garnered the FDA’s breakthrough device designation for opportunistic detection of enlarged heart chambers on non-contrast CT scans.
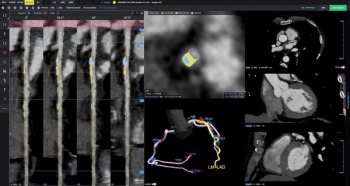
Al-powered quantitative assessment of coronary CT angiography (CCTA) revealed that non-calcified plaque volume was over 3.5 times higher in patients who had major adverse cardiovascular events, according to multicenter research presented at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT) conference.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
The Ezra Blueprint scan reportedly includes quantitative brain measurements, coronary calcium scoring (CAC) and a full-body MRI that provides screening for over 500 conditions.
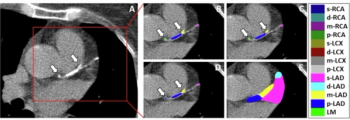
For segment-level coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring, a deep learning model had an accuracy rate of 73 percent for assigning calcifications to coronary artery segments and achieved a micro-average specificity of 97.8 percent.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
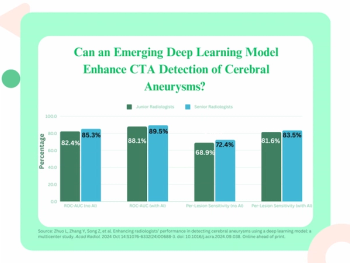
Adjunctive use of deep learning reportedly led to a 37 percent reduction of interpretation time for cerebral aneurysm assessment on computed tomography angiography (CTA) and greater than a 90 percent reduction in post-processing time.
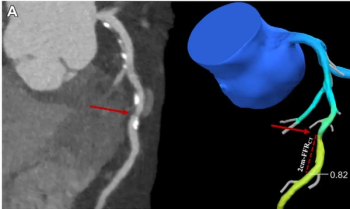
In nearly 5,300 patients with suspected coronary artery disease (CAD), adjunctive use of CT-based fractional flow reserve software significantly reduced the 90-day invasive coronary angiography (ICA) rate in comparison to unassisted use of coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA).
Four Medicare administrative contractors (MACs) will provide coverage of AI-enabled coronary plaque analysis and quantitative coronary tomography assessment of coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) for Medicare beneficiaries starting in November 2024.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
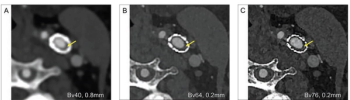
Researchers found that ultra-high resolution photon-counting significantly enhanced visualization of small vessels and facilitated improved reduction of blooming artifacts for head and neck computed tomography angiography (CTA) scans.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
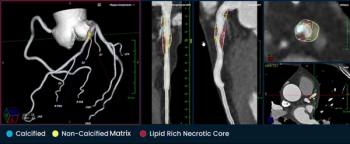
Through analysis of coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) images, the PlaqueIQ software provides quantification and classification of atherosclerosis, a common cause of myocardial infarction (MI) and ischemic stroke.
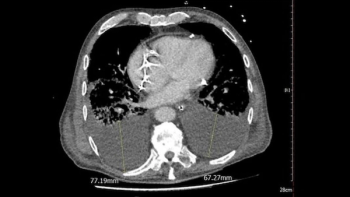
In a multicenter study of over 1,100 patients with COVID-19, pleural effusion was detected on CT scans in nearly a third of patients, who also had significantly higher ICU admission and 30-day mortality rates.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.