Women's Health CT
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
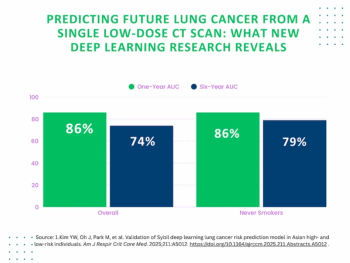
In never-smokers, deep learning assessment of single baseline low-dose computed tomography (CT) scans demonstrated a 79 percent AUC for predicting lung cancer up to six years later, according to new research presented today at the American Thoracic Society (ATS) 2025 International Conference.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
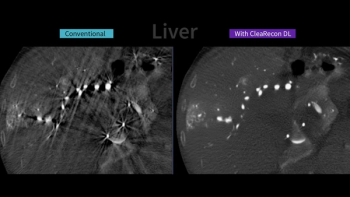
The CleaRecon DL software reportedly removes streak artifacts that can occur with the use of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) during interventional radiology procedures.

In a recent interview, C. Alberto Morales, M.D., discussed the impact of advances with CTA imaging and AI, and a shifting emphasis in cardiac risk stratification from stenosis to plaque burden.
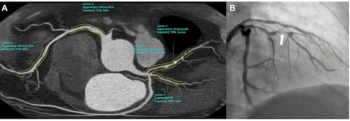
In a study involving over 1,000 patients who had coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) exams, AI software demonstrated a 90 percent AUC for assessments of cases > CAD-RADS 3 and 4A and had a 98 percent NPV for obstructive coronary artery disease.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
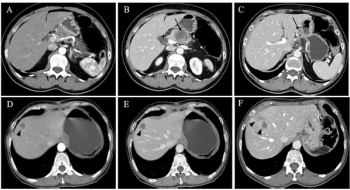
In comparison to American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM staging, an emerging CT-based scoring system for assessing early recurrence of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma demonstrated over a 22 percent higher AUC in testing and external validation cohorts in a new study.
The combination of the Aurora SPECT/CT system with AI-enabled Clarify DL image reconstruction reportedly offers the potential of enhanced image quality and streamlined workflows in nuclear medicine.

In a second part of a new podcast episode on recently published research on projected radiation-induced cancers from computed tomography (CT) scans, Mahadevappa Mahesh, MS, Ph.D., and Joseph Cavallo, M.D., offer current perspectives on cardiac CT dosing, AI advances and the importance of teamwork in ensuring appropriate dosing for CT.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In a new podcast, Mahadevappa Mahesh, MS, Ph.D., and Joseph Cavallo, M.D., share their perspectives on recently published research looking at projections for future radiation-induced cancers from computed tomography (CT) scans.
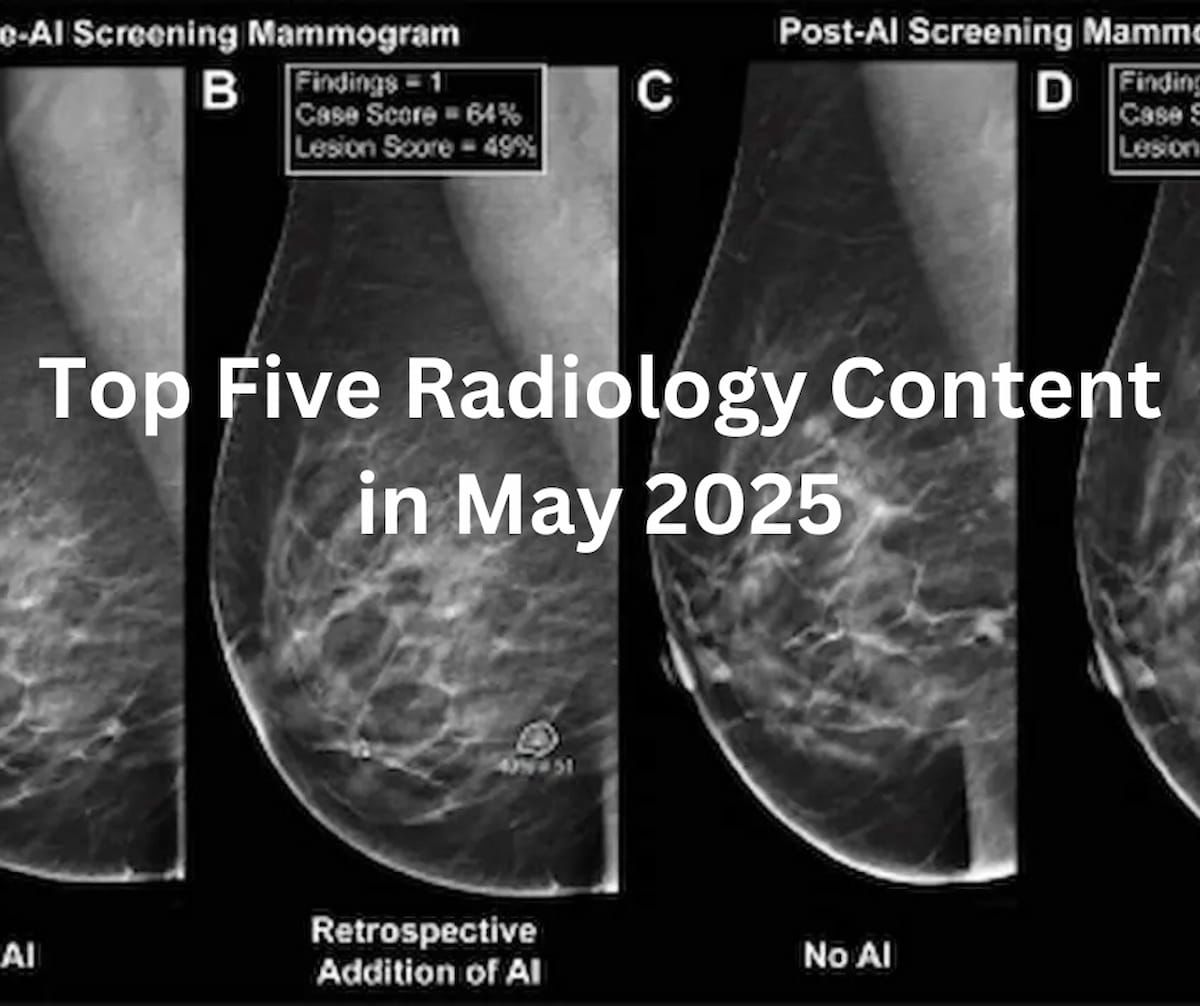
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in April 2025.
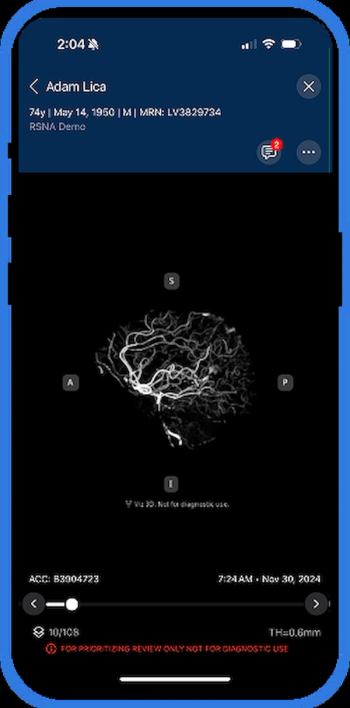
Offering automated conversion of computed tomography angiography (CTA) into 3D images, Viz 3D CTA reportedly facilitates real-time insights into complex neurovascular anatomy.

Catch up on the most well-viewed video interviews from Diagnostic Imaging in April 2025.
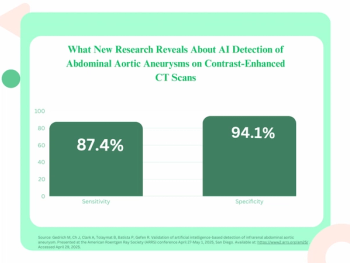
The AI software Viz AAA offered a sensitivity of 87.5 percent in detecting abdominal aortic aneurysms on contrast-enhanced CT, according to new retrospective research presented at the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) conference.
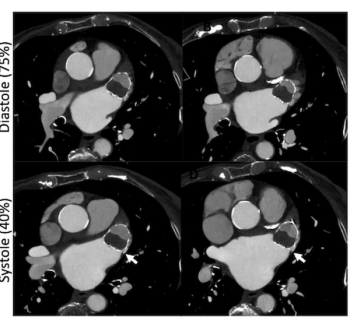
Cardiac CT angiography may provide insights on common post-op complications of left atrial appendage closure, ranging from peri-device leaks to device-related thrombus, according to research presented at the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) conference.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
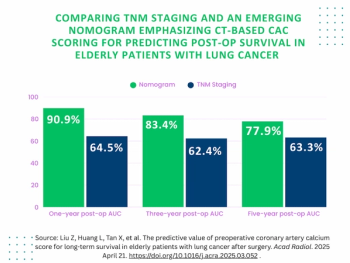
For elderly patients with lung cancer, a preoperative CT-based coronary artery calcium score > 40 was associated with a 53 percent higher risk of all-cause mortality after surgery, according to new study findings.

In a recent interview, Syam Reddy, M.D., discussed the rising incidence of colon cancer and a clinical pathway resource with Radiology Partners that facilitates the integration of computed tomography colonography (CTC) into radiology practice.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Recently published research projected that 103,000 future cases of radiation-induced cancer would result from 93 million computed tomography (CT) exams performed in the United States in 2023.
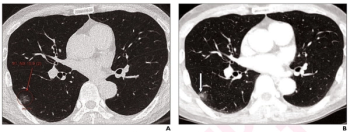
In comparison to radiologist assessment, the use of AI to pre-screen patients with low-dose CT lung cancer screening provided a 12 percent reduction in mean interpretation time with a slight increase in specificity and a slight decrease in the recall rate, according to new research.
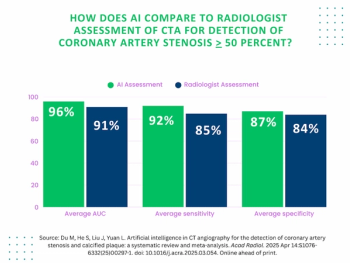
Meta-Analysis Shows Merits of AI with CTA Detection of Coronary Artery Stenosis and Calcified Plaque
Artificial intelligence demonstrated higher AUC, sensitivity, and specificity than radiologists for detecting coronary artery stenosis > 50 percent on computed tomography angiography (CTA), according to a new 17-study meta-analysis.

In a recent interview, Rebecca Smith-Bindman, M.D., offered key insights on new research examining the link between computed tomography scans and projected future cases of radiation-induced cancer.
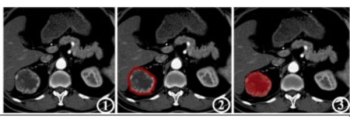
In comparison to a model based on clinicopathological risk factors, a CT radiomics-based machine learning model offered greater than a 10 percent higher AUC for predicting five-year recurrence-free survival in patients with non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC).