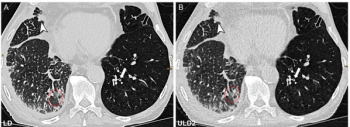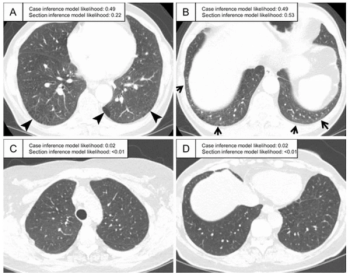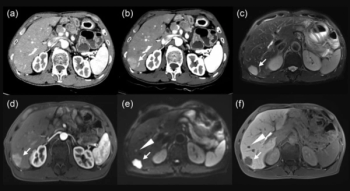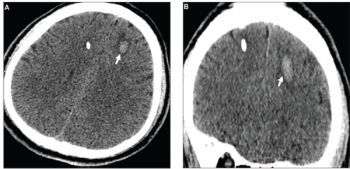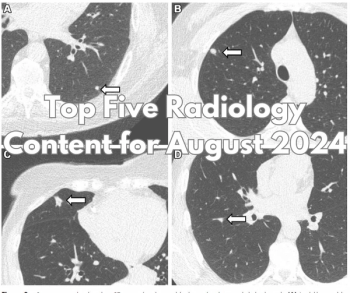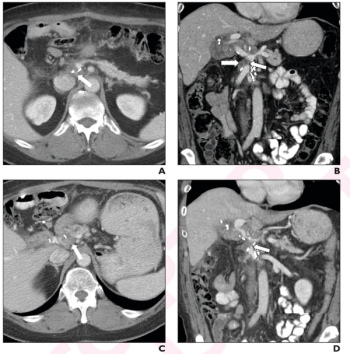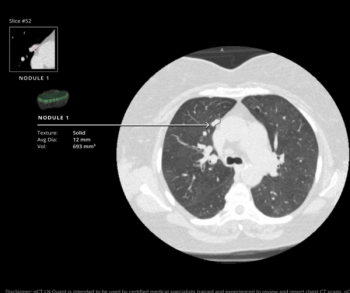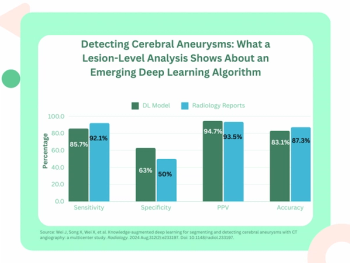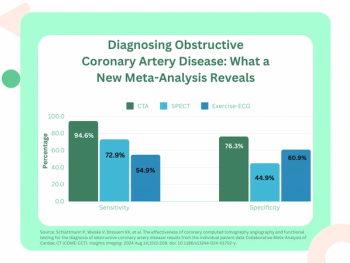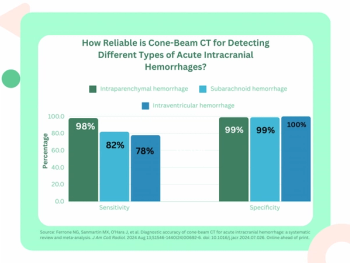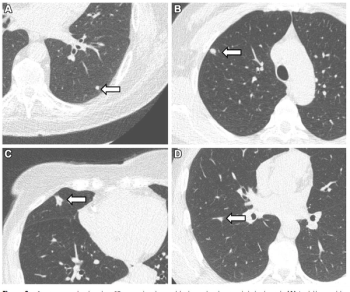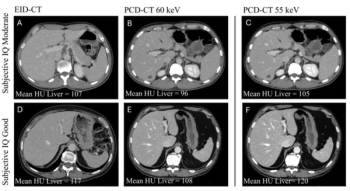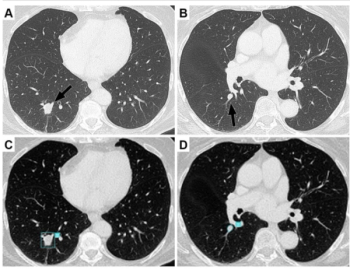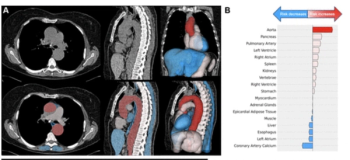
Emphasizing multi-structure segmentation and feature extraction from chest CT scans, an emerging AI model demonstrated an approximately 70 percent AUC for predicting significant incidental extrapulmonary findings as well as two-year and 10-year all-cause mortality.