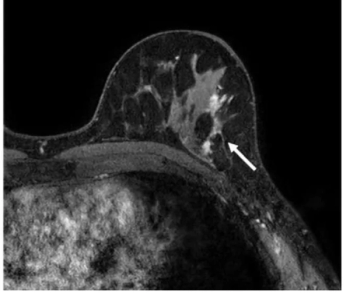
In a new literature review, researchers noted key findings on the use of breast MRI in facilitating breast cancer detection for women with dense breasts and others at high-risk for breast cancer.
Senior Editor, Diagnostic Imaging

In a new literature review, researchers noted key findings on the use of breast MRI in facilitating breast cancer detection for women with dense breasts and others at high-risk for breast cancer.

In a cohort of patients with invasive breast cancer and tumor sizes ranging between 0.3 to 9 cm, image-guided cryoablation was associated with a 10 percent recurrence rate at 16 months, according to research recently presented at the Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR) conference.
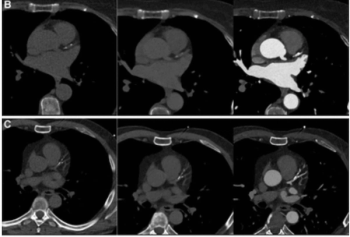
Emerging research on coronary artery calcium scoring for the assessment of coronary artery disease (CAD) suggests the use of virtual non-contrast images from photon-counting CT may lead to a nearly 20 percent reduction in radiation dosing.
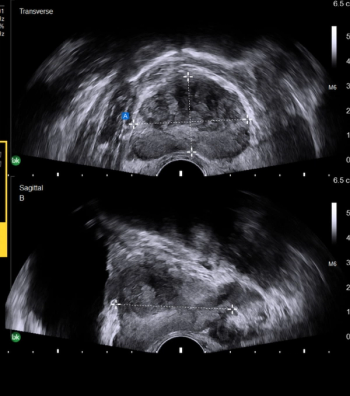
Featuring automated one-click functionality for capturing prostate volume, the AI-enabled software may help shorten workflows for prostate imaging, biopsies, and ultrasound-guided procedures.
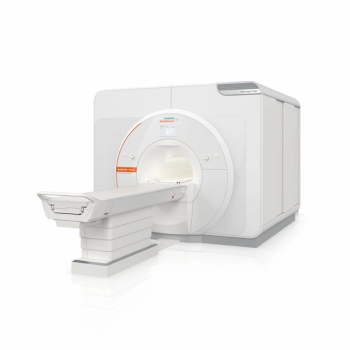
Offering improved image clarity capable of capturing details of subtle pathology, the Magnetom Terra.X 7T MRI system reportedly features the first eight-channel parallel transmit architecture for clinical use.
SyMRI 3D reportedly combines precise estimates of regional brain volume with improved resolution bolstering accuracy with lesion analysis.
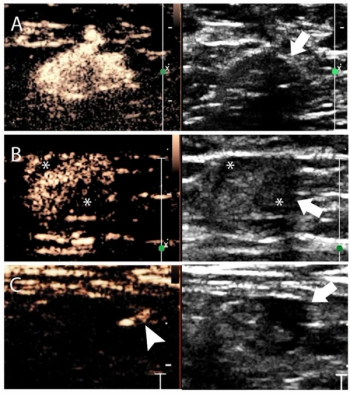
A nomogram that combines contrast-enhanced lymphatic ultrasound and grayscale ultrasound findings had an 88 percent AUC for prediction of three or more metastatic axillary lymph nodes in women with early breast cancer.

The artificial intelligence (AI) modalities CINA-iPE and CINA-ASPECTS may facilitate improved detection of incidental pulmonary embolism and stroke evaluation, respectively, based on computed tomography (CT) scans.

The multimodality system nCommand Lite reportedly facilitates real-time remote imaging guidance on scanning parameters and procedure assessments to licensed technologists for a variety of imaging modalities including CT and MRI.
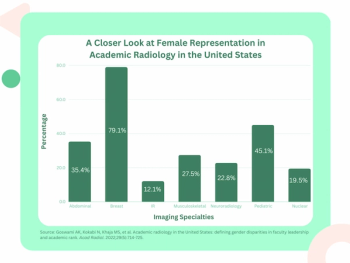
Women comprise nearly 80 percent of breast imaging departments and 45 percent of pediatric radiology departments at academic institutions, but burnout, the COVID-19 pandemic and discrimination have impeded further progress in radiology, according to a recently published literature review.
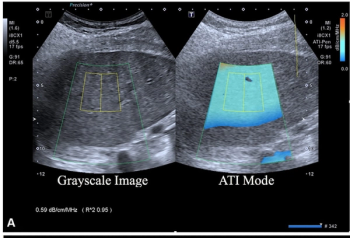
A multiparametric ultrasound model emphasizing attenuation coefficient assessment demonstrated a 77 percent AUC for detecting metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), according to validation testing from a new multicenter study.
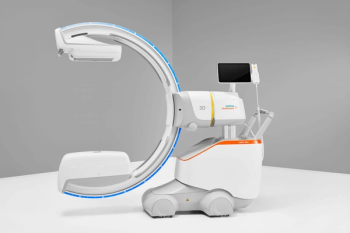
Offering ease of mobility and self-driving capabilities, the Ciartic Move C-arm device reportedly reduces the stress and potential for error associated with manual repositioning during intraoperative imaging with computed tomography and fluoroscopy.
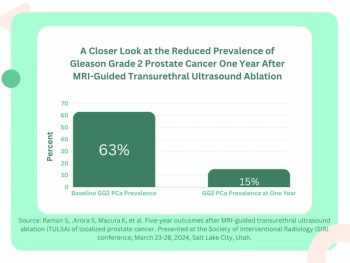
For men with prostate cancer, the use of MRI-guided transurethral ultrasound ablation (TULSA) led to a 92 percent decrease in median prostate volume at one year, according to new research recently presented at Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR) conference.
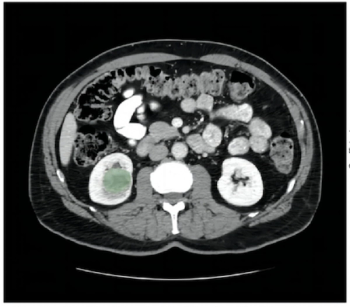
Emerging research suggests that a computed tomography (CT)-based radiomics model can predict FOXM1 expression and is independently prognostic for clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
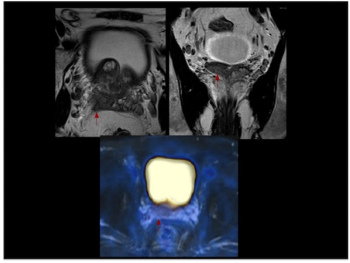
Ga-PSMA PET MRI offers nearly 22 percent higher sensitivity for localized prostate cancer and comparable specificity to multiparametric MRI, according to a recently published prospective study.
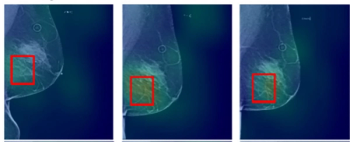
A proposed alternative to a previously validated deep learning neural network for assessing short-term breast cancer risk, the emerging AsymMirai deep learning mammography-based model showed comparable breast cancer risk prediction with an emphasis on bilateral dissimilarity, according to new research.
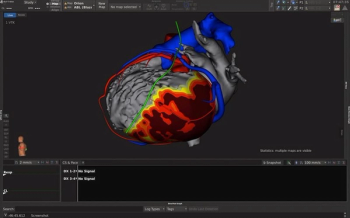
Three-dimensional interactive heart models created with AI-enabled segmentation of CT scans may reduce ventricular tachycardia ablation procedure times by 60 percent.

Incorporating an artificial intelligence (AI) platform into the radiology workflow at a stroke management-accredited hospital may lead to projected savings of 78 days in triage time and 41 days in reporting time for radiologists over a five-year period, according to new research.
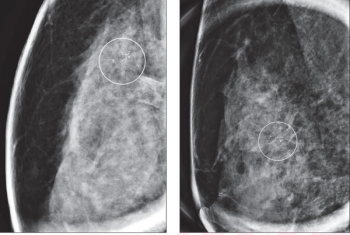
For women who have had radial scars detected on digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) exams, researchers noted a 5 percent upstaging rate to cancer, according to a recent study.
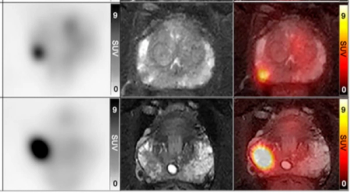
For men with PI-RADS 3 lesions, PRIMARY scores of 4-5 with PET/MRI had a sensitivity rate of 87.5 percent for clinically significant prostate cancer, according to newly published research.
In a comparison of image-to-text large language models (LLMs), ChatGPT 4.0 offered a 95 percent sensitivity rate and an 83 percent AUC that were comparable to that of two senior radiologists and one junior radiologist interacting with LLM to differentiate between malignant and benign thyroid nodules on ultrasound.
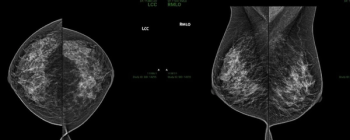
The newly launched Progressive Loading feature, available through RamSoft’s OmegaAI software, reportedly offers radiologist rapid uploading of images that is faster than on-site networks and other cloud-based systems regardless of the network radiologists are using.
In a recent interview, Atul Gupta, M.D. discussed the evolution and potential impact of Fiber Optic RealShape (FORS) technology, which uses light instead of radiation to facilitate real-time 3D imaging that may lead to significant efficiencies with complex aortic procedures.
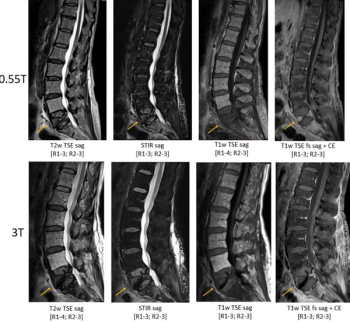
In a study of patients who had lumbar spine MRI exams at 0.55T, 1.5T and 3T, researchers found that 0.55T MRI provided acceptable diagnostic quality across all sequences for varying pathologies including degenerative joint disease, compression fractures and osseous metastatic disease.
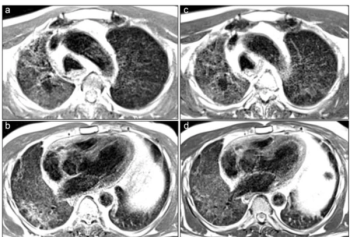
Emerging research with low-field MRI shows that persistently moderate to severe opacities were a common finding in patients up to two years after having acute COVID-19 pneumonia.
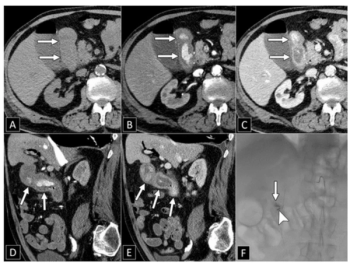
In joint consensus recommendations issued from the Society of Abdominal Radiology and the American College of Gastroenterology, researchers discussed key pearls, benefits, and limitations of CT angiography for imaging of overt lower GI bleeding and CT enterography for detecting small bowel bleeding.
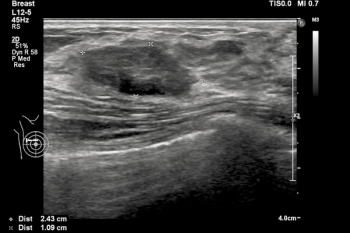
While adjunctive use of AI led to significantly higher specificity and accuracy rates in detecting cancer on breast ultrasound exams in comparison to unassisted reading by breast radiologists, researchers noted that 12 of 13 BI-RADS 3 lesions upgraded by AI were ultimately benign, according to research presented at the European Congress of Radiology.
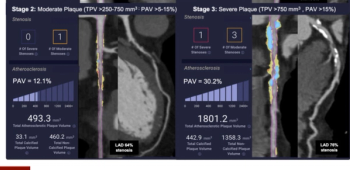
Employing quantitative computed tomography, the staging system’s insights on stenosis, ischemia and coronary atherosclerosis may facilitate individualized assessments of heart disease risk.
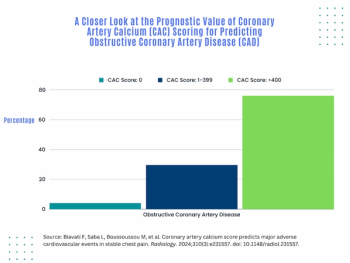
Computed tomography (CT) findings from over 1,700 patients with stable chest pain reveal that coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores of 0 are associated with a 4.1 percent prevalence of obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) whereas CAC scores of 400 or higher are linked to a 76.1 percent incidence of obstructive CAD, according to research from a multinational study.
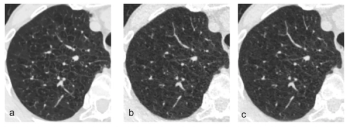
In comparison to standard-dose lung CT, the combination of deep learning image reconstruction with ultra-low-dose CT offered similar detection and characterization of pulmonary nodules at a nearly 93 percent reduction of radiation dosing, according to new research.