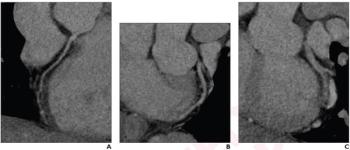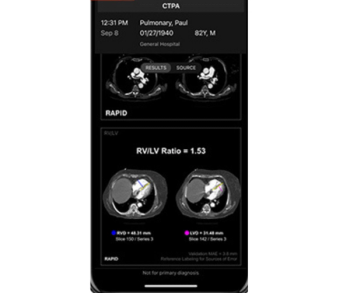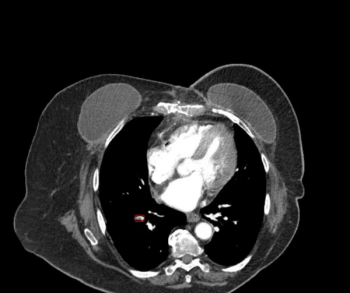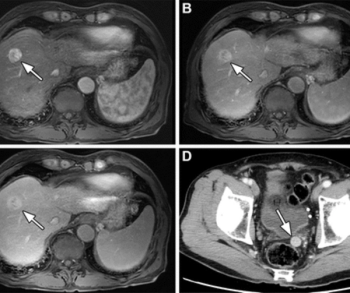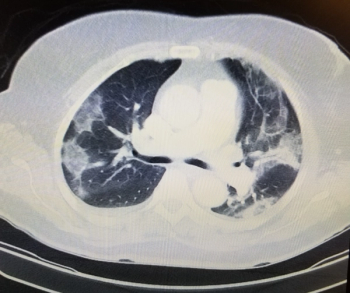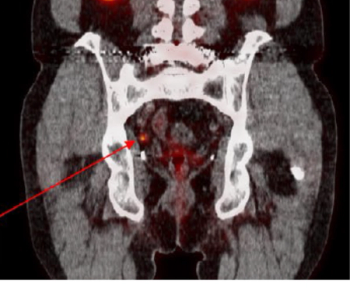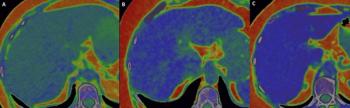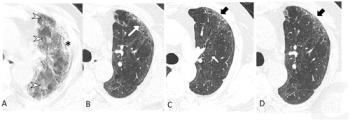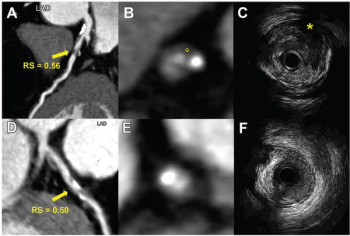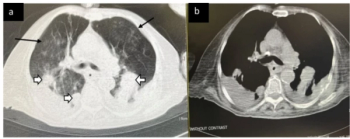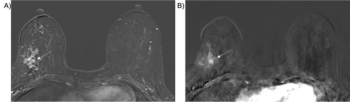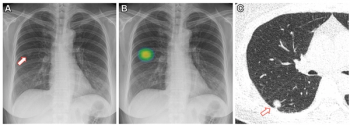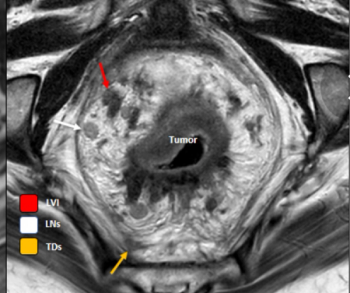
In a cum laude awarded presentation at the European Congress of Radiology (ECR), researchers discussed misconceptions and pertinent principles for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of patients with rectal cancer, ranging from the diagnosis of mucinous tumors to the impact of mesorectal fascia status for rectal cancer recurrence.