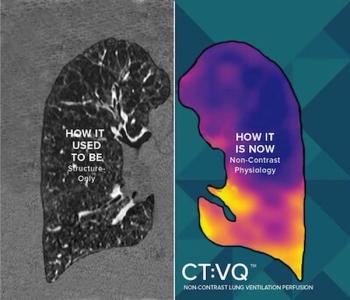
Offering the capability to convert a non-contrast chest CT into quantitative ventilation perfusion mapping, use of the CT:VQ software allows for additional Category III CPT reimbursement beyond the chest CT.

Offering the capability to convert a non-contrast chest CT into quantitative ventilation perfusion mapping, use of the CT:VQ software allows for additional Category III CPT reimbursement beyond the chest CT.
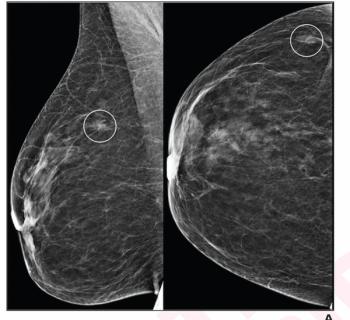
While the AI software offered nearly equivalent negative predictive value (NPV) to radiologist interpretation of digital mammograms and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) images, researchers noted that AI had significantly higher recall rates and false-positive results in patients with intermediate risk.
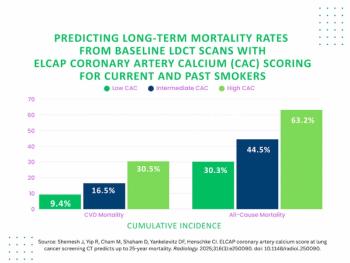
In a long-term follow-up analysis of the ELCAP CAC score for predicting cardiovascular mortality, over 30 percent of current or former smokers with high ELCAP CAC scoring on low-dose CT suffered cardiovascular disease death within a 25-year period.
The Revolution Vibe computed tomography system reportedly facilitates quality low-dose imaging for cardiac exams in patients with arrhythmias, heavily calcified coronaries and stents.
In a 10-study meta-analysis examining the use of whole-body MRI for asymptomatic individuals, researchers noted a pooled cancer detection rate of 1.57 percent.

How much of your sleep is sacrificed being in a ‘sleep-adjacent’ medical specialty?
From emerging research on disparities in breast cancer screening to the promising combination of contrast-enhanced mammography with DBT and a three-part podcast on abbreviated breast MRI, here is a look back at the most well-reviewed breast imaging content of the summer.
The AI-powered cardiovascular ultrasound device reportedly offers enhanced spatial and contrast resolution as well as bolstered 4D imaging that enables improved evaluation of cardiac function for a wide range of patients.
Featuring advanced detector technology, the Pharos PET scanner reportedly enhances detection of subtle anomalies across brain, breast and extremity imaging.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in August 2025.
Combining advances in imaging quality with access to 26 FDA-cleared applications for automated and accelerated tasks, the Transcend Plus software will be featured at the upcoming European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) conferences.

Emerging cloud and AI-driven technologies may help address resource gaps, bolster consistent imaging quality and provide improved access to radiology services.
Catch up on the most-well viewed prostate imaging content in August 2025.

While the research reveals key benefits with portable imaging, particularly point-of-care ultrasound applications with AI capabilities, these authors note challenges with variability in training and advocate for radiologist-led oversight.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
Amid the worsening imbalance of supply and demand in radiology and concerning scope of practice issues, one must keep in mind that course correction is often gradual in nature.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

The MyLab A50 and MyLab A70 ultrasound platforms reportedly enable a variety of detailed and multiparametric evaluations, including assessments for liver elastography and strain analysis echocardiography.
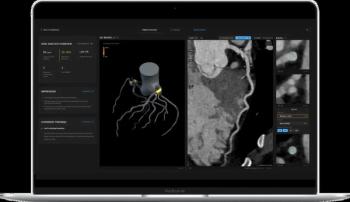
Use of the AI-powered Salix Coronary Plaque module, which offers detection of high-risk plaque within 10 minutes based off of CCTA scans, will reportedly qualify for $950 in Category 1 CPT reimbursement in 2026.

In a new podcast, Krishna Nallamshetty, M.D., shares his thoughts on key contributing factors to burnout in radiology, and discusses practical approaches and emerging technology that may help mitigate the issue.
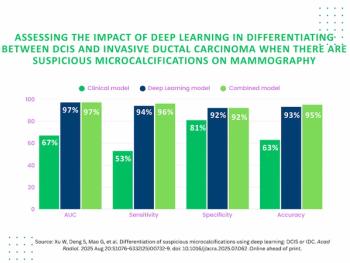
A model combining deep learning features and clinical variables demonstrated a 30 percent higher AUC than a clinical model for detecting DCIS and invasive ductal carcinoma from suspicious microcalcifications on mammography, according to a new study.
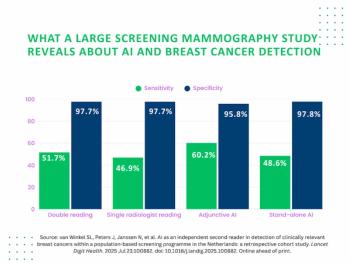
Over 26 percent of AI-detected future breast cancers and interval breast cancers missed by radiologists were invasive cancers, according to newly published research involving over 42,000 women who had 2D screening mammography.
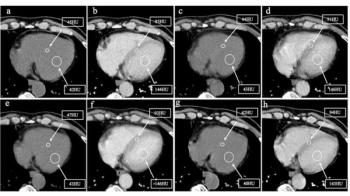
Nine months after initiation of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), prostate cancer patients with higher myocardial extracellular volume (ECV) — derived from chest contrast-enhanced CT — had over a fourfold higher risk for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), according to new research.

In a recent interview, Ioannis Sechopoulos, Ph.D, and Sarah D. Verboom, MSc discussed their new research examining the role of certainty in AI mammography screening assessment and the potential impact on workload reduction for radiologists.
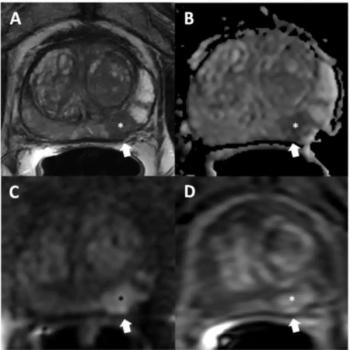
In a new review of MRI-based scoring systems for T-staging of prostate cancer, researchers discuss key literature findings and principles in evaluating the extent of prostate cancer (PCa) lesions, and whether a focus on specificity could enhance the staging of PCa.

In the second part of a recent interview, Tammie Benzinger, M.D., Ph.D., discusses recently presented research from the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference (AAIC) that showed the ability of portable low-field MRI to detect mild and moderate amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIAs).

Is there a proverbial line in the sand for reasonable pushback against seemingly extraneous addendum requests?

Catch up on the latest news, research and insights in radiology with our Weekly Scan.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Reportedly the only point-of-care ultrasound system that can estimate liver stiffness and attenuation that correlate to MRI-PDFF, Velacur One also may facilitate higher reimbursement than non-imaging elastography.