AI
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
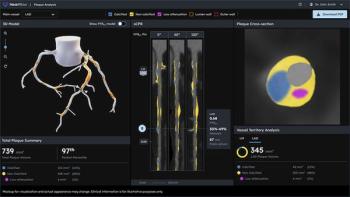
The updated Heartflow Plaque Analysis software reportedly offers enhanced 3D visualization of plaque type, volume and distribution based on coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) imaging.
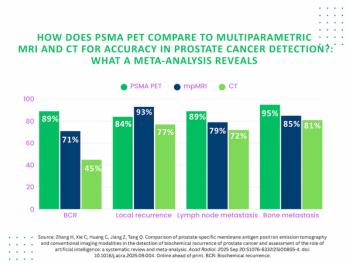
PSMA PET offered 18 percent higher accuracy for detecting biochemical recurrence of PCa in contrast to mpMRI, according to findings from a 67-study meta-analysis.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a recent interview with Diagnostic Imaging, Noa Antonissen, M.D., and Colin Jacobs, Ph.D., discussed new research findings demonstrating robust risk stratification with a CT-based deep learning model for lung nodules as well as a 39.4 percent reduction in false positives in comparison to traditional classification.
The Voluson Performance 18 and 16 ultrasound devices reportedly combine enhanced imaging capabilities with AI-enabled efficiencies.

The AI-powered Tempus Pixel software update provides T1 and T2 inline maps to augment cardiac MRI assessment.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In a recent interview, Zeeshan Shah, M.D., discussed the challenges of addressing rising breast imaging volume amid the radiologist shortage, the potential of emerging AI solutions for bolstering efficient triage and an increasing incidence of breast cancer presentations in younger patients.
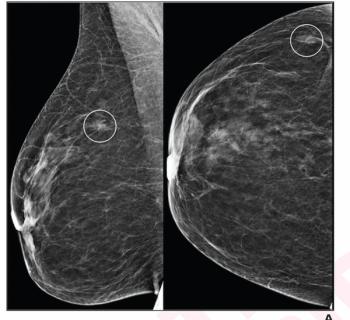
While the AI software offered nearly equivalent negative predictive value (NPV) to radiologist interpretation of digital mammograms and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) images, researchers noted that AI had significantly higher recall rates and false-positive results in patients with intermediate risk.
The Revolution Vibe computed tomography system reportedly facilitates quality low-dose imaging for cardiac exams in patients with arrhythmias, heavily calcified coronaries and stents.
The AI-powered cardiovascular ultrasound device reportedly offers enhanced spatial and contrast resolution as well as bolstered 4D imaging that enables improved evaluation of cardiac function for a wide range of patients.
Combining advances in imaging quality with access to 26 FDA-cleared applications for automated and accelerated tasks, the Transcend Plus software will be featured at the upcoming European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) conferences.
Catch up on the most-well viewed prostate imaging content in August 2025.

While the research reveals key benefits with portable imaging, particularly point-of-care ultrasound applications with AI capabilities, these authors note challenges with variability in training and advocate for radiologist-led oversight.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

The MyLab A50 and MyLab A70 ultrasound platforms reportedly enable a variety of detailed and multiparametric evaluations, including assessments for liver elastography and strain analysis echocardiography.
Use of the AI-powered Salix Coronary Plaque module, which offers detection of high-risk plaque within 10 minutes based off of CCTA scans, will reportedly qualify for $950 in Category 1 CPT reimbursement in 2026.
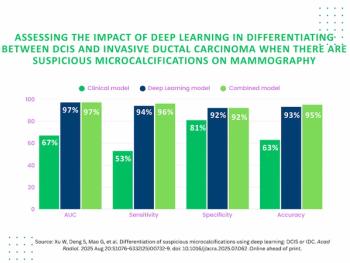
A model combining deep learning features and clinical variables demonstrated a 30 percent higher AUC than a clinical model for detecting DCIS and invasive ductal carcinoma from suspicious microcalcifications on mammography, according to a new study.
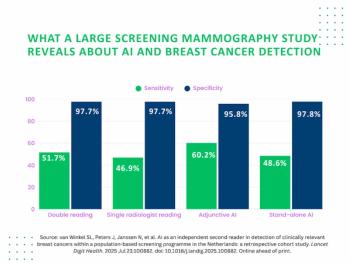
Over 26 percent of AI-detected future breast cancers and interval breast cancers missed by radiologists were invasive cancers, according to newly published research involving over 42,000 women who had 2D screening mammography.

In a recent interview, Ioannis Sechopoulos, Ph.D, and Sarah D. Verboom, MSc discussed their new research examining the role of certainty in AI mammography screening assessment and the potential impact on workload reduction for radiologists.
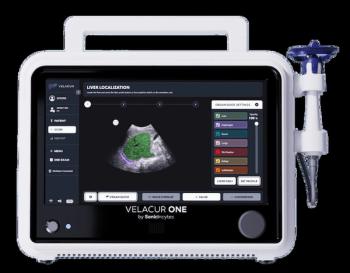
Reportedly the only point-of-care ultrasound system that can estimate liver stiffness and attenuation that correlate to MRI-PDFF, Velacur One also may facilitate higher reimbursement than non-imaging elastography.

Incorporating technology from Siemens Healthineers’ Magnetom Skyra Fit system, the Invision 3T Recharge Operating Suite offers AI-powrred protocols and automated image reconstruction capabilities.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
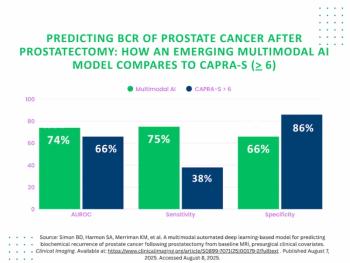
A deep learning multimodal model that incorporates MRI features offered nearly double the sensitivity for predicting post-prostatectomy biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer in comparison to the traditional CAPRA-S scoring system.