AI
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
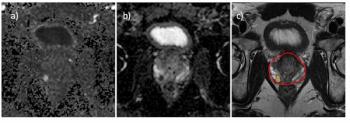
Offering an 87 percent sensitivity for clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa), the deep learning model demonstrated an 86 percent AUC for predicting > PI-RADS 3 lesions on prostate MRI.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
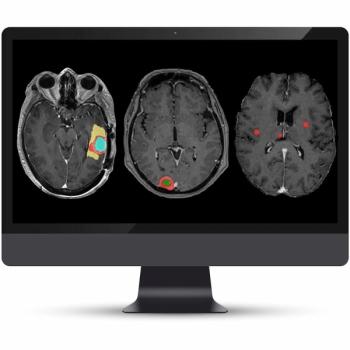
The addition of two new AI-enabled models for the latest version of the NeuroQuant Brain Tumor software facilitates automated tracking of the progression of brain tumors and meningiomas.
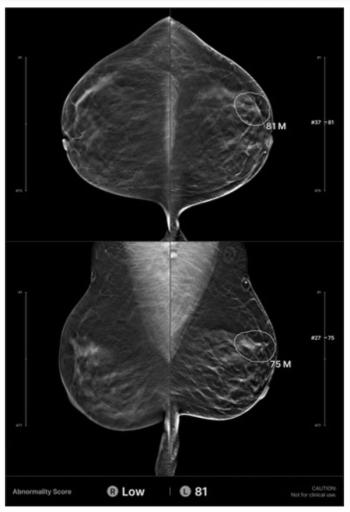
In a retrospective review of screening digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) exams for over 200 women with interval breast cancers, researchers found that AI provided accurate localization of cancers in 32.6 percent of the cases.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
The newly launched Definium Pace Select ET X-ray platform reportedly provides increased automation and advanced image processing.

Catch up on the latest MRI studies, AI innovations, and expert insights on abbreviated breast MRI with our Weekly Scan.
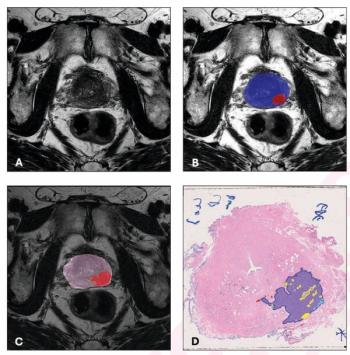
The use of adjunctive bpMRI-based AI led to 10 percent and greater increases in lesion-level PPV for csPCa and PCa with a threshold of PI-RADS > 3.

The dual FDA clearances for the Accuro 3S point-of-care ultrasound device and the SpineNav-AI machine learning-based software may enhance precision and safety with ultrasound-guided neuraxial procedures.
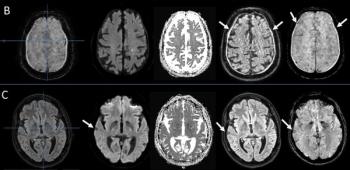
Noting a 7.4 percent incidence of motion artifacts on brain MRI scans for suspected stroke patients, the authors of a new study found that motion artifacts can reduce radiologist and AI accuracy for detecting hemorrhagic lesions.
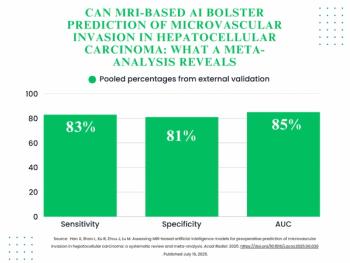
In external validation findings from a 29-study meta-analysis, MRI-based AI had a pooled AUC of 85 percent for preoperative prediction for microvascular invasion in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
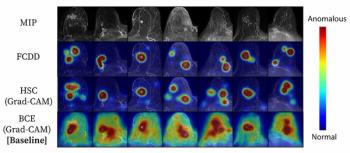
A fully convolutional data description (FCDD) model for identifying anomalies on breast MRI demonstrated an 84 percent AUC for detection tasks in a balanced cohort with a 20 percent malignancy prevalence and a 72 percent AUC for detection tasks in an imbalanced group with a 1.85 percent cancer prevalence.

A cloud-based and AI-native radiology operating system, MosaicOS reportedly enables the combination of diagnostic AI tools and workflow enhancements into one scalable platform.
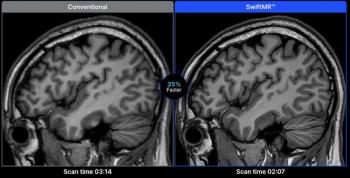
The updated capabilities of SwiftMR include personalized scan settings within the software, artifact reduction and cloud integration.
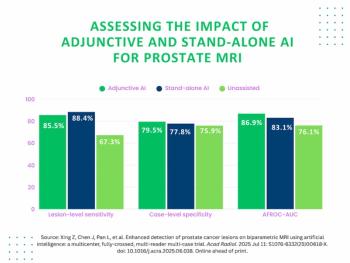
Emerging research revealed significantly enhanced sensitivity for prostate cancer detection with adjunctive and stand-alone use of AI.

Stay updated with the latest in radiology, including PET, MRI, and AI research, plus essential insights on mammography and cardiac imaging.
EchoGo Amyloidosis, an echocardiography-based AI screening software, demonstrated a 93 percent AUROC for cardiac amyloidosis detection in a new multicenter study.
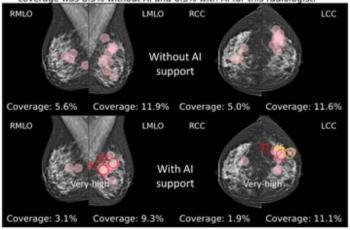
While noting no differences in sensitivity, specificity or reading time with adjunctive AI for mammography screening, the authors of a new study noted a 4 percent higher AUC and increased fixation time on lesion regions.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
The diagnostic tomographic 3D ultrasound imaging technology PIUR tUS inside will reportedly be available with select GE HealthCare Logiq systems.
The deep learning reconstruction software reportedly facilitates accelerated MRI scanning and significantly enhanced image sharpness.

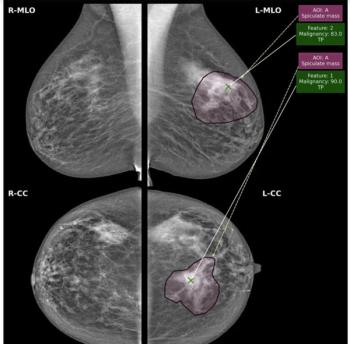
While there was a decline of AUC for mammography AI software from breast-level assessments to lesion-level evaluation, the authors of a new study, involving 1,200 women, found that AI offered over a seven percent higher AUC for lesion-level interpretation in comparison to unassisted expert readers.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
Offering a cost- and resource-saving DryCool magnet technology, the Magnetom Flow.Ace MRI system reportedly requires 0.7 liters of liquid helium for cooling over the lifetime of the device in contrast to over 1,000 liters commonly utilized with conventional MRI platforms.