AI
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
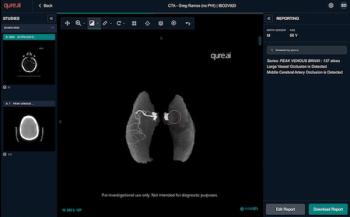
Facilitating timely triage, the qER-CTA software enables AI assessment of the internal carotid artery and M1 segment of the middle cerebral artery for possible large vessel occlusions (LVOs).

In a recent interview, Deepa Sheth, M.D., discussed the rising incidence of breast cancer, key considerations in supplemental imaging for women with dense breasts and use of the CIVIE RadPod platform to facilitate consistent quality and imaging reads by fellowship-trained breast radiologists.
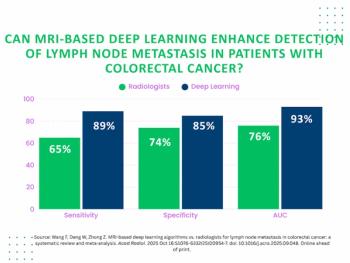
Deep learning assessment of MRI offered a 24 percent higher sensitivity than radiologist interpretation for detecting lymph node metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer, according to a new meta-analysis.
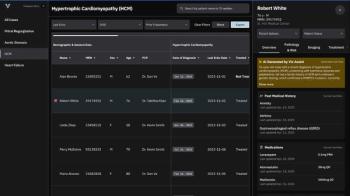
Through the use of a multimodal system, Viz Assist provides generative AI summaries of patient histories that may ehance care coordination and facilitate more timely interventions.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
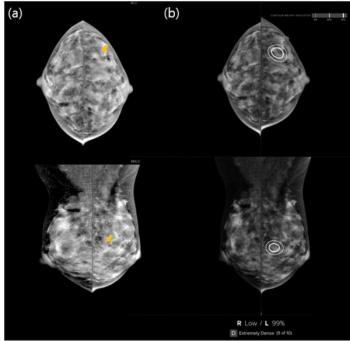
Concordant mammography detection of breast cancer by radiologists and AI had over a threefold higher likelihood of future incidental breast cancer in comparison to positive radiologist assessment and negative AI evaluation, according to new research involving over 82,000 women.

The AI-enabled LungQ® 4 software reportedly offers enhanced segmentation of peripheral airways and estimates of chronic perfusion deficits based on analysis of chest CT scans.
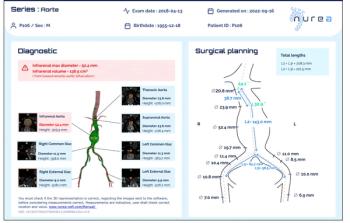
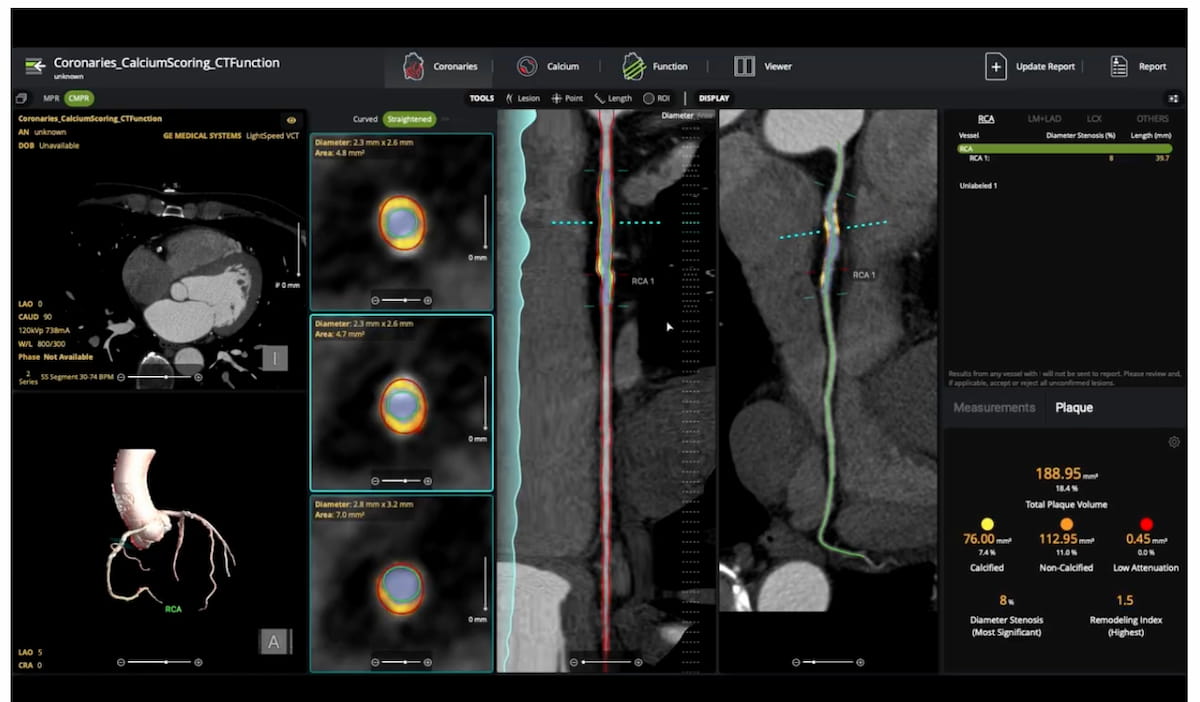
Facilitating timely detection and follow-up management of patients with aortic aneurysms, the PRAEVAorta2 software reportedly enables automated measurement of aortic diameters on computed tomography (CT) scans.

Through enhanced data interoperability and access to patient histories, the cloud-based InteleHeart may facilitate better communication and workflow efficiencies for radiologists and cardiologists.
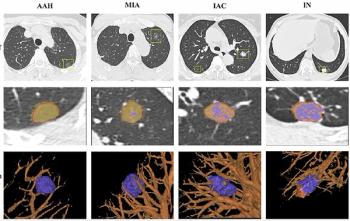
A deep learning AI platform, which incorporated radiomic features including CT attenuation metrics, demonstrated a 93.6 percent AUC for detecting invasive adenocarcinoma on chest CT.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In a recent interview, Morris Panner offered his perspective on cultural hurdles to interoperability in health care, emerging trends with enterprise imaging and an answer first approach to integrating AI in radiology.
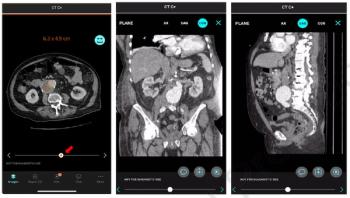
In a study involving over 500 patients, researchers noted that the CT-based AI software led to a 24 percent increase of evaluations for aortic abdominal aneurysms within six months of detection.

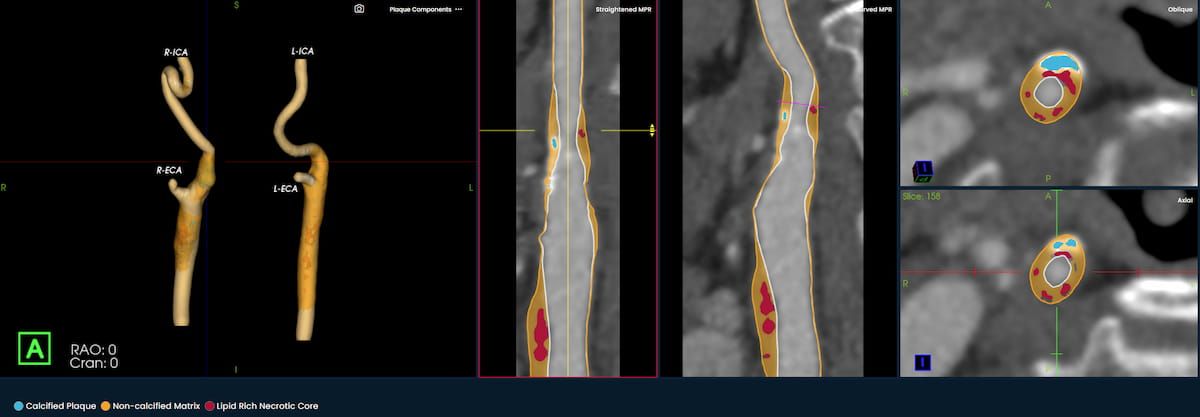
The AI-powered Bunkerhill MAC software reportedly facilitates chest CT detection and quantification of mitral annular calcification, which has been linked to higher cardiovascular risk and related mortality.
In a recent interview, Arthy Saravanan, M.D., discussed the recent launch of the Mammo Enhance Heart program from Radiology Partners and its potential impact in facilitating dual screening for breast cancer and cardiovascular risk.
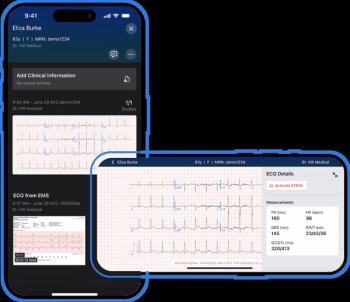
The AI-powered Viz ACS platform may facilitate improved communication between clinicians and more rapid treatment for cases involving acute coronary syndrome.

In a recent interview, Manisha Bahl, M.D., discussed new research showing significant associations between AI detection and the histologic grade and lymph node status of breast cancer.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
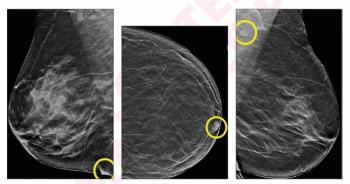
In comparison to false positives with unassisted radiologist interpretations of DBT exams, AI-only false positive assessments were associated with a significantly higher total of false-positive findings as well as a 33 percent lower frequency of dense breasts, according to a new study of nearly 3,000 women who had screening DBT exams.
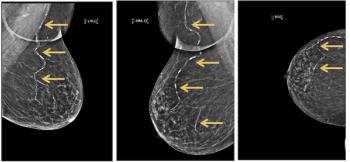
The Mammo Enhance Heart program combines AI detection of breast arterial calcification (BAC) on screening mammography and subsequent follow-up with a local network of cardiologists.
Providing adjunctive AI detection for multiple conditions on CT through a single workflow, the multi-triage platform would be available through Aidoc’s aiOS platform.
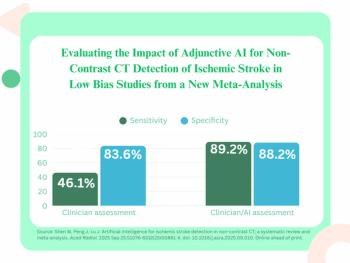
While pooled data from 38 studies showed markedly higher sensitivity rates for the use of adjunctive AI for ischemic stroke detection on non-contrast CT exams, researchers noted a high degree of bias and lack of external validation in many of the studies.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in September 2025.

The new X-ray platform reportedly offers AI-enhanced automation with patient positioning, quality control and image processing.