AI
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
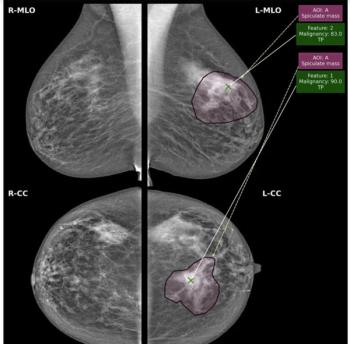
While there was a decline of AUC for mammography AI software from breast-level assessments to lesion-level evaluation, the authors of a new study, involving 1,200 women, found that AI offered over a seven percent higher AUC for lesion-level interpretation in comparison to unassisted expert readers.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
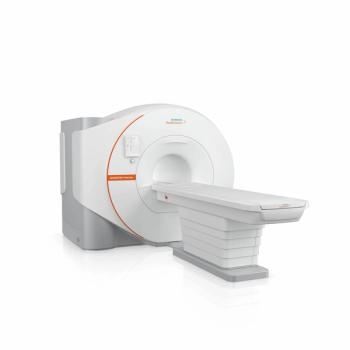
Offering a cost- and resource-saving DryCool magnet technology, the Magnetom Flow.Ace MRI system reportedly requires 0.7 liters of liquid helium for cooling over the lifetime of the device in contrast to over 1,000 liters commonly utilized with conventional MRI platforms.
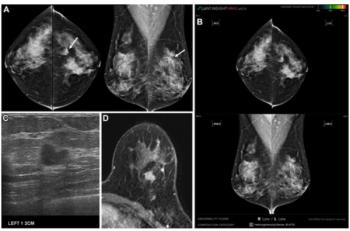
Artificial intelligence (AI) software had a 14 percent false negative rate in a new study involving over 1,082 women with invasive breast cancer.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
The AI software reportedly facilitates ease of use and improved accuracy in fetal ultrasound evaluations.
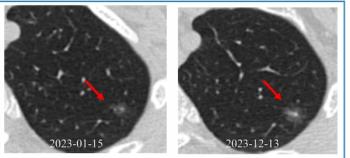
Emerging research shows that a multiple time-series deep learning model assessment of CT images provides 20 percent higher sensitivity than a delta radiomic model and 56 percent higher sensitivity than a clinical model for prognostic evaluation of ground-glass nodules.
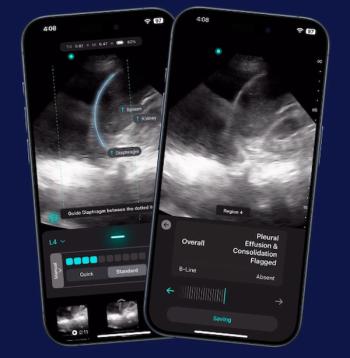
The 14th FDA-cleared AI software embedded in the Exo Iris ultrasound device reportedly enables automated detection of key pulmonary findings that may facilitate detection of pneumonia and tuberculosis in seconds.
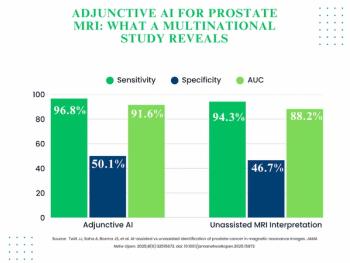
The use of adjunctive AI in biparametric prostate MRI exams led to 3.3 percent and 3.4 percent increases in the AUC and specificity, respectively, for clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa) in a 360-person cohort drawn from 53 facilities.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
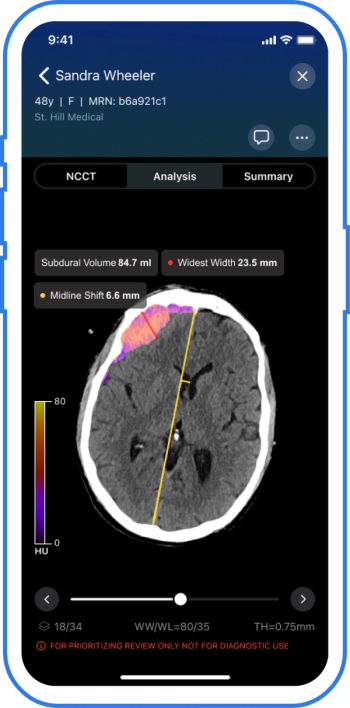
The AI-powered Viz Subdural Plus reportedly provides automated measurements and labeling of subdural collections, including subdural hemorrhages (SDHs), based on non-contrast CT scans.
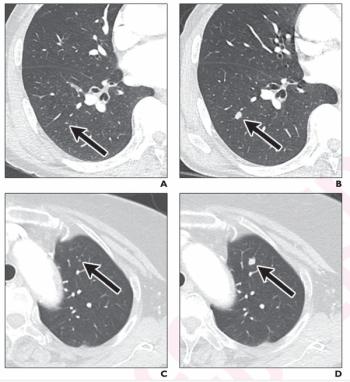
Researchers also noted a greater than 30 percent increase in treatment management changes resulting from the use of CT-based adjunctive AI to detect lung metastases in colorectal cancer patients.
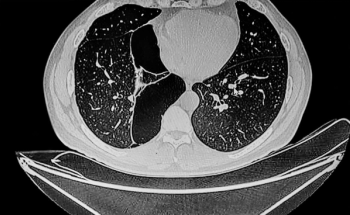
Through AI assessment of chest CT scans, the SeleCT Screening may help identify candidates for bronchoscopic lung volume reduction to improve lung function.


In a recent interview, Samir Abboud, M.D., discussed new research examining the impact of generative AI in maximizing efficiency and reducing the time-consuming nature of radiology reporting.
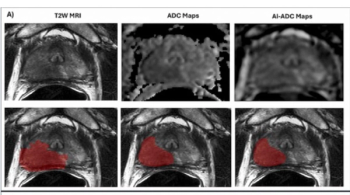
Emerging research showed that AI-generated ADC mapping from MRI led to significant increases in accuracy, PPV and specificity in comparison to conventional ADC mapping while achieving a 93 percent sensitivity for PCa.
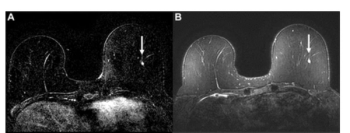
Assessing the simulated use of AI-generated suspicion scores for determining whether one should continue with full MRI or shift to an abbreviated MRI, the authors of a new study noted comparable sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value for biopsies between the MRI approaches.
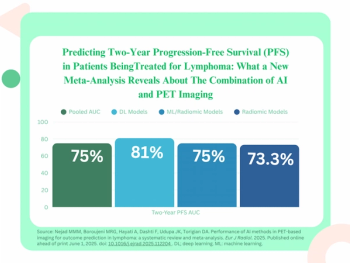
The use of adjunctive AI software with pre-treatment PET imaging demonstrated over a fourfold higher likelihood of predicting progression-free survival (PFS) in patients being treated for lymphoma, according to a new meta-analysis.
Through AI recognition of subtle patterns in breast tissue on screening mammograms, the Clairity Breast software reportedly provides validated risk scoring for predicting one’s five-year risk of breast cancer.
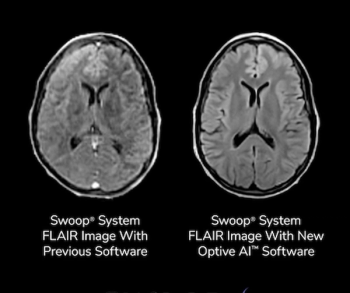
The Optive AI software, the tenth software release for the Swoop portable MRI system, reportedly offers enhanced clarity and anatomical detail for ultra-low-field MRI of the brain.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in May 2025.
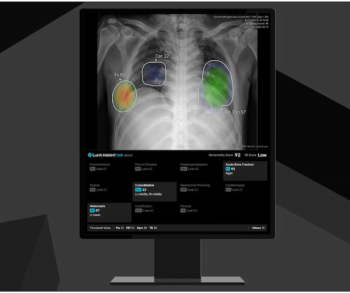
The Lunit Insight CXR4 update reportedly offers new features such as current-prior comparison of chest X-rays (CXRs), acute bone fracture detection and a 99.5 percent negative predictive value (NPV) for identifying normal CXRs.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
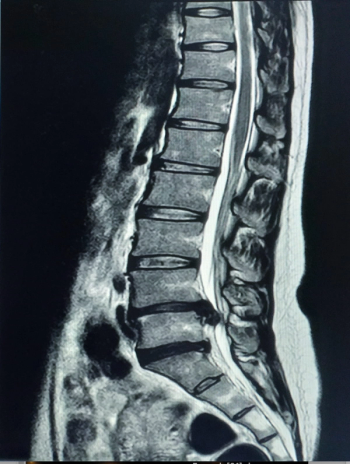
The MSKai software provides AI-powered segmentation, labeling, and measurement tools for assessment of T2-weighted MRIs of the lumbar spine.