AI
Latest News
Latest Videos
CME Content
More News
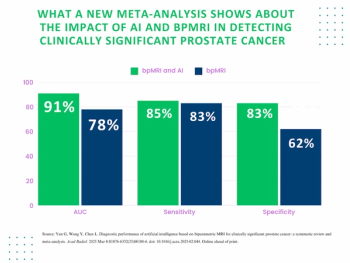
Researchers noted the combination of AI and bpMRI had an average AUC of 91 percent for csPCa detection in contrast to 78 percent for unassisted radiologist interpretation in a recent meta-analysis.
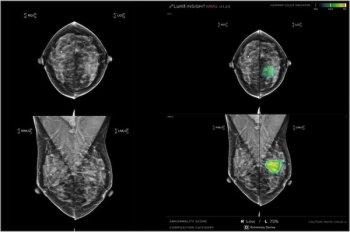
In a study involving over 24,000 women, two-thirds of whom had dense breasts, adjunctive AI led to a significantly higher rate of cancer detection for breast radiologists with no difference in recall rates.
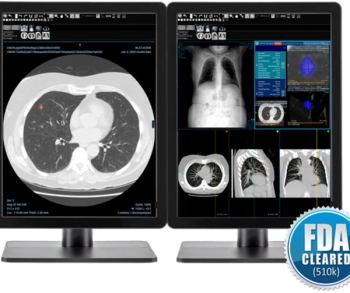
The F.A.S.T. aiCockpit CT Lung Nodule reportedly facilitates enhanced CT workflow and automated reporting for evaluation of lung nodules
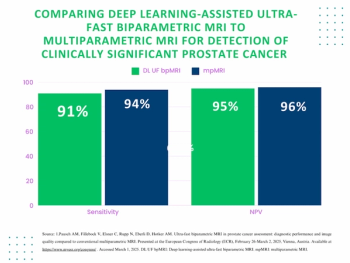
A deep learning-enhanced ultra-fast bpMRI protocol offered similar sensitivity for csPCa as mpMRI with an 80 percent reduction in scan time, according to research findings presented at the European Congress of Radiology (ECR) conference.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
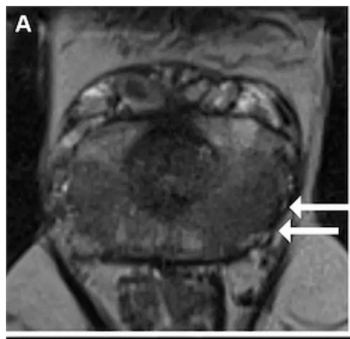
In a multicenter study involving over 1,000 patients, a deep learning software offered comparable sensitivity and specificity for Gleason grade group > 2 tumors in comparison to radiologist interpretation.

In a recent interview, Emily Conant, M.D., discussed findings from two studies presented at the European Congress of Radiology (ECR) conference that showed the potential impact of image-based AI risk models and breast arterial calcification detection in mammography screening.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in February 2025.

In a recent interview, Abhinav K. Jha, Ph.D., discussed key challenges with the use of SPECT MRI and how an emerging deep learning model may facilitate attenuation compensation without the need for an additional computed tomography (CT) scan.
The updated software reportedly enables a threefold improvement in MRI scan time and enhanced image sharpness.
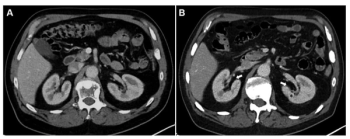
In patients who had at least four cycles of 177Lu-PSMA-I&T for mCRPC, new research shows that a 10 percent or greater decrease in total kidney volume on CT at six months has a 90 percent AUC for predicting estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFRs) of 30 percent or greater at one year.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
Recent multicenter research showed a 22 percent improvement in the detection of fetal anomalies with the Sonio Suspect AI-powered ultrasound module.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
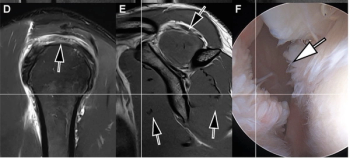
Researchers found that the use of seven-minute threefold parallel imaging-accelerated deep learning 3T MRI had 89 percent sensitivity for supraspinatus-infraspinatus tendon tears and 93 percent sensitivity for superior labral tears.
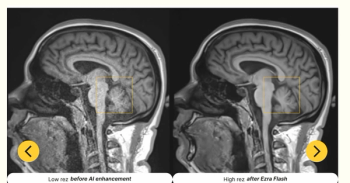
The updated AI-enabled software reportedly facilitates enhanced MRI imaging of the brain, abdomen, and pelvis.
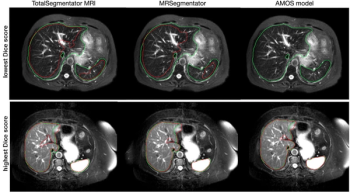
The open-source, deep learning MRI segmentation tool reportedly offers over a 10 percent higher Dice score than similar segmentation models for 40 anatomical structures.
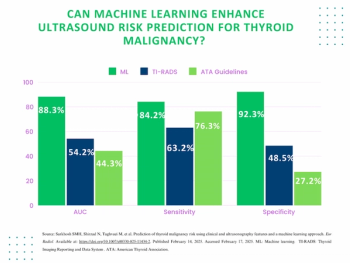
In a study involving assessment of over 1,000 thyroid nodules, researchers found the machine learning model led to substantial increases in sensitivity and specificity for estimating the risk of thyroid malignancy over traditional TI-RADS and guidelines from the American Thyroid Association.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
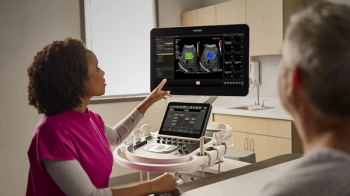
Offering an array of AI-powered automation and image optimization, the new Elevate software is geared to maximizing workflow efficiencies for the EPIQ Elite and Affiniti ultrasound systems.
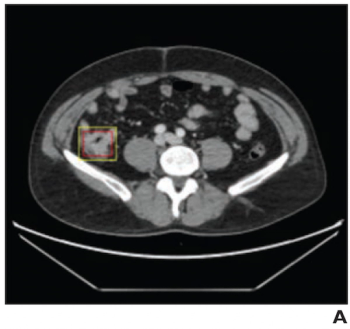
For the assessment of contrast-enhanced abdominopelvic CT exams, an artificial intelligence model demonstrated equivalent or better sensitivity than radiologist readers, and greater than 90 percent specificity for the diagnosis of colorectal cancer.
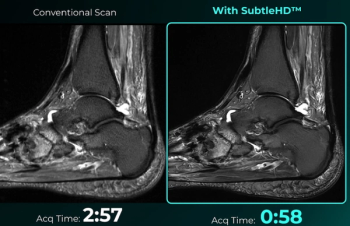
Enabling up to 80 percent faster MRI scan times, the SubtleHD software is included in the newly launched AI software suite Subtle-Elite.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a video interview from the International Stroke Conference (ISC), Jeremy Heit, M.D., Ph.D., discussed new research revealing over 90 percent sensitivity and specificity rates for AI detection of subdural hematomas on non-contrast-enhanced head CTs.
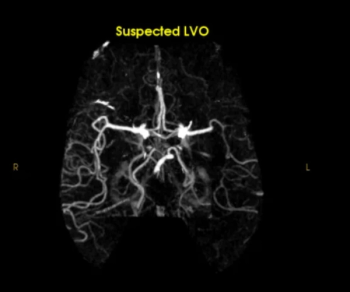
The Rapid LVO AI software detected 33 percent more cases of large vessel occlusion (LVO) on computed tomography angiography (CTA) than Viz LVO AI software, according to a new comparative study presented at the International Stroke Conference (ISC).