Technology
Latest News
Latest Videos

More News
The cloud-based platform reportedly facilitates AI-enhanced teleradiology workflow efficiencies across multiple systems and facilities.
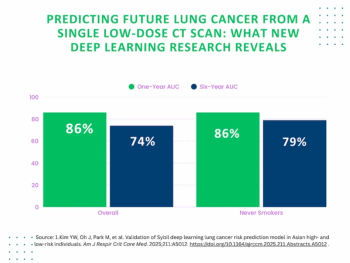
In never-smokers, deep learning assessment of single baseline low-dose computed tomography (CT) scans demonstrated a 79 percent AUC for predicting lung cancer up to six years later, according to new research presented today at the American Thoracic Society (ATS) 2025 International Conference.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
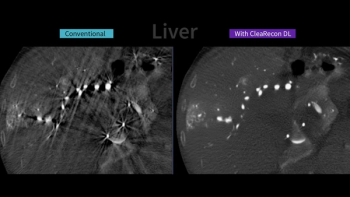
The CleaRecon DL software reportedly removes streak artifacts that can occur with the use of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) during interventional radiology procedures.

In a recent interview, C. Alberto Morales, M.D., discussed the impact of advances with CTA imaging and AI, and a shifting emphasis in cardiac risk stratification from stenosis to plaque burden.
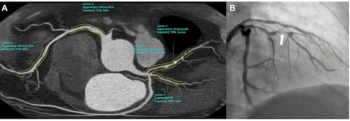
In a study involving over 1,000 patients who had coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) exams, AI software demonstrated a 90 percent AUC for assessments of cases > CAD-RADS 3 and 4A and had a 98 percent NPV for obstructive coronary artery disease.
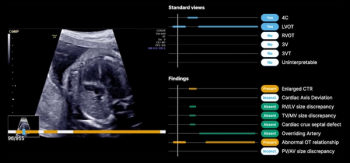
The latest FDA 510(k) clearance is for B-Right Views, an AI-enabled device, which provides automated detection of required views necessary for second- and third-trimester fetal heart ultrasound exams.
Employing intelligent robotics and enhanced low-dose image quality, the uAngio AVIVA X-ray system also offers hands-free image review and movement.
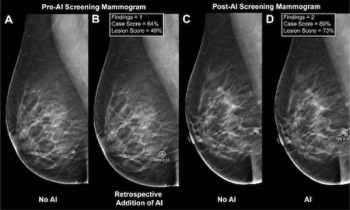
The use of AI software for digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) facilitated a higher cancer detection rate and over double the PPV for exams with abnormal interpretation, according to a newly published study.
The combination of high-performance gradient technology and AI tools with the Signa Sprint MRI reportedly facilitate enhanced MRI workflow efficiencies in cardiac and oncology imaging.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
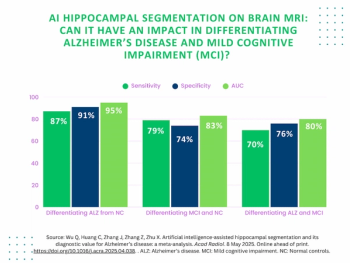
While AI-enabled hippocampal segmentation on MRI offered a 95 percent AUC for differentiating between Alzheimer’s disease and normal controls in a 27-study meta-analysis, it offered significantly lower sensitivity and specificity in differentiating mild cognitive impairment.
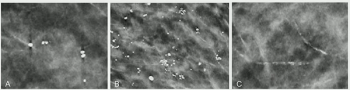
For DBT breast cancer screening, 47 percent of radiologist-only flagged false positives involved mass presentations whereas 40 percent of AI-only flagged false positive cases involved benign calcifications, according to research presented at the recent American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) conference.
The combination of the Aurora SPECT/CT system with AI-enabled Clarify DL image reconstruction reportedly offers the potential of enhanced image quality and streamlined workflows in nuclear medicine.

In a second part of a new podcast episode on recently published research on projected radiation-induced cancers from computed tomography (CT) scans, Mahadevappa Mahesh, MS, Ph.D., and Joseph Cavallo, M.D., offer current perspectives on cardiac CT dosing, AI advances and the importance of teamwork in ensuring appropriate dosing for CT.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Capable of segmenting over 37 organs and structures in the head, neck and pelvis, the MR Contour DL software is currently being showcased at the European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology (ESTRO) conference.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in April 2025.
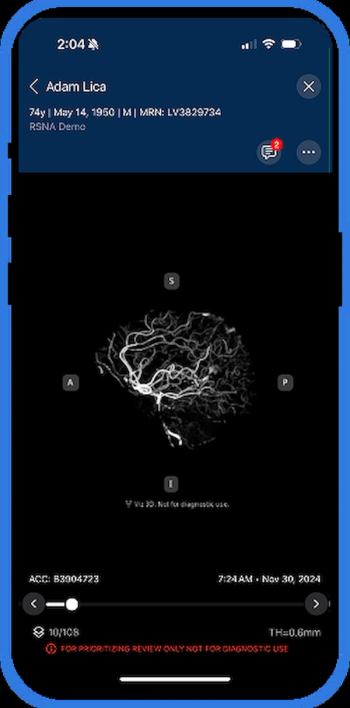
Offering automated conversion of computed tomography angiography (CTA) into 3D images, Viz 3D CTA reportedly facilitates real-time insights into complex neurovascular anatomy.

Catch up on the most well-viewed video interviews from Diagnostic Imaging in April 2025.
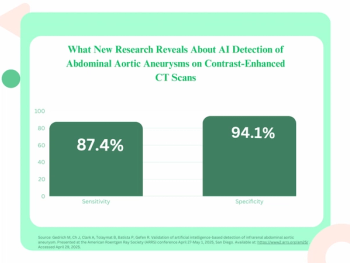
The AI software Viz AAA offered a sensitivity of 87.5 percent in detecting abdominal aortic aneurysms on contrast-enhanced CT, according to new retrospective research presented at the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) conference.
In a recent interview, Wayne Brisbane, M.D., discussed new research, presented at the American Urological Association (AUA) conference, which revealed a 15 percent higher AUC for an emerging AI software in detecting seminal vesicle invasion (SVI) in comparison to prostate MRI alone.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In a recent interview, Manisha Bahl, M.D., discussed key findings from a new study on AI and digital breast tomosynthesis that she presented at the Society for Breast Imaging (SBI) conference.
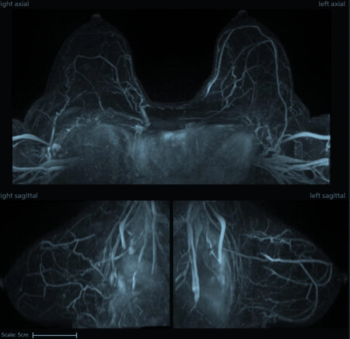
An artificial intelligence algorithm for dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MRI offered a 93.9 percent AUC for breast cancer detection, and a 92.3 percent sensitivity in BI-RADS 3 cases, according to new research presented at the Society for Breast Imaging (SBI) conference.