Precision DL, a deep learning-based software which will be available on GE HealthCare’s Omni Legend PET/CT device, reportedly increases the detectability of small, low-contrast lesions by 42 percent.

Precision DL, a deep learning-based software which will be available on GE HealthCare’s Omni Legend PET/CT device, reportedly increases the detectability of small, low-contrast lesions by 42 percent.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.
In what may be the first comparative study of the polygenic risk score and the computed tomography (CT)-derived coronary artery calcium (CAC) score for assessing coronary heart disease (CHD) risk, researchers found that the CAC score was associated with significant improvements in assessing and stratifying risk for the development of CHD in middle-aged to older adults.
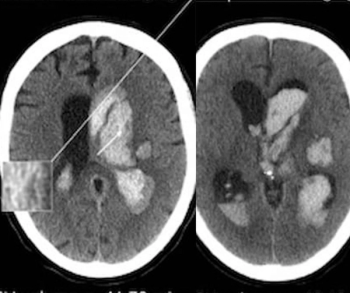
In a subgroup analysis of patients with intracerebral hemorrhage who had intraventicular hemorrhage (IVH) growth, researchers found that hypodensities on non-contrast computed tomography (CT) were associated with more than double the risk for greater than 1 mL of expanded IVH (eIVH).

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
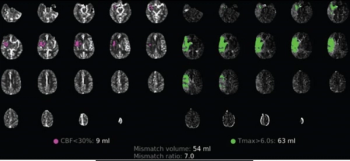
Unvaccinated people with COVID-19 who undergo angiographic reperfusion after acute ischemic stroke may have a greater than fivefold risk of continued infarct growth in comparison to unvaccinated people without COVID-19, according to computed tomography perfusion (CTP) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings from a recently published study.
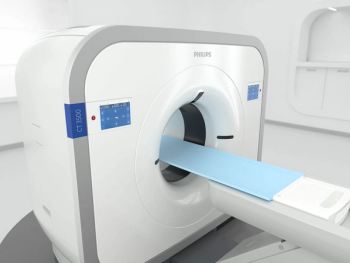
The artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled CT 3500 system reportedly reduces patient positioning time by 23 percent, improves low-contrast detectability by 60 percent and facilitates up to an 80 percent reduction in radiation dosing.
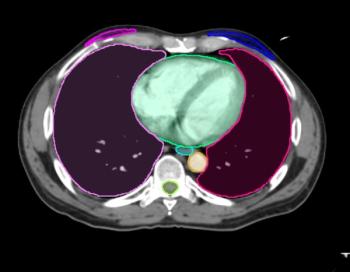
Updates to Contour ProtegeAI 4.0 reportedly include enhanced algorithms for radiation oncology segmentation and molecular radiotherapy.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
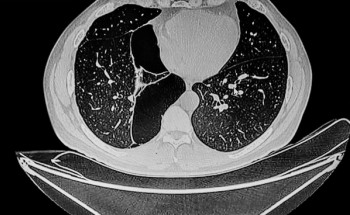
In a large retrospective study of 26,455 participants from the National Lung Screening Trial, low dose computed tomography (LDCT) exams revealed significant incidental findings (SIFs), ranging from emphysema to suspicious lesions, in 8,954 participants.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a study involving 201 consecutive patients presenting to emergency departments (EDs) with abdominal pain, researchers found that radiology faculty accuracy rates in interpreting non-contrast, abdominopelvic computed tomography (CT) scans ranged from 68 to 74 percent.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
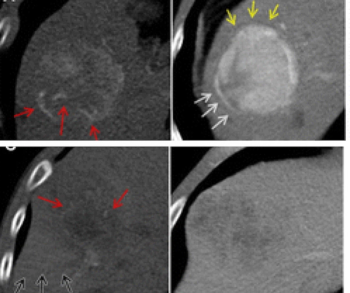
A hybrid computed tomography radiomics model demonstrated up to an 86 percent area under the curve in predicting microvascular invasion in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in a recently published study.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.
While one computed tomography (CT) scan appears to have no elevated cancer risk in pediatric patients, four or more pediatric exposures to CT scans are associated with increased risks for intracranial tumor, leukemia, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma, according to newly published research out of Taiwan.

Lamenting a lack of control over imaging requests from referring clinicians, this author suggests that a more collaborative approach between referrers and radiologists may facilitate more efficient use of imaging.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
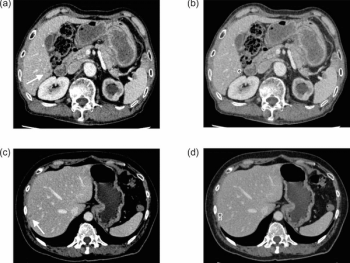
An emerging artificial intelligence (AI) software reportedly detected liver metastases in 53.7 percent of cases involving missed findings by radiologists.
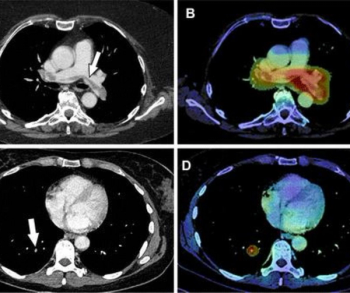
In a new study involving over 11,700 chest computed tomography (CT) scans in oncology patients, adjunctive artificial intelligence software demonstrated a sensitivity rate of 91.6 percent for incidental pulmonary embolism (IPE) and reduced median detection and notification time for IPE-positive scans from multiple days to one hour for a radiology department at a comprehensive cancer center.
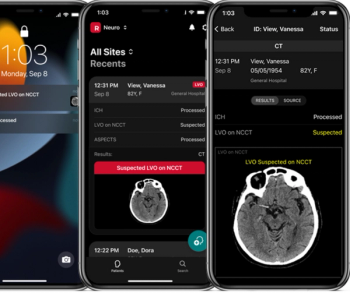
Powered by artificial intelligence (AI), the Rapid NCCT Stroke modality is reportedly the first medical device to gain FDA 510(k) clearance for detecting suspected large vessel occlusion and intracranial hemorrhage based on assessment of non-contrast computed tomography (NCCT).

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
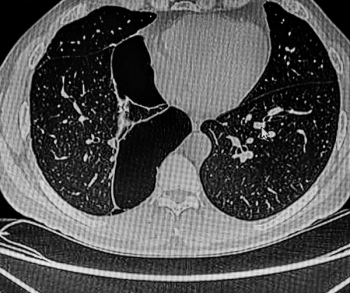
Over the course of a decade, people with preexisting emphysema who continued smoking had the greatest decline in lung density, according to computed tomography (CT) findings from a study involving over 8,400 total participants and over 4,100 current smokers.