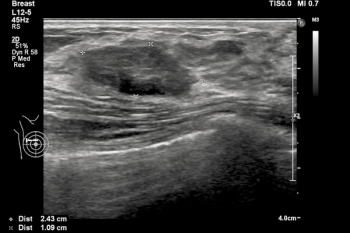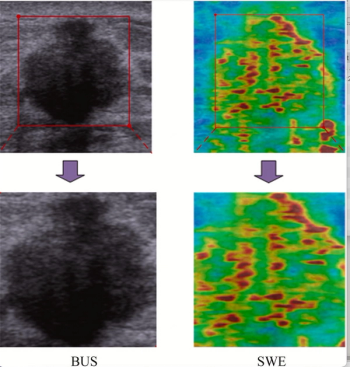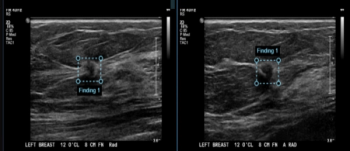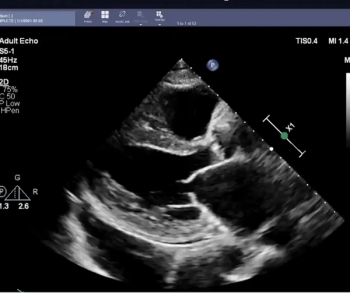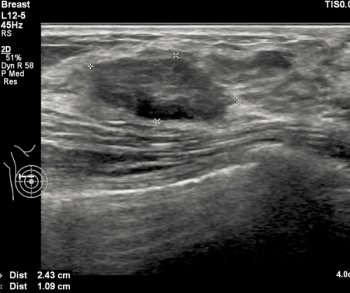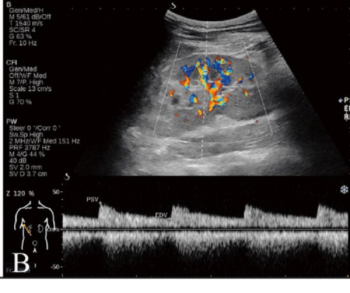
In a recent video interview, Stephen Rose, M.D., reviewed a variety of factors that can impact interpretation of breast imaging for women with breast implants and discussed recent research showing a 22 percent reduction in cancer detection rate for this population in comparison to women without breast implants.