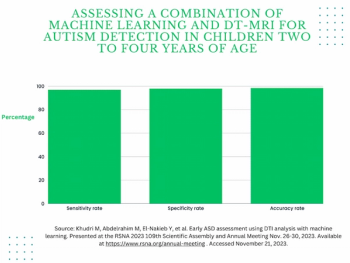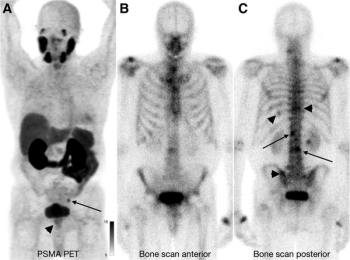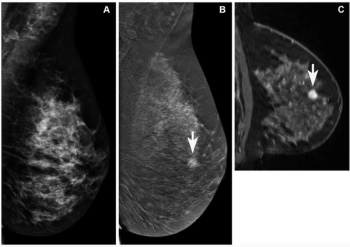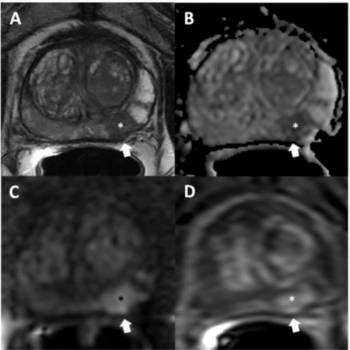
Utilizing a deep learning-based AI algorithm to differentiate between diagnostic and non-diagnostic quality of prostate MRI facilitated a 10 percent higher specificity rate for diagnosing extraprostatic extension on multiparametric MRI, according to research presented at the recent RSNA conference.