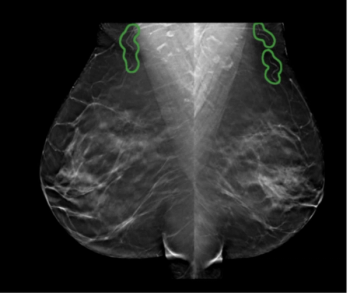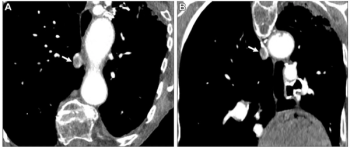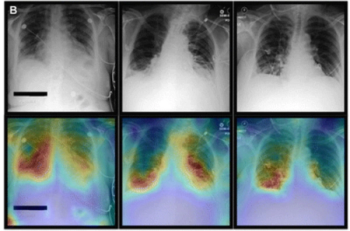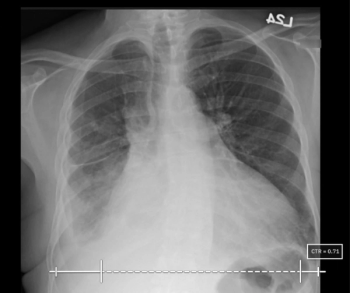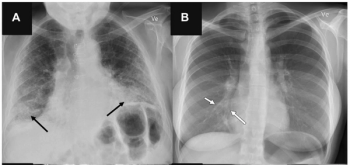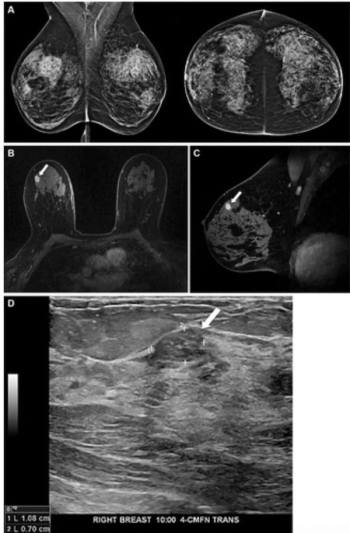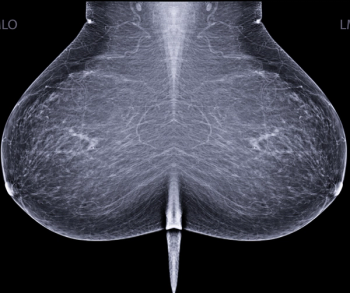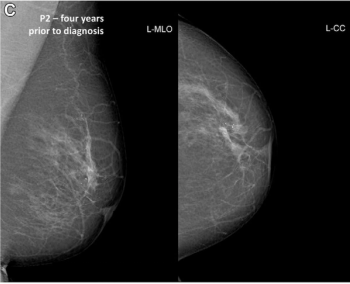
Artificial intelligence (AI) software assigned high malignancy risk scores to mammography exams completed up to two years prior to breast cancer diagnosis in over 38 percent of screen-detected cancer cases and over 39 percent of interval cancer cases, according to newly published research.