
Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
The Biograph Vision.X positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) reportedly offers an industry-leading time of flight (TOF) and detector technology that facilitates the diagnosis of smaller lesions.
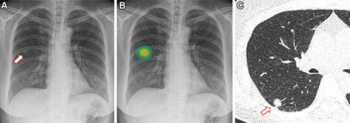
Artificial intelligence (AI) assessments of chest X-rays identified 28 percent of a 17,000 plus cohort of never-smokers as being at high-risk for lung cancer, according to research to be presented at the annual Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference next week.
Pixyl.Neuro reportedly leverages generative artificial intelligence (AI) technology to accelerate brain MRI assessment and improve early detection of abnormal atrophy.
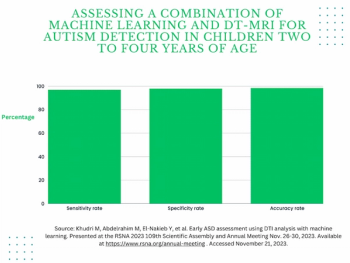
Through assessment of diffusion tensor MRI of the brain, a new AI system reportedly offers a 97 percent sensitivity rate in diagnosing autism in children between two to four years of age, according to research to be presented at the annual Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference next week.

The artificial intelligence (AI)-powered technology reportedly offers decreased noise magnitude while enhancing image reconstruction for cardiovascular computed tomography (CT) scanners.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
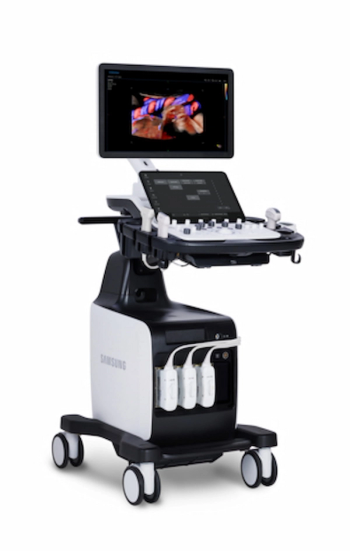
Combining enhanced imaging capabilities, workflow efficiencies and artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled technology to improve the diagnosis and management of health conditions in women, Samsung has launched the V6 ultrasound system.
Providing automated brain volume calculations based on MRI images, NeuroShield’s artificial intelligence (AI)-powered technology may help facilitate treatment for neurodegenerative conditions ranging from Alzheimer’s disease to epilepsy.
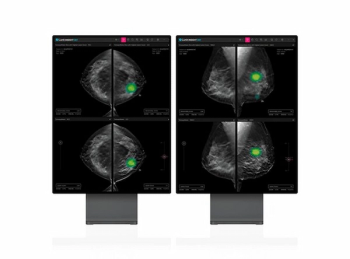
Lunit Insight DBT may facilitate improved detection and efficiency for radiologists interpreting digital breast tomosynthesis images.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Mammography-based artificial intelligence (AI) models demonstrated an 11 percent higher median AUC for predicting breast cancer than traditional clinical risk factors, according to a new systematic review of 16 retrospective studies.
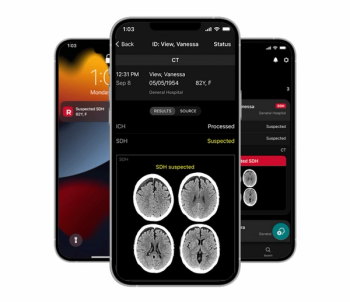
The Rapid SDH module on the RapidAI platform reportedly offers a sensitivity rate of 93 percent for detection of hemispheric subdural hematoma on non-contrast computed tomography (CT) scans.

Reimbursement for use of the artificial intelligence (AI)-powered EchoGo Heart Failure platform in hospital outpatient settings for Medicare and Medicaid patients is expected to increase from $99.81 to $284.88 in 2024.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
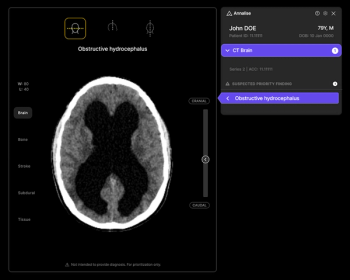
Featuring 12 prior FDA clearances for chest X-ray and non-contrast head CT, the Annalise Triage platform may help streamline radiology workflows and prioritize timely diagnosis of urgent conditions.

The executive order seeks to promote continued innovation and growth with artificial intelligence (AI) while ensuring monitoring of AI models for safety, privacy, and equity.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
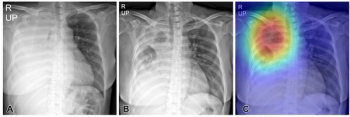
An emerging deep learning algorithm can reportedly triage 40 percent of no-change X-rays while providing 88 to 90 percent accuracy for detecting changes with X-rays obtained in the emergency department and intensive care unit at a tertiary referral hospital, according to recently published research.
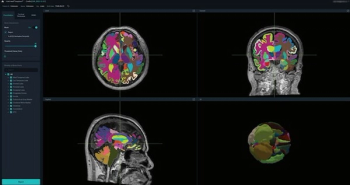
The artificial intelligence (AI)-powered software VUNO Med-DeepBrain reportedly automates brain MRI segmentation and provides access to volumetric data on over 100 regions of the brain.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
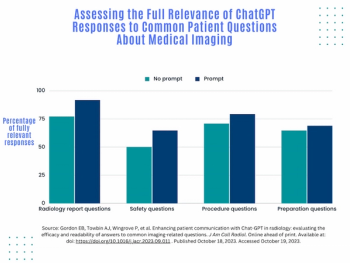
While ChatGPT has the potential to help streamline responses to imaging-related questions from patients, the authors of a new study found that a third of ChatGPT responses to unprompted questions on medical imaging were not “fully relevant.”
In a multicenter cohort of patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD), a deep learning classification tool demonstrated an 81 percent sensitivity rate and a 77 percent specificity rate for predicting usual interstitial pneumonia on computed tomography (CT) scans.
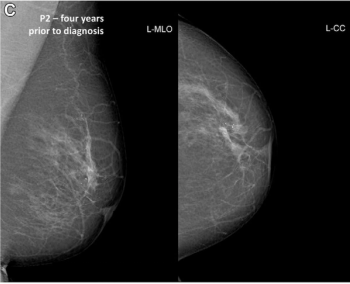
Artificial intelligence (AI) software assigned high malignancy risk scores to mammography exams completed up to two years prior to breast cancer diagnosis in over 38 percent of screen-detected cancer cases and over 39 percent of interval cancer cases, according to newly published research.