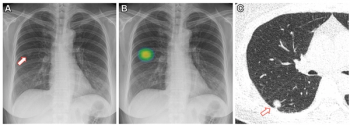
In newly published research, researchers found that an artificial intelligence (AI) computer-aided detection (CAD) system was more than twice as likely as non-AI assessment to diagnose actionable lung nodules on chest X-rays.

In newly published research, researchers found that an artificial intelligence (AI) computer-aided detection (CAD) system was more than twice as likely as non-AI assessment to diagnose actionable lung nodules on chest X-rays.
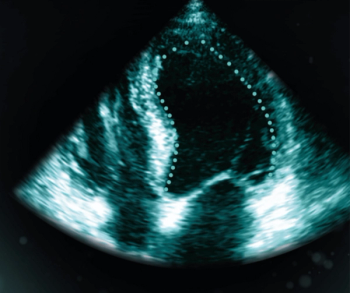
Employing an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered scoring system, LVivo IQS reportedly provides real-time assessment of the quality of cardiac ultrasound images.
From enhanced image quality and workflow efficiencies to an improved patient experience and potential synergies wih enterprise cloud services, artificial intelligence continues to redefine possibilities in radiology.
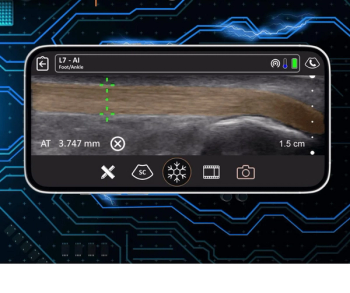
In what is reportedly the first Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 510(k) clearance for the use of artificial intelligence (AI) for musculoskeletal ultrasound, the model provides automated measurements of tendons in the knee, ankle, and foot.
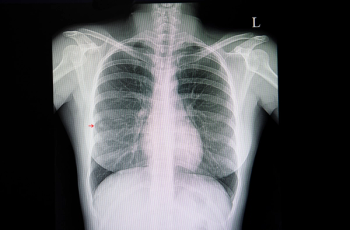
In an external validation data set for a deep learning bone-suppressed (DLBS) model, researchers found that adjunctive use of the DLBS model led to a nearly 15 percent increase in sensitivity for detecting pulmonary nodules on chest X-rays in comparison to radiologist assessment.
Researchers showed that adjunctive use of a deep learning algorithm resulted in an eight percent increase in sensitivity and a nearly 10 percent increase in specificity for differentiating between colon carcinoma and acute diverticulitis on computed tomography (CT) scans.

In a new survey, 83 percent of radiology residents agreed that artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML) should be part of their curriculum but approximately 24 percent of residents said there are currently no AI/ML educational offerings in their residency program.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
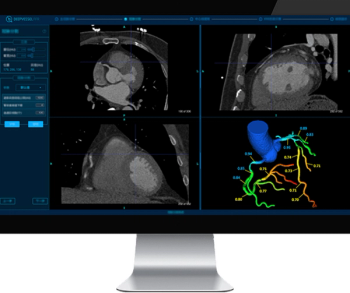
Employing deep learning capabilities, the DeepVessel FFR reportedly provides enhanced non-invasive evaluation of coronary arteries through semi-automated analysis of coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) imaging.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research of the past month.
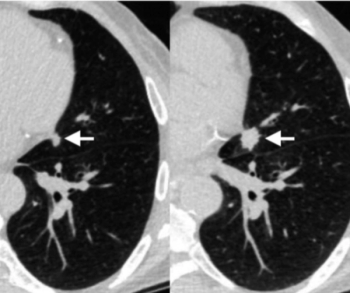
Trained and developed on over 35,000 low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) scans and validated in three independent data sets, a deep learning algorithm demonstrated an average area under the curve (AUC) of 90.6 percent for predicting lung cancer within one year.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
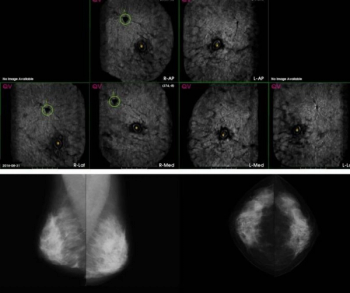
Emerging research suggests combined artificial intelligence (AI) assessment of digital mammography and automated 3D breast ultrasound provides enhanced detection of breast cancer in women with dense breasts and may be a viable alternative in areas where radiologists are scarce.
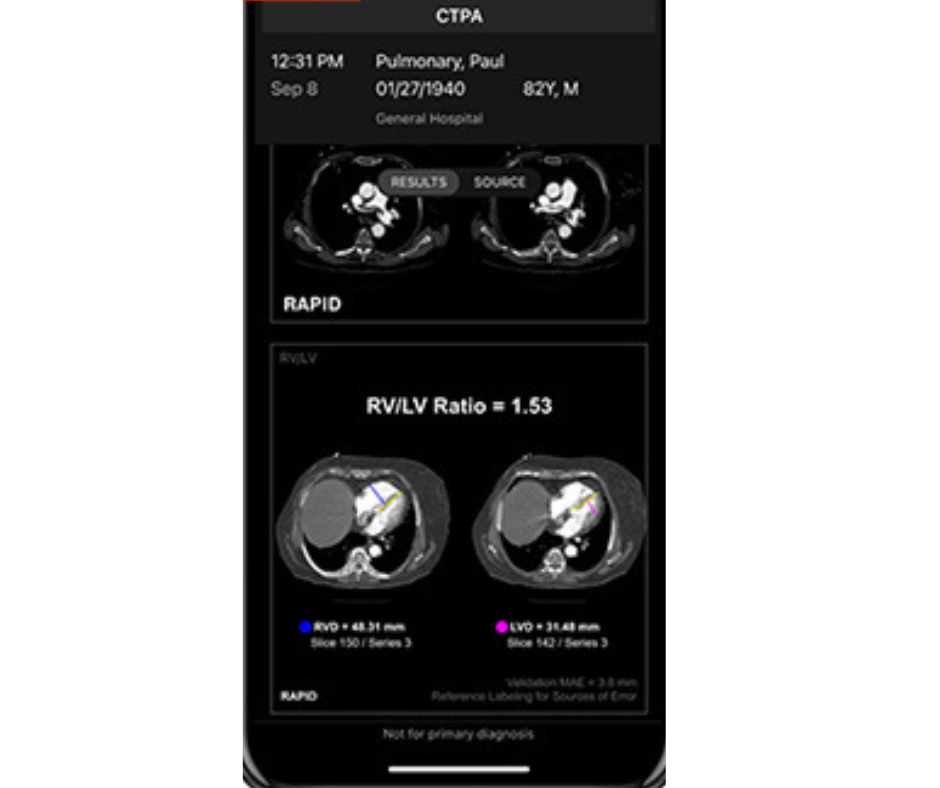
In a study involving patients who presented to emergency departments with acute chest pain, a deep learning model demonstrated significantly improved prediction of aortic dissection and all-cause mortality and indicated that additional pulmonary and cardiovascular testing could be deferred in seven times as many patients as suggested by conventional risk factors and testing measures.
In a provocative new article, radiology researchers discuss the impact of social determinants of health (SDoH) upon access to care and patient outcomes, and present strategies within the realms of radiology education, research, clinical care, and innovation that may help mitigate health-care disparities.
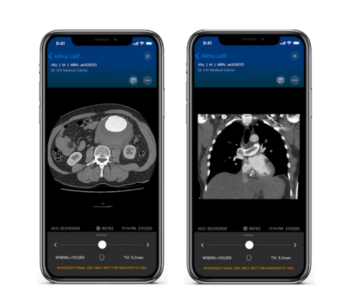
The artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled Viz™ Vascular Suite reportedly allows automated detection of vascular conditions, shown on computed tomography (CT) and other imaging modalities, and facilitates timely triage among interdisciplinary teams.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
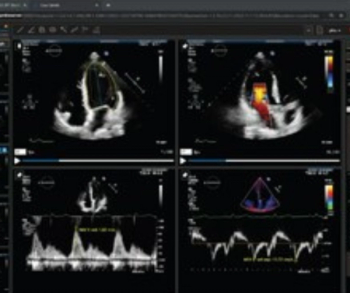
CAAS Qardia 2.0, an updated version of the CAAS Qardia echocardiography software platform, reportedly incorporates artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled workflows, and provides enhanced imaging and analysis of key cardiac measures.
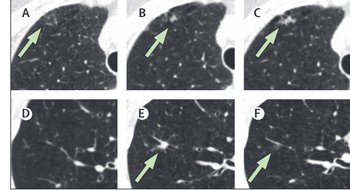
From incidental findings and screening for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) to surveillance imaging protocols and the advent of artificial intelligence (AI), the authors of a new meta-analysis examine insights and emerging trends from the last two decades of research on the use of low-dose computed tomography (CT) in lung cancer screening.

Check out the top radiology content of the past week.
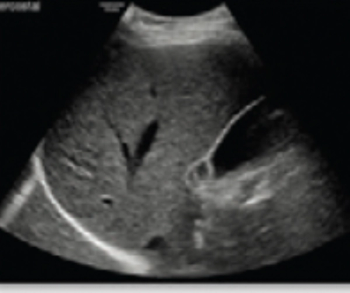
In a new prospective study, an emerging deep learning model, which incorporates parametric mapping with quantitative ultrasound to estimate liver fat fraction, demonstrated a 90 percent sensitivity rate and a 91 percent specificity rate for diagnosing hepatic steatosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).

Catch up on the most well-read magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) articles from 2022.
Catch up on the most well-read mammography articles from 2022.

Catch up on the most well-read artificial intelligence (AI) articles from 2022.

Check out the top radiology content of the past week.