
Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
For patients with suspected interstitial lung disease, the digital biomarker solution Fibresolve offers machine learning capability of diagnosing idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) based on assessment of lung computed tomography (CT) scans.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Utilizing brain MRI and cognitive assessments, the newly FDA-approved, AI-powered software platform BrainSee can reportedly predict the progression of amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) to Alzheimer’s dementia within five years.
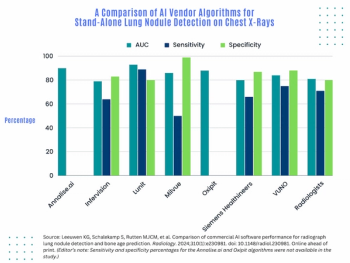
In part of an ongoing multicenter study evaluating commercial artificial intelligence (AI) products in radiology, AI lung nodule detection software from four out of seven vendors demonstrated stand-alone AUCs ranging from 5 to 12 percent higher than the mean AUC of 17 reviewing radiologists.

Offering enhanced utility for assessing urinary incontinence, bladder emptying and urinary retention, the Clarius Bladder AI ultrasound software reportedly provides bladder volume measurement in seconds.
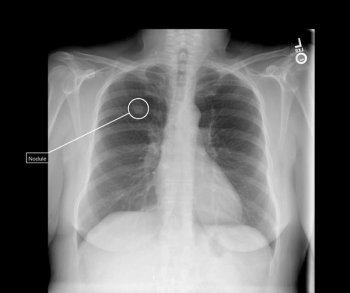
Tailored for incidental findings on chest radiographs, the qXR for Lung Nodule (qXR-LN) software utilizes artificial intelligence (AI) to help detect suspected pulmonary nodules ranging between 6 to 30 mm.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
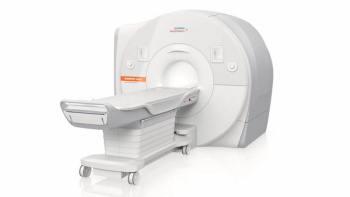
At an amplitude of 200 mT/m and a slew rate of 200 T/m/s, the gradients for the FDA-cleared MAGNETOM Cima.X are reportedly the strongest for currently available whole-body MRI scanners.
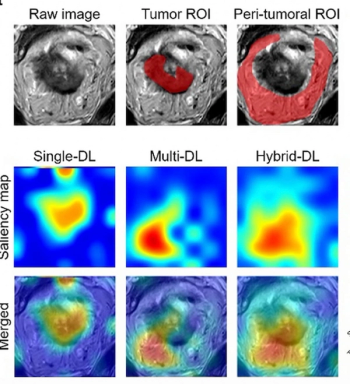
An emerging deep learning model, which incorporates T2-weighted MRI and clinical data, demonstrated an 83.9 percent AUC and an 85 percent specificity rate for preoperative prediction of tumor deposits in patients with rectal cancer.
Catch up on the most viewed content on AI in radiology from 2023.
Touching on a variety of topics in radiology, here are the top five most well-viewed content from Diagnostic Imaging in 2023.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a study examining the potential of the large language models ChatGPT-4 and Bard to follow ACR Appropriateness Criteria for breast cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer and colorectal cancer screening, researchers noted “impressive accuracy in making radiologic clinical decisions.”
Catch up on the most well-read ultrasound articles from 2023.
Catch up on the most well-read magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) articles from 2023.
In addition to offering a 98.5 percent sensitivity rate in diagnosing fractures on X-ray, an emerging artificial intelligence (AI) software reportedly helped reduce mean turnaround time on X-ray fracture diagnosis from 48 hours to 8.3 hours, according to new research presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
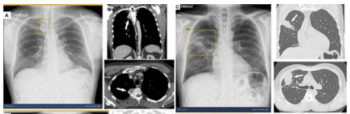
Emerging research suggests that adjunctive artificial intelligence (AI) improves sensitivity for a variety of abnormalities on chest X-rays regardless of radiologist experience level, including an average 26 percent increase in sensitivity for pneumothorax.
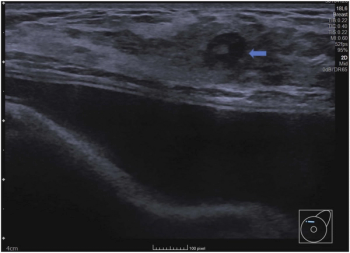
Emerging research suggests that stand-alone artificial intelligence (AI) assessment of breast ultrasound exams could eliminate over 45 percent of unnecessary follow-up exams.

Will AI-powered diagnostic workups without on-site docs be a new reality in 2024?

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
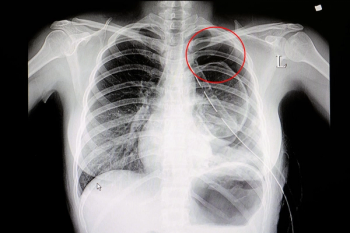
BraveCX, an artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled software, reportedly has an area under the curve (AUC) of 98 percent for detecting pneumothorax on chest X-rays.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.