The study demonstrated that the combined model yielded improved risk assessment for both interval and long-term breast cancers.

The study demonstrated that the combined model yielded improved risk assessment for both interval and long-term breast cancers.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
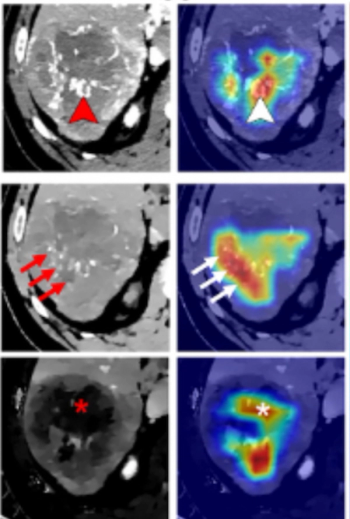
In comparison to clinical-radiologic assessment, a deep learning CT radiomics nomogram had a 10 percent higher AUC and a 27 percent higher specificity for predicting the macrotrabecular massive subtype of hepatocellular carcinoma in external data testing.
The Echelon Synergy MRI system reportedly uses deep learning technology to accelerate image acquisition and enhance image quality.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
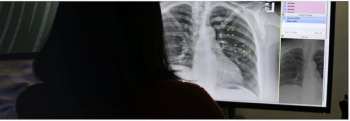
The artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled VisiRad XR reportedly demonstrated an 83 percent sensitivity rate for detecting lung nodules and masses on chest X-rays in one retrospective study.

The De Novo approval for Viz HCM, which assesses electrocardiograms with artificial intelligence (AI) to identify possible cases of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), is the 12th FDA clearance of algorithms on the Viz.ai Platform.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In what may represent the first CMS approval of a new technology add-on payment (NTAP) for an artificial intelligence (AI)-based heart failure detection platform, use of the EchoGo Heart Failure system will be eligible for up to $1,023.75 in NTAP reimbursement per acute hospital in-patient stay as of October 1, 2023.
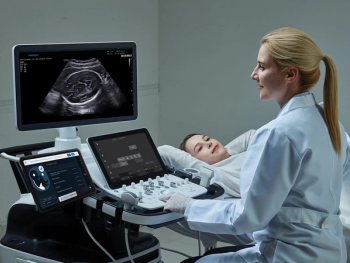
With reported performance validation on over 17,000 ultrasound images, Sonio Detect employs artificial intelligence (AI) to help ensure quality criteria for fetal ultrasound imaging of the brain and heart.
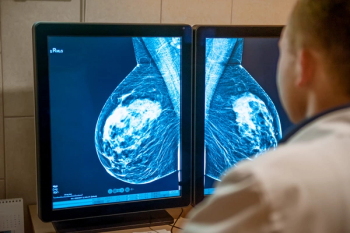
Reportedly the first randomized trial to examine the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on screening mammography, researchers found AI-aided screening led to a 20 percent increase in breast cancer detection and a 44.3 percent decrease in mammography screening workload.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.
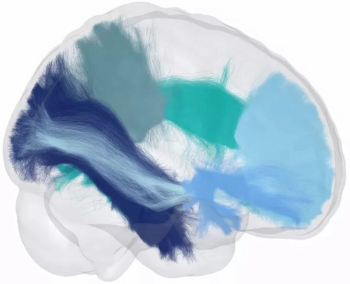
Through automated processing of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, the Advanced Neuro Diagnostic Imaging (ANDI) software performs detailed analysis of white matter microstructure.

Catch up on the top radiology news of the past week.
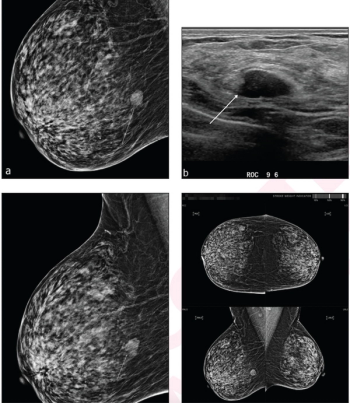
In a study of over 1.300 women with dense breasts, the combination of mammography and ultrasound had a recall rate of 11.7 percent, a specificity rate of 89.1 percent and an accuracy rate of 89.2 percent in comparison to a 21.4 percent recall rate, 79.4 percent specificity and 79.5 percent accuracy for the combination of mammography, ultrasound, and artificial intelligence (AI).
Indicated for use in two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography (2D-TTE) in adults, the AI Guidance software reportedly enables novice ultrasound users to obtain real-time cardiac imaging at the point of care.
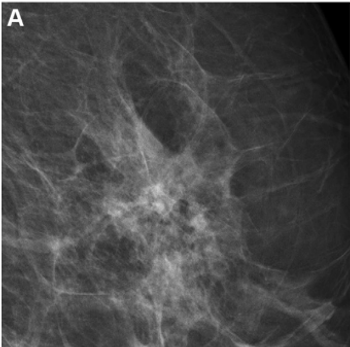
In a dataset enriched for African American women, BRCA mutation carriers and those with benign breast disease, a mammography-based deep learning model demonstrated a five-year AUC of 63 percent for predicting breast cancer in comparison to 54 percent for BI-RADS assessment.
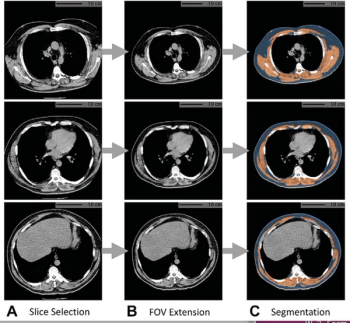
In a study of over 20,700 people, researchers found that artificial intelligence (AI) analysis of body composition measurements via lung cancer screening computed tomography (CT) exams improves the prediction of mortality risks for lung cancer, cardiovascular disease, and all-cause mortality.

Catch up on the top radiology news of the past week.
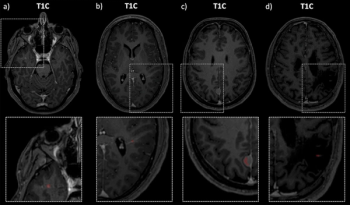
An artificial intelligence model, trained on MRI and FLAIR imaging from over 900 patients with multiple sclerosis, demonstrated a 96 percent accuracy rate and 99 percent specificity rate for contrast-enhancing lesions in this patient population.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

An artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled platform that can reportedly diagnose heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) through analysis of a single echocardiogram view, the EchoGo Heart Failure now has a HCPCS code for use of the technology in outpatient settings for Medicare beneficiaries.
Reportedly receiving the first Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) III code from the American Medical Association (AMA) for artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) software, Icometrix says its adjunctive quantification software can be utilized for diagnosis and assessment of conditions ranging from Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy to stroke and dementia.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.