Mammography
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
Noting an increased incidence of false negatives in screening and diagnostic mammography, researchers found that a personal history of breast cancer was associated with over a 3.6-fold higher likelihood of false negatives.
Concordant mammography detection of breast cancer by radiologists and AI had over a threefold higher likelihood of future incidental breast cancer in comparison to positive radiologist assessment and negative AI evaluation, according to new research involving over 82,000 women.
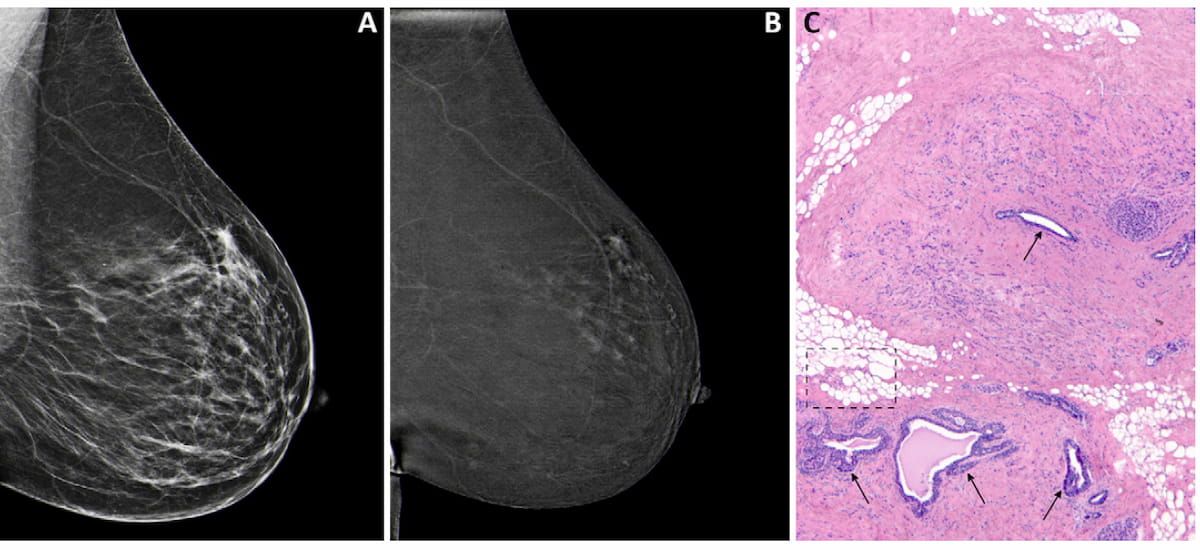
While dynamic contrast enhanced breast MRI may help reduce biopsies for suspicious calcifications on mammograms, quantitative MRI features and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) may not provide additional diagnostic benefit in these cases, according to a new study.

In a recent interview, Manisha Bahl, M.D., discussed new research showing significant associations between AI detection and the histologic grade and lymph node status of breast cancer.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
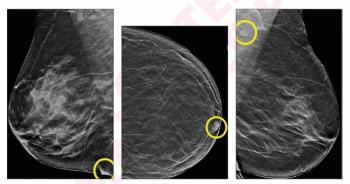
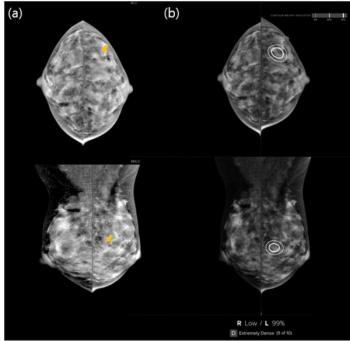
In comparison to false positives with unassisted radiologist interpretations of DBT exams, AI-only false positive assessments were associated with a significantly higher total of false-positive findings as well as a 33 percent lower frequency of dense breasts, according to a new study of nearly 3,000 women who had screening DBT exams.
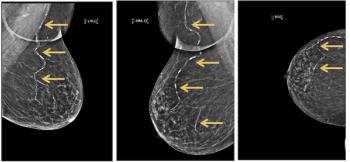
The Mammo Enhance Heart program combines AI detection of breast arterial calcification (BAC) on screening mammography and subsequent follow-up with a local network of cardiologists.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in September 2025.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
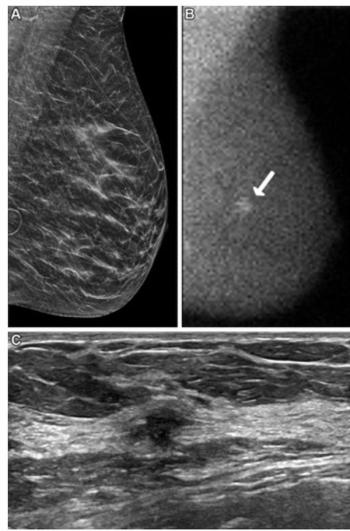
The combination of digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and molecular breast imaging (MBI) offered more than double the detection of invasive breast cancer with DBT in the first year of screening, according to a prospective study of nearly 3,000 women with dense breasts.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
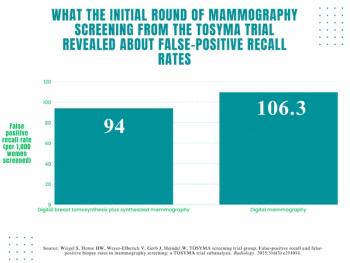
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and synthesized mammography offered a true-positive recall rate of 8.4 per 1,000 women screened vs. 6.2 for digital mammography alone, according to a study involving over 99,000 women.

In light of emerging research suggesting an increased incidence of breast cancer among women under the age of 40, breast radiologists discuss what they’re seeing in practice and emphasize increased vigilance to facilitate early detection.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In a recent interview, Zeeshan Shah, M.D., discussed the challenges of addressing rising breast imaging volume amid the radiologist shortage, the potential of emerging AI solutions for bolstering efficient triage and an increasing incidence of breast cancer presentations in younger patients.
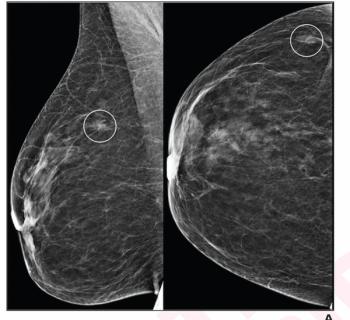
While the AI software offered nearly equivalent negative predictive value (NPV) to radiologist interpretation of digital mammograms and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) images, researchers noted that AI had significantly higher recall rates and false-positive results in patients with intermediate risk.
From emerging research on disparities in breast cancer screening to the promising combination of contrast-enhanced mammography with DBT and a three-part podcast on abbreviated breast MRI, here is a look back at the most well-reviewed breast imaging content of the summer.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in August 2025.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
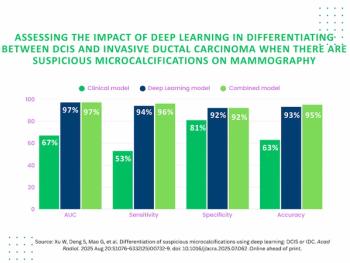
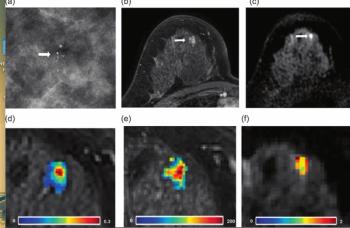
A model combining deep learning features and clinical variables demonstrated a 30 percent higher AUC than a clinical model for detecting DCIS and invasive ductal carcinoma from suspicious microcalcifications on mammography, according to a new study.
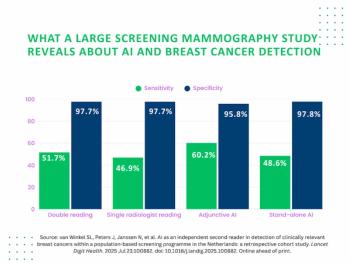
Over 26 percent of AI-detected future breast cancers and interval breast cancers missed by radiologists were invasive cancers, according to newly published research involving over 42,000 women who had 2D screening mammography.

In a recent interview, Ioannis Sechopoulos, Ph.D, and Sarah D. Verboom, MSc discussed their new research examining the role of certainty in AI mammography screening assessment and the potential impact on workload reduction for radiologists.

Catch up on the latest news, research and insights in radiology with our Weekly Scan.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.