Mammography
Latest News
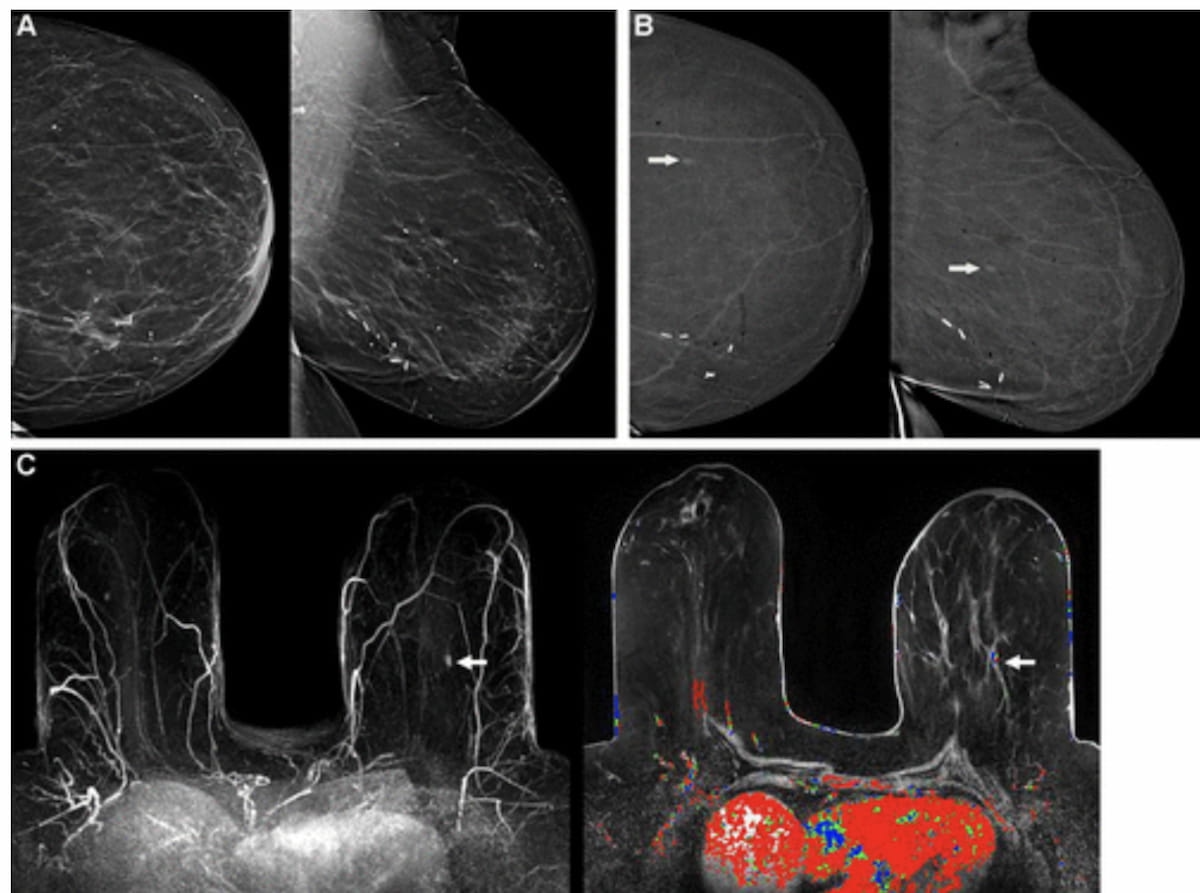
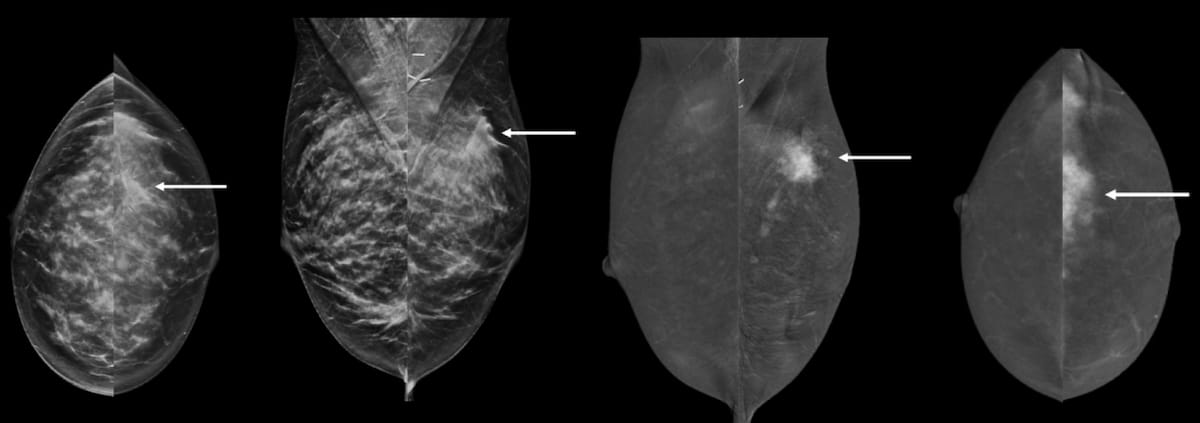
For over 1,200 women with a previous history of breast cancer, interim findings from a prospective trial suggest that adding contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) to digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) enhances detection of second malignancies with a limited increase in recalls.
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
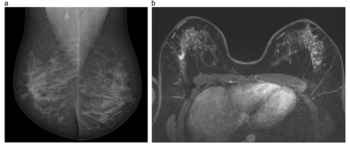
One of the recommendations from the European Society of Breast Imaging (EUSOBI) is annual breast MRI exams starting at 25 years of age for women deemed to be at high risk for breast cancer.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
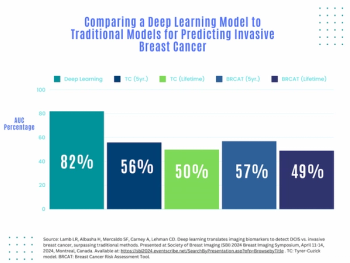
Artificial intelligence (AI) assessment of mammography images may significantly enhance the prediction of invasive breast cancer and ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) in women with breast cancer, according to new research presented at the Society for Breast Imaging (SBI) conference.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Patients with Medicaid or means-tested insurance were over 27 percent more likely to miss mammography appointments, and only 65 percent of women with three of more adverse social determinants of health had a mammography exam in a two-year period covering 2020 and 2021, according to new research and a report from the CDC.
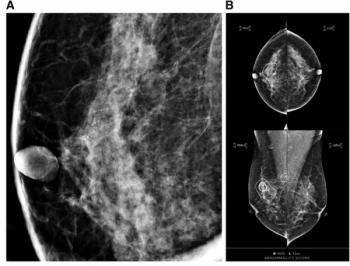
Emerging research suggests that an artificial intelligence (AI) score of 75 or greater for mammography abnormalities more than doubles the likelihood of invasive upgrade of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) diagnosed with percutaneous biopsy.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In addition to full-field digital mammography and titanium contrast-enhanced mammography capabilities, the Mammomat B.brilliant system also offers ergonomic, workflow and patient comfort benefits.
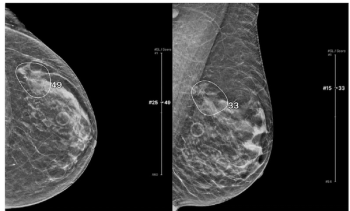
An emerging artificial intelligence (AI) model demonstrated more than 12 percent higher specificity and reduced image reading time by nearly six seconds in comparison to unassisted radiologist interpretation of digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) images.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
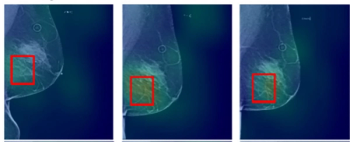
A proposed alternative to a previously validated deep learning neural network for assessing short-term breast cancer risk, the emerging AsymMirai deep learning mammography-based model showed comparable breast cancer risk prediction with an emphasis on bilateral dissimilarity, according to new research.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
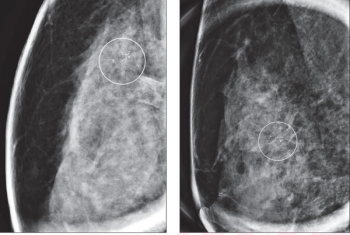
For women who have had radial scars detected on digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) exams, researchers noted a 5 percent upstaging rate to cancer, according to a recent study.
Noting that technique issues, patient positioning miscues and atypical features can all contribute to faulty interpretation with contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM), researchers at the European Congress of Radiology shared their insights on navigating artifacts and limitations with CEM.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
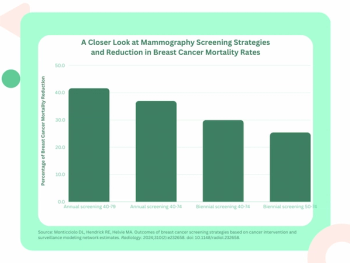
In comparison to biennial mammography screening between the ages of 50 to 74, researchers found that annual screening between 40 and 79 years of age resulted in a greater than 16 percent higher reduction in breast cancer mortality.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
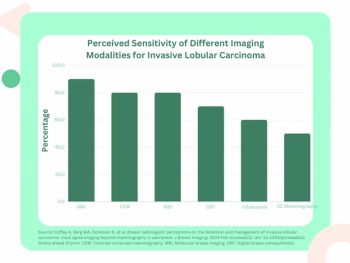
For women with dense breasts, only 25 percent of breast radiologists are confident in the use of mammography for diagnosing invasive lobular carcinoma, according to newly published survey results from the Society of Breast Imaging.
Women with an increasing number of unmet social needs were 26 percent less likely to have mammography screening, according to a recent study of over 300 women with breast cancer.

In a recent interview, Vivianne Freitas, M.D., discussed new research findings on positron emission mammography (PEM), pertinent benefits of the technology and its potential as a viable alternative in the future to conventional imaging techniques for breast cancer screening.
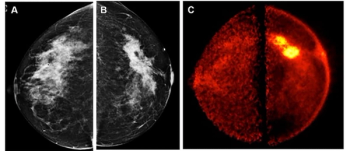
Findings from a new pilot study showed that low-dose positron emission mammography (PEM) detected 96 percent of malignant index lesions and had a 46 percent lower false-positive rate in comparison to breast MRI.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
In a recently issued statement from multiple radiology societies including the RSNA and ACR, researchers offer practical advice for evaluating artificial intelligence (AI) tools, implementing AI into current workflows and monitoring of the technology to help ensure optimal benefit and effectiveness.