Mammography
Latest News

Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

As recommendations have become a commonplace expectation on radiology reports, is there a point where we are crossing the line?
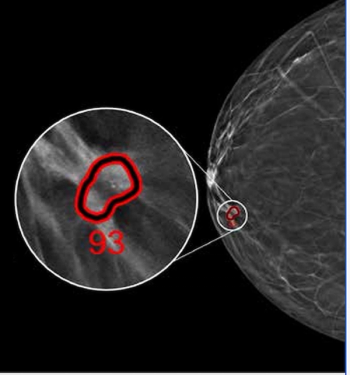
Employing advanced deep learning convolutional neural networks, ProFound Detection Version 4.0 reportedly offers a 50 percent improvement in detecting cancer in dense breasts in comparison to the previous version of the software.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a recent interview, Stamatia Destounis, M.D., discussed the impact of national breast density notification for mammography reports and key considerations with staffing and ongoing education for patients, staff and referring providers on the merits of supplemental breast imaging.
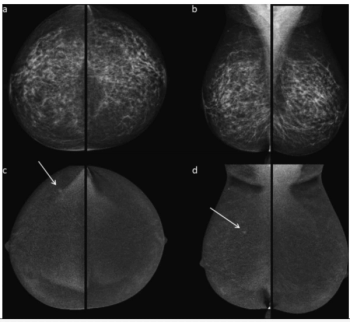
In a 10-year study involving over 5,400 women with nearly 85 percent having dense breasts, contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) demonstrated a 95.9 percent sensitivity rate for breast cancer.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in October 2024.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
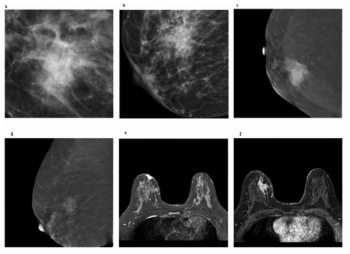
Is the Kaiser Score More Effective than BI-RADS for Assessing Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and MRI?
For women with breast-enhanced masses, Kaiser scoring (KS) demonstrated a 20 percent higher AUC than BI-RADS classification for contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) and was comparable to KS for breast MRI.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
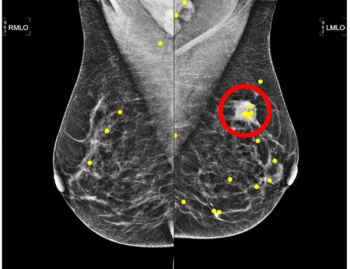
New research suggests that reviewing mammography images in order of ascending volumetric breast density as opposed to random reading of exams demonstrated reduced reading time and less fixation time on malignant lesions.
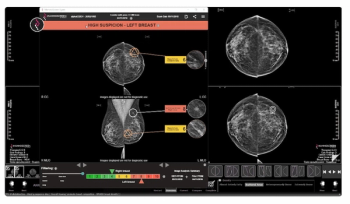
Therapixel’s MammoScreen suite has received 510(k) FDA clearances for a breast density assessment feature and updated software that includes automated pre-reporting, which reportedly expedites reporting of mammography findings.
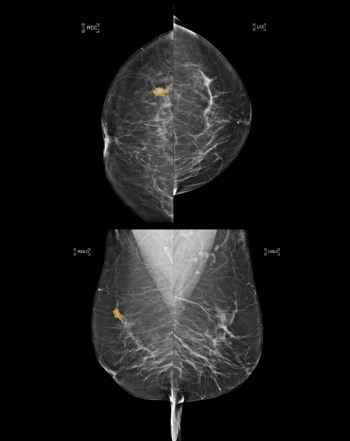
The combination of FDA-cleared AI software for mammography triage with a medical grade edge AI platform may allow the embedding of enhanced AI detection capability within existing mammography devices.
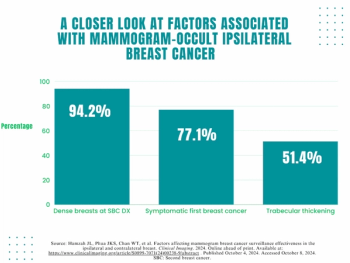
A symptomatic first breast cancer diagnosis, prevailing breast density at a second breast cancer diagnosis and trabecular thickening on surveillance mammography were linked to mammogram-occult ipsilateral breast cancer, according to new research.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
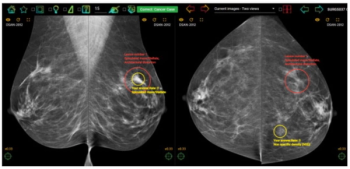
In a study looking at the impact of experience and case volume of breast screening radiologists, researchers found that reviewing more than 150 cases per week was necessary to achieve an 80 percent rate of true-positive assessments for malignant calcifications.
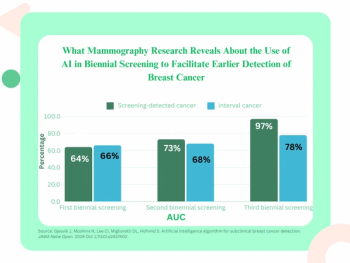
Mean artificial intelligence (AI) scoring for breasts developing cancer was double that of contralateral breasts at initial biennial screening and was 16 times higher at the third biennial screening, according to a study involving over 116,000 women with no prior history of breast cancer.
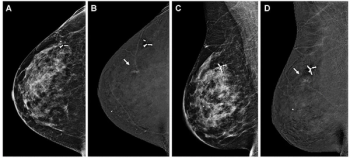
For patients with extremely dense breasts, contrast-enhanced mammography offered greater than 60 percent higher sensitivity than low-energy mammography for diagnosing breast cancer, according to new research.

The inclusion of the 3D imaging technology PlatinumTomo in the Mammomat B.brilliant device reportedly enables clinicians to obtain 50-degree 3D images in less than five seconds.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
While researchers noted no significant impact on sensitivity rates, they found that access to a patient’s prior mammograms resulted in a nearly 15 percent increase in sensitivity for current mammography interpretation.
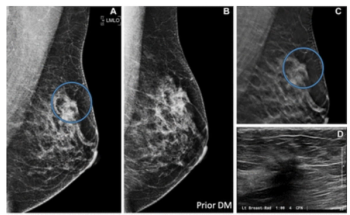
In a study involving over 272,000 breast cancer screening exams, digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) had a higher breast cancer detection rate and a lower rate of advanced cancer presentation at the time of diagnosis in comparison to digital mammography.
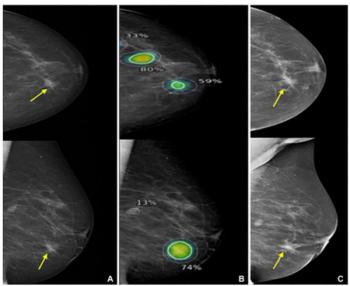
Identifying over 23 percent of interval breast cancers with a 96 percent sensitivity in mammography interpretation, an emerging AI software also facilitated correct localization in over 75 percent of cases involving interval breast cancer, according to new research.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
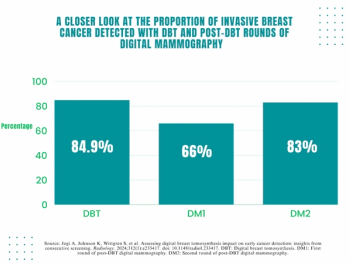
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) had a significantly higher cancer detection rate (CDR) in comparison to two consecutive post-DBT rounds of digital mammography, according to a new secondary analysis of the Malmo Breast Tomosynthesis Screening Trial (MBTST).