Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in September 2024.

Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in September 2024.
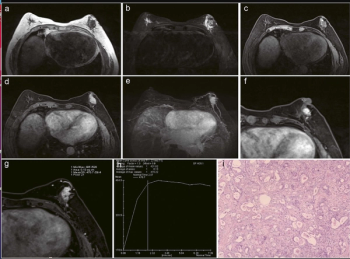
The addition of parameters such as patient age, MIP sign and associated imaging features to the Kaiser score demonstrated a 95.6 percent AUC for breast cancer detection of enhancing lesions on breast MRI in recently published research.

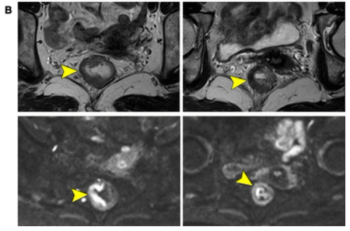
Catch up on the most-well viewed prostate imaging content in September 2024.
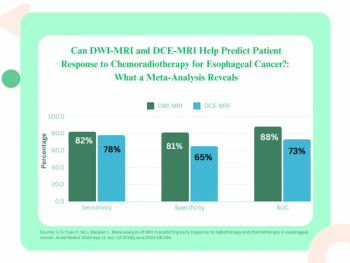
Diffusion-weighted MRI provided pooled sensitivity and specificity rates of 82 percent and 81 percent respectively for gauging patient response to concurrent chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer, according to new meta-analysis.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
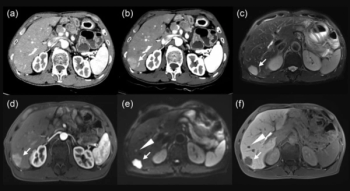
In a study involving 396 confirmed neuroendocrine tumor liver metastases, researchers found that Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI offered 19 percent higher sensitivity than polyenergetic CT.
In a comparison of imaging assessments to gauge the effectiveness of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for rectal adenocarcinoma, researchers found the combination of diffusion-weighted imaging and MR tumor regression grading had a 90 percent area under the curve (AUC) and a negative predictive value (NPV) of 93 percent.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in August 2024.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
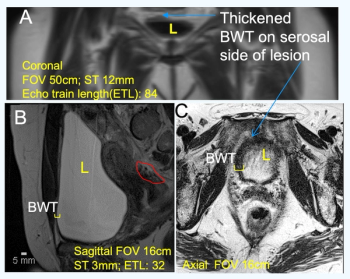
A new MRI contrast agent may provide a viable non-invasive alternative for the detection of interstitial cystitis, according to preliminary research presented at the 5th International Consultation on Interstitial Cystitis Japan (ICICJ) in Kyoto, Japan.
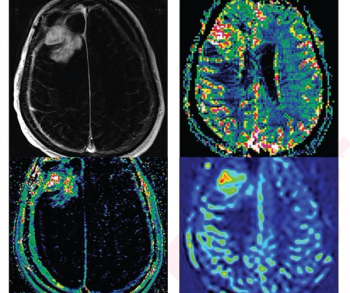
Based on surveys of neuro-oncologists taken before and after the use of MRI perfusion imaging and spectroscopy in patients with high-grade gliomas, researchers found the advanced imaging would have led to a greater than fivefold change in patient management in comparison to previous research.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
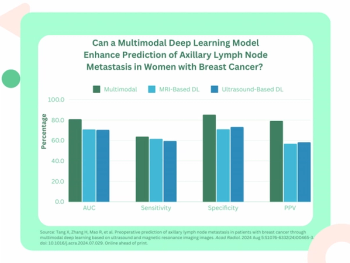
External validation testing revealed a deep learning combination of breast MRI, ultrasound and clinical factors had a 10 percent higher AUC for predicting axillary lymph node metastasis than sole use of MRI- or ultrasound-based deep learning models in patients with breast cancer.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
The absence of ipsilateral breast hypervascularity is three times more likely to be associated with false-negative findings on breast MRI and non-mass enhancement lesions have a 4.5-fold likelihood of being linked to false-positive results, according to new research.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
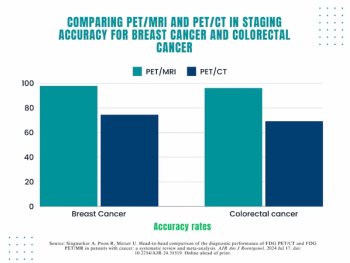
While PET/MRI and PET/CT had comparable sensitivity for patient-level regional nodal metastases and lesion-level recurrence, the authors of a systematic review noted that PET/MRI had significantly higher accuracy in breast cancer and colorectal cancer staging.
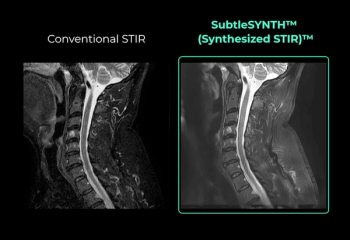
The deep learning SubtleSynth software creates synthetic STIR images that are reportedly interchangeable with conventional sequences obtained from T1 and T2-weighted MRI.

The Aperto Lucent open 0.4T MRI platform reportedly offers enhanced fat suppression and spatial resolution capabilities in addition to its open architecture design.
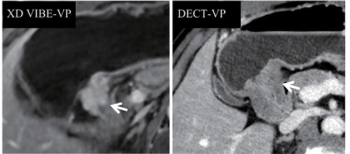
Researchers found that mpMRI was 18 percent more accurate than dual-energy CT (DECT) for T1 staging and 19 percent more accurate for N3 staging of gastric cancer.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
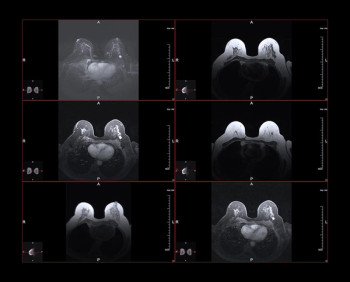
In the study of over 1,400 women with breast cancer, researchers noted that Black women with dense breasts or lobular histology were significantly less likely to have preoperative MRI exams than White women with the same clinical characteristics.
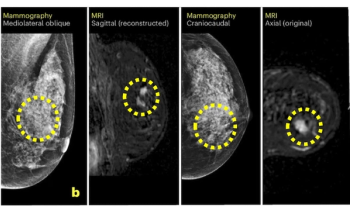
The AISmartDensity software facilitated a cancer detection rate (CDR) with breast MRI that was nearly four times higher than the CDR previously reported in trials involving traditional breast density assessment.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.