Oncology MRI
Latest News

Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
Offering a cost- and resource-saving DryCool magnet technology, the Magnetom Flow.Ace MRI system reportedly requires 0.7 liters of liquid helium for cooling over the lifetime of the device in contrast to over 1,000 liters commonly utilized with conventional MRI platforms.
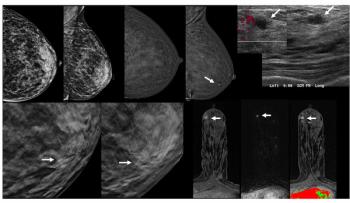
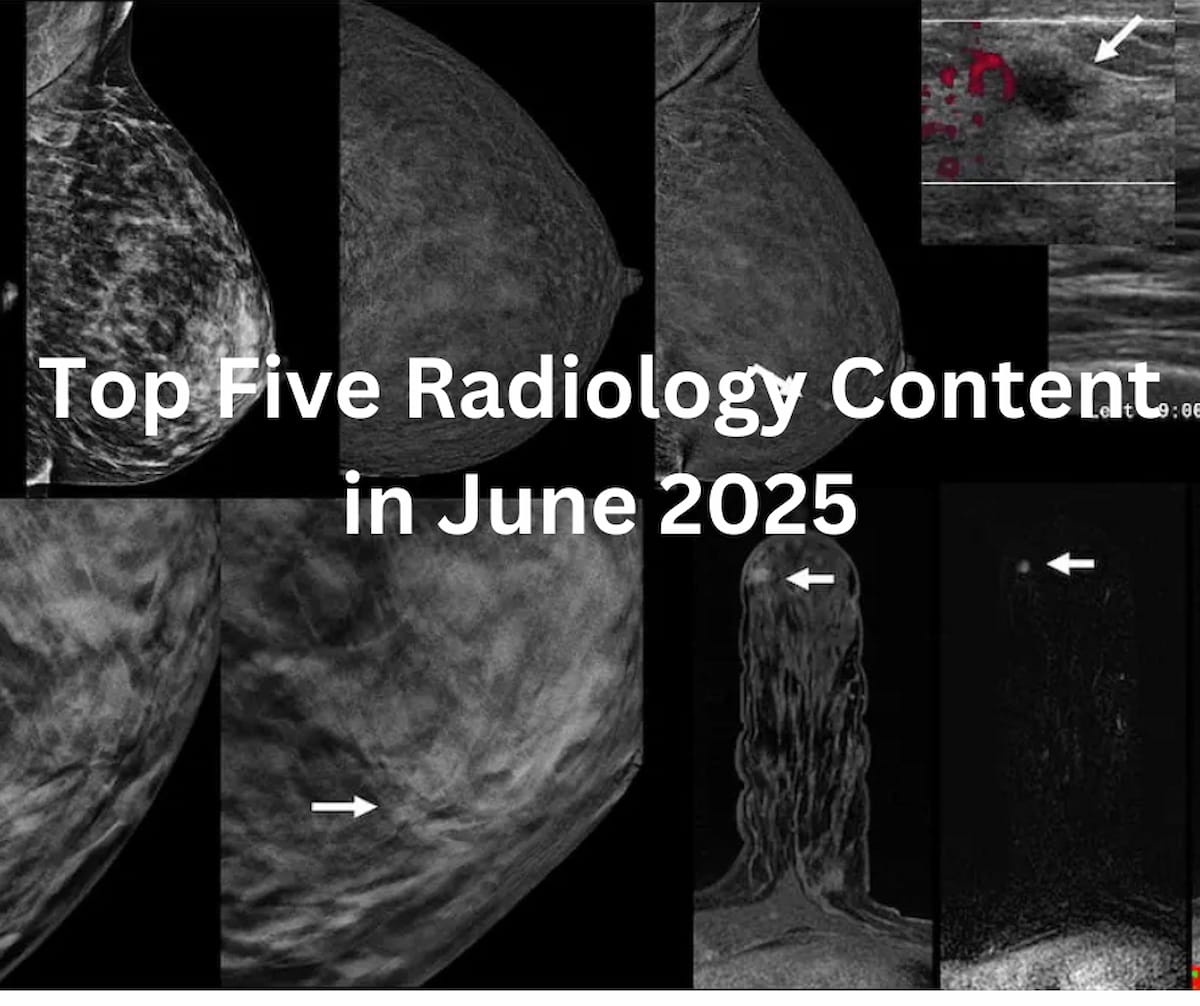
While the addition of contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) to digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) led to over a 13 percent increase in false positive cases, researchers also noted over double the cancer yield per 1,000 women in comparison to DBT alone.
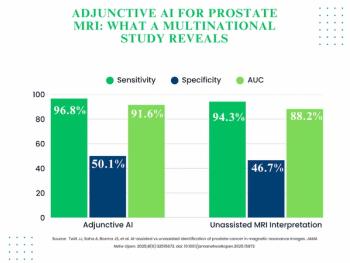
The use of adjunctive AI in biparametric prostate MRI exams led to 3.3 percent and 3.4 percent increases in the AUC and specificity, respectively, for clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa) in a 360-person cohort drawn from 53 facilities.

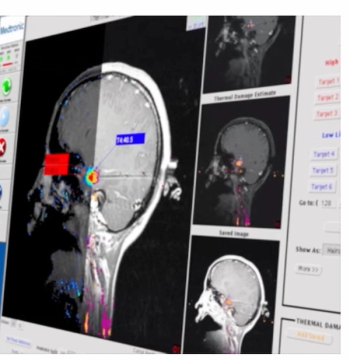
An alternative to an open neurosurgical approach, the Visualase V2 MRI-Guided Laser Ablation System reportedly utilizes laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) for targeted soft tissue ablation in patients with brain tumors and focal epilepsy.
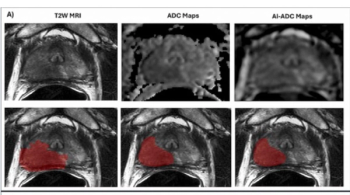
Emerging research showed that AI-generated ADC mapping from MRI led to significant increases in accuracy, PPV and specificity in comparison to conventional ADC mapping while achieving a 93 percent sensitivity for PCa.
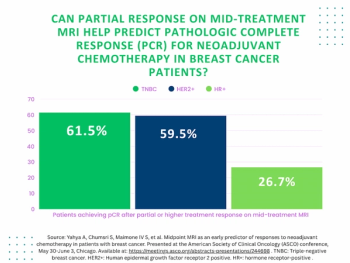
A partial response rate to neoadjuvant chemotherapy on mid-treatment MRI preceded a higher pathologic complete response (pCR) in 61.5 percent of women with triple-negative breast cancer, according to research presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) conference.
Assessing the simulated use of AI-generated suspicion scores for determining whether one should continue with full MRI or shift to an abbreviated MRI, the authors of a new study noted comparable sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value for biopsies between the MRI approaches.
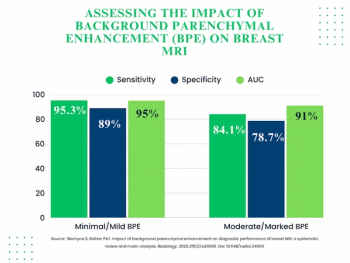
Moderate or marked background parenchymal enhancement (BPE) reduces the sensitivity and specificity of MRI for breast cancer detection by more than 10 percent in comparison to scans with minimal or mild BPE, according to a new meta-analysis.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in May 2025.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
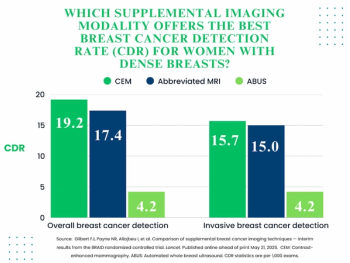
For women with dense breasts and negative mammograms, contrast-enhanced mammography and abbreviated MRI provided respective cancer detection rates of 19.2 per 1000 exams and 17.4 per 1000 exams, according to new research.
The MSKai software provides AI-powered segmentation, labeling, and measurement tools for assessment of T2-weighted MRIs of the lumbar spine.
Emerging research suggests that abbreviated breast MRI offers comparable sensitivity and specificity as multiparametric MRI in women with extremely dense breasts with a nearly 50 percent reduction in reading time for radiologists.
New guidelines from the European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) offer pertinent principles and recommendations for MRI use in considering fertility-sparing treatments for women with ovarian, endometrial, or cervical cancer.
The combination of high-performance gradient technology and AI tools with the Signa Sprint MRI reportedly facilitate enhanced MRI workflow efficiencies in cardiac and oncology imaging.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
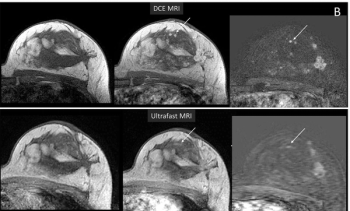
New research findings suggest that image quality and lesion conspicuity are significantly lower with ultrafast breast MRI in comparison to standard dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MRI.
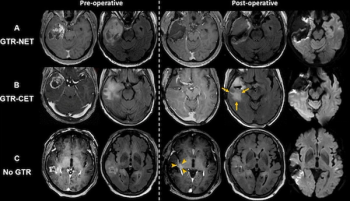
Irrespective of age or O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation status, gross total resection of IDH wild-type glioblastomas was associated with a median overall survival of 32.6 months, according to new MRI research.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Capable of segmenting over 37 organs and structures in the head, neck and pelvis, the MR Contour DL software is currently being showcased at the European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology (ESTRO) conference.

Catch up on the most well-viewed video interviews from Diagnostic Imaging in April 2025.
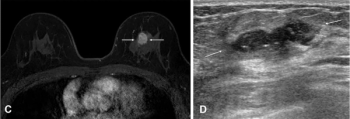
Preoperative breast MRI had no impact upon recurrence-free survival and overall survival for women with HER-2 positive, hormone receptor-negative breast cancer, according to a multivariable analysis of a new study involving nearly 1,100 women.
In a recent interview, Wayne Brisbane, M.D., discussed new research, presented at the American Urological Association (AUA) conference, which revealed a 15 percent higher AUC for an emerging AI software in detecting seminal vesicle invasion (SVI) in comparison to prostate MRI alone.