Disease Spotlight: Prostate Cancer
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
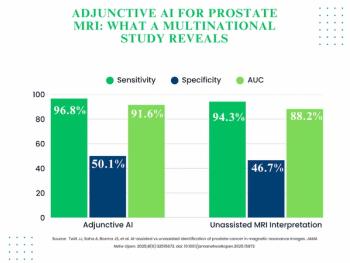
The use of adjunctive AI in biparametric prostate MRI exams led to 3.3 percent and 3.4 percent increases in the AUC and specificity, respectively, for clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa) in a 360-person cohort drawn from 53 facilities.
Offering an extended shelf life, the FDA-approved Gozellix, a preparation kit for gallium-68 (68Ga) gozetotide injection, is indicated for use in PSMA PET imaging of prostate cancer patients with suspected recurrence or metastasis.
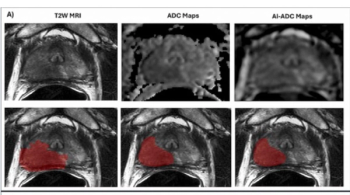
Emerging research showed that AI-generated ADC mapping from MRI led to significant increases in accuracy, PPV and specificity in comparison to conventional ADC mapping while achieving a 93 percent sensitivity for PCa.
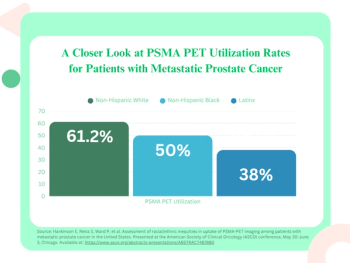
Latinx patients with metastatic prostate cancer were 63 percent less likely than non-Hispanic White patients to have PSMA PET scans, according to a study of 550 patients presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) conference.
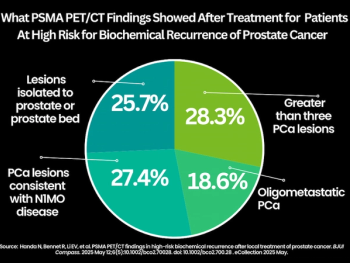
For patients at high-risk for biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer, PSMA PET/CT findings revealed that 77 percent had one or more prostate lesions after undergoing local radiation therapy or radical prostatectomy, according to a recent study.
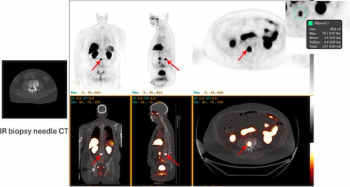
For patients with recurrent or metastatic prostate cancer, new research findings showed no significant difference in the sensitivity of 18F-piflufolastat PET/CT between patients on concurrent hormone therapy and those without hormone therapy.
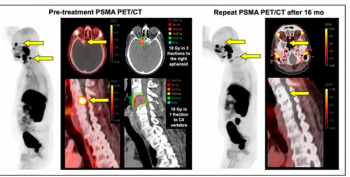
While PSMA PET/CT revealed an 87 percent local remission rate after metastasis-directed radiotherapy for oligometastatic prostate cancer in a new study, researchers also found that 80 percent of patients had biochemical progression at a median 32-month follow-up.
In a recent interview, Wayne Brisbane, M.D., discussed new research, presented at the American Urological Association (AUA) conference, which revealed a 15 percent higher AUC for an emerging AI software in detecting seminal vesicle invasion (SVI) in comparison to prostate MRI alone.
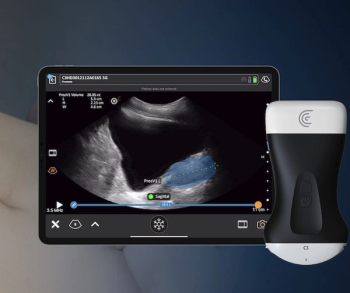
Offering expedited calculation of prostate volume, Clarius Prostate AI is reportedly the first AI-enabled prostate measurement tool to garner FDA clearance for use with handheld ultrasound.
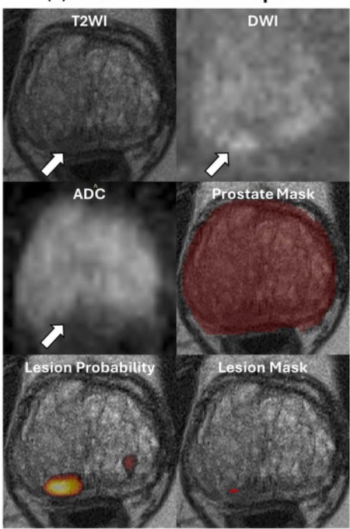
Demonstrating no significant difference with radiologist detection of clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa), a biparametric MRI-based AI model provided an 88.4 percent sensitivity rate in a recent study.

Recent research demonstrated a 59 percent reduced risk of progression or death with the radioligand therapy Pluvicto in comparison to a change of androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI) for patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
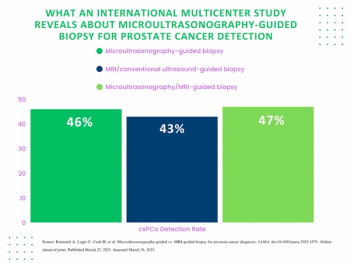
Microultrasonography-guided biopsy offered comparable detection as MRI/conventional ultrasound-guided biopsy in detection of Gleason grade group 2 or higher prostate cancer, according to a new international multicenter study.
Indicated for use in cases involving suspected metastasis with PCa or suspected PCa recurrence due to elevated PSA level, Gozellix reportedly has a longer shelf life than other gallium-based PET imaging products.
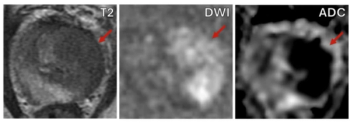
While DCE MRI was deemed helpful in over 67 percent of cases in which it was used, researchers found that monitored prostate MRI exams, which facilitated a 75 percent reduction of DCE MRI sequences, had comparable sensitivity for prostate cancer as non-monitored exams.
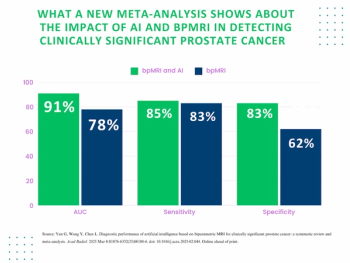
Researchers noted the combination of AI and bpMRI had an average AUC of 91 percent for csPCa detection in contrast to 78 percent for unassisted radiologist interpretation in a recent meta-analysis.
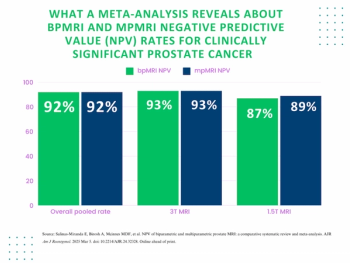
In an 18-study meta-analysis involving over 4,600 patients, researchers found that bpMRI and mpMRI had equivalent pooled negative predictive value (NPV) of 92 percent for clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa).
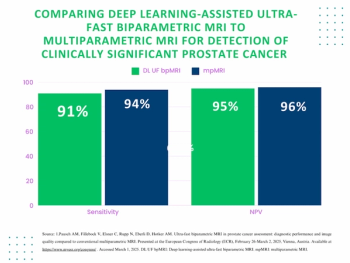
A deep learning-enhanced ultra-fast bpMRI protocol offered similar sensitivity for csPCa as mpMRI with an 80 percent reduction in scan time, according to research findings presented at the European Congress of Radiology (ECR) conference.
Catch up on the most-well viewed prostate imaging content in February 2025.
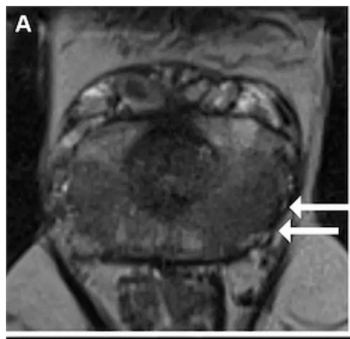
In a multicenter study involving over 1,000 patients, a deep learning software offered comparable sensitivity and specificity for Gleason grade group > 2 tumors in comparison to radiologist interpretation.
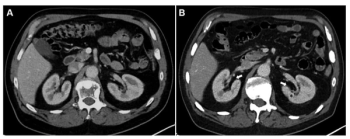
In patients who had at least four cycles of 177Lu-PSMA-I&T for mCRPC, new research shows that a 10 percent or greater decrease in total kidney volume on CT at six months has a 90 percent AUC for predicting estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFRs) of 30 percent or greater at one year.
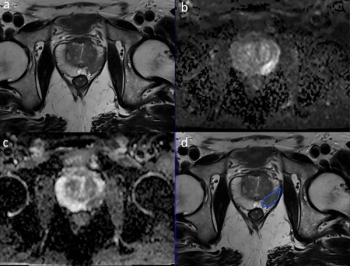
In a recent literature review, researchers offered insights on current considerations with prostate MRI and discussed keys to effective use of the modality in screening for prostate cancer.
The PET radiopharmaceutical SAR-bisPSMA has garnered three FDA fast track designations in a six-month period for use in the detection and management of prostate cancer.
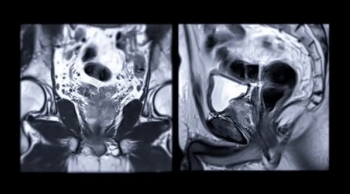
Researchers found that patients with high PSA density have more than double the risk of false-negative findings on prostate MRI and those with low PSA density are significantly less likely to have false-positive results.
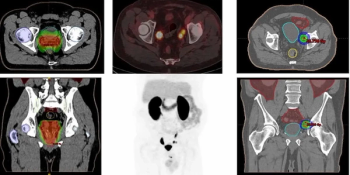
18F-DCFPyL facilitated detection of recurrent prostate cancer in 51 percent of patients with PSA levels ranging between 0.2 to 0.5 ng/ml, according to new research presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary Cancers (ASCO-GU) Symposium.

The PET/CT agent 18F-PSMA-1007 offered the highest surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) out of nine radiotracers at the patient and lesion level for detecting clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa), according to a meta-analysis.