
Disease Spotlight: Prostate Cancer
Latest News


Emerging PET Agent Garners Second FDA Fast Track Designation for Prostate Cancer Imaging

Study Examines Prognostic Value of Baseline PSMA PET/CT Factors in Patients with mCRPC
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
Employing baseline MRI and clinical data, an emerging deep learning model was 32 percent more likely to predict the progression of low-risk prostate cancer (PCa) to clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa), according to new research.

In patients with high-risk, hormone sensitive prostate cancer who had no evidence of metastasis on conventional imaging, PSMA PET revealed polymetastatic disease in 24 percent of patients and M1 disease staging in 46 percent of patients.
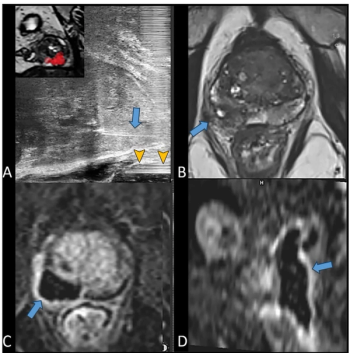
For patients with localized prostate cancer and PI-RADS 3 or higher lesions, MRI-guided micro-ultrasound multifiber focal laser ablation had an 18 percent recurrence rate at one year, according to newly published research.

Touching on a variety of topics in radiology, here are the top five most well-viewed content from Diagnostic Imaging in 2024.
Catch up on the most well-viewed prostate imaging content from 2024.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Catch up on the most well-viewed magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) content from 2024.
In a new study involving nearly 600 biopsy-naïve men, researchers found that only 4 percent of those with negative prostate MRI had clinically significant prostate cancer after three years of active monitoring.
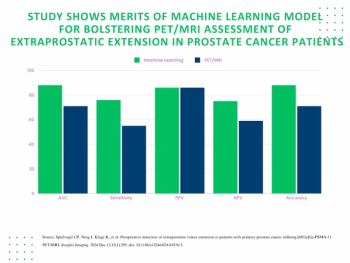
The use of an adjunctive machine learning model led to 17 and 21 percent improvements in the AUC and sensitivity rate, respectively, for PET/MRI in diagnosing extraprostatic tumor extension in patients with primary prostate cancer.
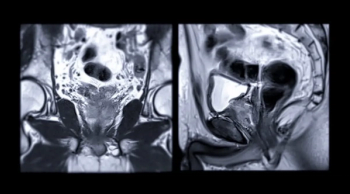
In a new point-counterpoint discussion published in the American Journal of Roentgenology, researchers debate the merits and limitations of the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) version 2.1.
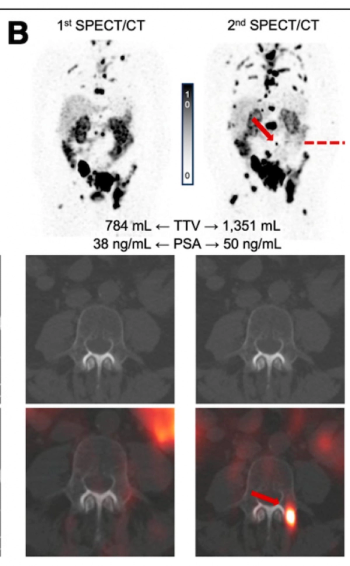
Researchers found that new prostate lesion detection on SPECT/CT at the beginning of a second cycle of 177 Lu-PSMA-617 for mCRPC was associated with an over sevenfold higher mortality risk.
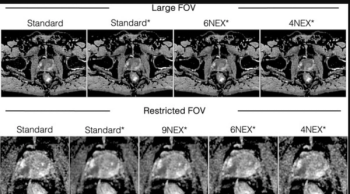
Employing deep learning reconstruction at four excitations for DWI MRI may lead to an average five-minute reduction in exam time for prostate mpMRI, according to a new study.
Catch up on the most-well viewed prostate imaging content in October 2024.
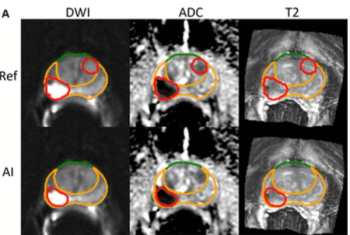
For patients who received radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer, total intraprostatic tumor volume derived from AI segmentation had a 10 percent higher AUC for predicting seven-year metastases in comparison to a risk model from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN).
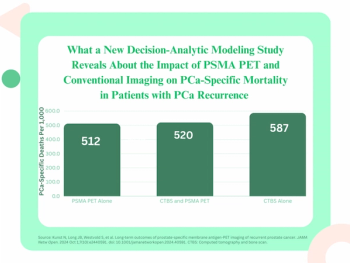
For patients with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer, PSMA PET imaging may facilitate a 12.8 percent lower incidence of prostate cancer mortality in contrast to the combination of CT and bone scan, according to long-term outcome estimates from a new decision-analytic modeling study.
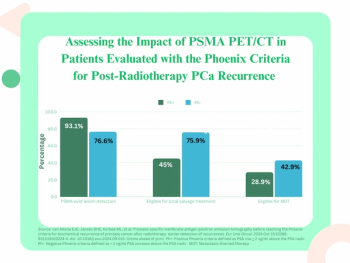
Earlier detection of PSMA-avid lesions in post-radiotherapy patients with increases in PSA levels < 2 ng/ml above nadir were reportedly associated with a significantly lower incidence of distant metastases and lower overall mortality rates.
When employing a PI-RADS > 4 cutoff, researchers found that the mdprostate software provided an 85.5 percent sensitivity rate for diagnosing clinically significant prostate cancer on mpMRI.

In a recent interview, Lisa F. Newcomb, Ph.D., discussed the merits of active surveillance for low-risk prostate cancer (PCa) and key findings from multicenter research involving over 2,100 men with localized PCa.
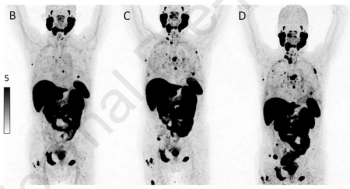
PSMA PET/CT revealed progressive PCa in 31 percent of patients who demonstrated greater than a 50 percent decline in PSA level after treatment with either an androgen receptor-targeted agent or chemotherapy.

In a recent interview, Bridget Koontz, M.D., discussed the capability of the PET imaging agent 18F-flotufolastat for diagnosing post-prostatectomy recurrence of prostate cancer in patients with PSA values less than 1 ng/mL, based on research presented at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) conference.
Study Shows MRI-Targeted Biopsies Reduce Overdiagnosis of Clinically Insignificant PCa by 57 Percent
Omitting biopsy procedures in men with PSA levels > 3 ng/ml and negative MRI findings for prostate cancer (PCa) was associated with significantly lower risks of diagnosing clinically insignificant PCa in comparison to the use of systematic biopsy, according to an approximately four-year study of over 13,000 men who had prostate cancer screening.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in September 2024.

Catch up on the most-well viewed prostate imaging content in September 2024.
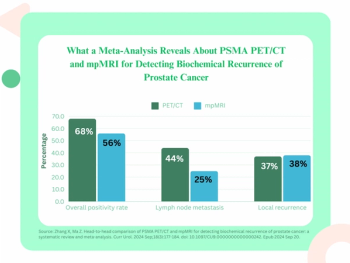
A new meta-analysis found that PSMA PET/CT offers a 12 percent higher positivity rate for detecting biochemical recurrence of PCa and a 19 percent higher positivity rate for identifying lymph node metastasis in comparison to mpMRI.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.










